by Calculated Risk on 4/27/2009 12:52:00 PM
Monday, April 27, 2009
Q1 2009: Homeownership Rate at 2000 Levels
The homeownership rate is back to the level of Q2 2000. So much for the homeownership gains of the last 8+ years. Gone.
This morning the Census Bureau reported the homeownership and vacancy rates for Q1 2009. Here are a few graphs ... Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.
The homeownership rate decreased to 67.3% and is now back to the levels of Q2 2000.
Note: graph starts at 60% to better show the change.
The homeownership rate increased because of demographics and changes in mortgage lending. The increase due to demographics (older population) will probably stick, so I expect the rate to decline to the 66% to 67% range - and not all the way back to 64% to 65%.
The homeowner vacancy rate was 2.7% in Q1 2009.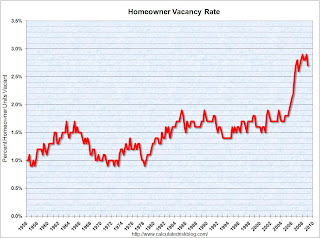 A normal rate for recent years appears to be about 1.7%. There is some noise in the series, quarter to quarter, so perhaps the vacancy rate has stabilized in the 2.7% to 2.9% range.
A normal rate for recent years appears to be about 1.7%. There is some noise in the series, quarter to quarter, so perhaps the vacancy rate has stabilized in the 2.7% to 2.9% range.
This leaves the homeowner vacancy rate about 1.0% above normal, and with approximately 75 million homeowner occupied homes; this gives about 750 thousand excess vacant homes.
The rental vacancy rate was steady at 10.1% in Q1 2009.  It's hard to define a "normal" rental vacancy rate based on the historical series, but we can probably expect the rate to trend back towards 8%. According to the Census Bureau there are close to 40 million rental units in the U.S. If the rental vacancy rate declined from 10.1% to 8%, there would be 2.1% X 40 million units or about 820,000 units absorbed.
It's hard to define a "normal" rental vacancy rate based on the historical series, but we can probably expect the rate to trend back towards 8%. According to the Census Bureau there are close to 40 million rental units in the U.S. If the rental vacancy rate declined from 10.1% to 8%, there would be 2.1% X 40 million units or about 820,000 units absorbed.
This would suggest there are about 820 thousand excess rental units in the U.S.
There are also approximately 100 thousand excess new homes above the normal inventory level (for home builders) - plus some uncounted condos.
If we add this up, 820 thousand excess rental units, 750 thousand excess vacant homes, and 100 thousand excess new home inventory, this gives about 1.7 million excess housing units in the U.S. that need to be absorbed over the next few years. (Note: this data is noisy, so it's hard to compare numbers quarter to quarter, but this is probably a reasonable approximation).
These excess units will keep pressure on housing starts and prices for some time.
Another House "Deal of the Week"
by Calculated Risk on 4/27/2009 12:19:00 PM
Zach Fox at the North County Times brings us another house "Deal of the Week": Come to Murrieta, 70 percent off!
Murrieta is in south Riverside County, just north of Temecula. This is part of the notorious Inland Empire.
Here is the price history for the featured 1,442-square-foot home:
July 1997: $60,000
August 2006: $330,545
January 2009: $96,000
Zach writes:
When we started Deal of the Week in February, we focused on outliers that posted huge declines. No more. This isn't an outlier; this is pretty much the neighborhood average. Homes similar to this 1,442-square-foot, single-family house have been selling left and right in the $100,000 to $120,000 range in this area of Murrieta. Dipping into five figures isn't uncommon.I'm always amazed by the peak prices - usually in 2005 and 2006. What is the payment on a $96K home? Probably just over $500 per month PITI with 10% down. (principal, interest, taxes and insurance).
Bank Failure: FDIC Payout Transactions
by Calculated Risk on 4/27/2009 09:28:00 AM
There have been two large payout bank seizures this month (as opposed to finding a buyer). The first was New Frontier Bank in Greeley, Colorado on April 10th, and the second was First Bank of Beverly Hills, California last Friday.
A former regulator told me that payouts are very rare except in rural areas (where there are no buyers). He told me:
These two recent payouts are kinda stunning. I can't stress how hard FDIC works to avoid payouts. They are highly disruptive to customers and quite expensive for the Agency. ... A payout is an operational nightmare for FDIC. ... It's a bigger and messier job than it might appear to anyone who hasn't been through it....that was a pretty story on 60 Minutes a while back, but that wasn't a payout. The pressure is incredible.From the Denver Post: Bank liquidation a blow to Greeley (ht David)
Greeley's largest bank was so larded with troubled assets that, for the first time in three decades, federal officials couldn't find another bank willing to do the liquidation. On April 10, they appointed themselves bank executives to hasten its demise.Pretty amazing story about a bank growing from a trailer in 1998 to $2 billion in assets this year.
"It's a phantom," said Fred Ozyp, the receivership specialist for the Federal Deposit Insurance Corp. heading the liquidation over the next two weeks.
The dream started in a double-wide trailer on Greeley's west side.First Bank of Beverly Hills had total assets of $1.5 billion. Two fairly sizable banks with no buyers.
It was 1998, and Seastrom, a former Eaton bank manager, decided to go into business for himself. He rounded up at least $6 million from investors and hung out the "New Frontier Bank" shingle on a mobile-home awning. The logo featured the company's initials at the center of a galaxy.
His lending universe: the growing housing market and sprawling agriculture industry of Weld County.
GM Restructuring Plan
by Calculated Risk on 4/27/2009 08:54:00 AM
From CNBC: GM Confirms Plans to Cut Jobs, Eliminate Pontiac
General Motors said it would .... eliminate its Pontiac brand ... expects to cut its hourly work force [by 21,000 for the current] level of 61,000 ... It will cut its number of plants to 34 in 2010 from 47 now....Here is the press conference at 9 AM ET:
Sunday, April 26, 2009
GM to Announce New Restructuring Plan at 9 AM ET
by Calculated Risk on 4/26/2009 10:22:00 PM
GM press release: GM President and CEO Fritz Henderson to Update Media on Revised GM Viability Plan
General Motors President and CEO Fritz Henderson will host a press conference on Monday, April 27, to update the media on GM's revised viability plan.Here is a story about the ever changing auto forecasts: G.M.’s Ever-Changing Art of Financial Forecasting
The press conference will run from 9 to 10 a.m. EDT
...
The press conference will also be webcast at http://media.gm.com.
Also a Chrysler story: Chrysler and Union Agree to Deal Before Federal Deadline
Summers: Expect "sharp declines in employment"
by Calculated Risk on 4/26/2009 07:47:00 PM
From Bloomberg: Summers Says U.S. Economy to Decline ‘For Some Time’
“I expect the economy will continue to decline,” with “sharp declines in employment for quite some time this year,” Summers said today on “Fox News Sunday.”Reuters has more quotes: Summers says no unremitting freefall in US economy
...
Summers said the economy will pick up as manufacturers rebuild depleted inventories and consumers replace aging cars. “These imbalances can’t continue forever,” he said. “When they are repaired they will be a source of impetus for the economy.”
...
Summers said the Obama administration is “on a path toward containment and toward building a path toward expansion,” he said, adding that “even sharp plans take time” to work, perhaps six months or more.
“Six or eight weeks ago, there were no positive statistics to be found anywhere. The economy felt like it was falling vertically. Today, the picture is much more mixed,” Summers said.The "unremitting freefall" might be ending, but what will be the source of growth? Usually residential investment (RI) and personal consumption lead the economy out of a recession - and both remain severely impaired this time. There is too much excess inventory for any meaningful recovery in RI, and the process of repairing household balance sheets has just begun (I expect the savings rate to continue to rise for some time).
“There are some negative indicators, to be sure. There are also some positive indicators. And no one knows what the next turn will be,” he said. “But I think that sense of unremitting freefall that we had a month or two ago is not present today. And that’s something we can take some encouragement from.”
Krugman spoke about this in Cincinnati:
"I'm in the camp that really worries about the L-shaped recession. We level off but we don't get the recovery. We hope it isn't, but it has all the markings of it. This looks like the kind of slump that has all the markings of where normal recovery forces are very, very weak.
It's hard to see where recovery comes from."
Bank Balance Sheet: Liquidity and Solvency, Part II
by Calculated Risk on 4/26/2009 03:26:00 PM
In the previous post, I tried to present a conceptual overview of a liquidity crisis using a bank's balance sheet: Bank Balance Sheet: Liquidity and Solvency, Part I. Note: I combined various types of financial institutions to illustrate a few points.
As we continue the story, the bank has suffered some losses, but the bank run has been halted by the efforts of the FDIC (increasing insurance limit), or the Fed (by providing liquidity).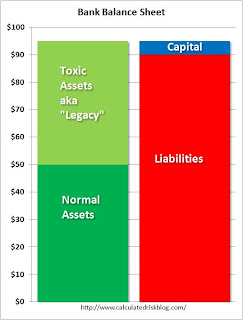 Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.
This time we look at the bank's assets. What I've labeled as "normal assets" are various categories of assets, perhaps commercial & industrial (C&I) loans, consumer loans, and others. Although the charge-offs are increasing for all of these loans during the recession, these assets have a market value or otherwise are in OK shape.
The larger problem is the toxic assets (now known as legacy assets). These are mostly related to residential real estate, but there are many other toxic loans (Construction & Development, foreign loans, LBO PE loans, etc.)
The banks are facing huge additional losses for these legacy assets, and these losses will make some banks "balance sheet" insolvent (liabilities will be great than assets). However, the bank is not insolvent in the business sense, because the bank can still pay their debts as they come due - at least for now.
But these future losses (even just the fear of future losses) will make it impossible for the banks to borrow or raise additional private capital. So Paulson's solution was to remove the legacy assets from the bank's balance sheet. This was the purpose of the Master Liquidity Enhancement Conduit (MLEC), the original purpose of the TARP, and even the goal of Geithner's PPIP. Basically the goal is to replace the legacy assets with money from the MLEC, TARP (original plan) or the PPIP.
Basically the goal is to replace the legacy assets with money from the MLEC, TARP (original plan) or the PPIP.
All of these programs suffer from the same problem. If they buyer's pay too little, the banks will be insolvent, and if the buyer's pay too much for the assets, this is a transfer of wealth from the buyers to the stakeholders of the banks.
The PPIP uses private buyers to set the price, but it suffers from the same problems as the MLEC and TARP (original). Because of the structure (with a non-recourse loan), the buyers can pay more than market value because they have a put option (they have minimal downside risk). This put option is a transfer of wealth from taxpayers to the stakeholders of the banks. If the PPIP buyers bid too little, the banks will reject the bid - I think this is a likely outcome. Because of pricing issues for legacy assets, the TARP was changed to inject additional capital into the banks with preferred stock.
Because of pricing issues for legacy assets, the TARP was changed to inject additional capital into the banks with preferred stock.
This additional capital provides the banks with a little more cushion to handle losses, but if the value of the legacy assets is - say - cut in half, the banks will still be balance sheet insolvent. This might help some banks, but other banks will still need additional capital.
And there is the question of what percentage of the bank should the government own with the additional capital. If the banks were seriously insolvent, why aren't the original shareholders wiped out? Once again this is a transfer of wealth from the taxpayers to the existing stakeholders.
So what is the solution?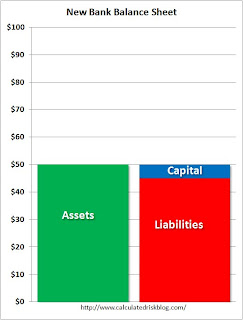 The FDIC approach (aka Preprivatization) would be to seize the bank, and wipe out the shareholders.
The FDIC approach (aka Preprivatization) would be to seize the bank, and wipe out the shareholders.
The government would take all the legacy assets and create a new Resolution Trust Corporation (RTC) like institution to dispose of the assets. The bank would be recapitalized and eventually sold to the public as a much smaller institution.
There are a range of possibilities on how to handle the debtholders. They could receive a haircut, and perhaps an interest in the RTC assets (above a certain price), and maybe an equity interest in the New Bank. Or, at the other end of the spectrum, they could be paid off in full.
This would probably depend on any systemic issues. The Geithner approach is to keep injecting capital into the banks to cover the losses. This is known as the "Zombie" bank approach.
The Geithner approach is to keep injecting capital into the banks to cover the losses. This is known as the "Zombie" bank approach.
In essence the balance sheet looks like this with liabilities greater than total assets. To make the zombie balance sheet "balance", I've added "??????" to the assets.
These "??????" assets are either future retained earnings or additional money from the government. Although the bank is balance sheet insolvent, the bank will never be business insolvent because the government will continue to provide money to cover losses.
If only a small percentage of financial assets are held by zombie banks, then this approach will probably work. These banks will be crippled, but the other banks can meet the financing needs of the economy.
This is why the stress tests are so important in helping identify zombie banks - and why financial institutions relying on government support should be required to make the entire test results public. If there are too many zombies, we need to insist on preprivatization.
Bank Balance Sheet: Liquidity and Solvency, Part I
by Calculated Risk on 4/26/2009 11:57:00 AM
Note: I took some short cuts to make this simple - think of this conceptually. I'm intentionally mixing financial institutions. For commercial banks, the FDIC stopped the bank run by upping the FDIC insurance. For investment banks, the Fed provided the liquidity. Please think of this conceptually or I'll have to write 100 pages ...
This post looks at a bank balance sheet and a liquidity crisis. In a subsequent post, I'll look at a solvency crisis and two possible solutions.
A special hat tip to This American Life’s Alex Blumberg and NPR’s Adam Davidson who presents some of the same ideas (although I'm going to go further). Here is the website for their presentation.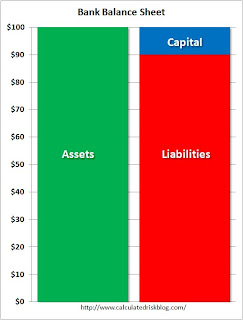 Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.
If you watch the Planet Money presentation, they explain the basics of a bank from a balance sheet perspective. It doesn't matter if the left scale is in dollars or billions of dollars - the structure is the same.
Capital is the amount of money investors put into the bank plus any retained earnings. Liabilities is the money the bank borrows from depositors or other sources. And assets are loans that the bank makes (and a little cash and other assets). (see Alex and Adam's presentation to make this clear).
The balance is: Assets = Capital + Liabilities
Banks make money by lending at a higher rate than they borrow. In the Planet Money example, the banks borrowed at 3%, loaned the money at 6%, for a spread of 3%. The difference between 6% and 3% is called the "net interest spread".
Banks report something a little different called the "net interest margin". The difference between the "spread" and the "margin" is because not all assets are loans (some might be held as cash for regulatory reasons). Net Interest Margin (NIM) is the interest earned, minus the interest paid, divided by total assets. As an example, Wells Fargo just reported a net interest margin of "approximately 4.1 percent".
Now look at how profitable a bank could be. If this bank had $100 billion in assets, and a NIM of 4.1% that would be $4.1 billion in annual profits before expenses and charge-offs - on just $10 billion in capital (Note: The diagram shows 10-to-1 leverage; many banks were levered 30-to-1 or more).
Of course the bank has expenses (all those nice buildings and employees) - and there are always charge-offs for loans that don't get repaid, even in good times. For reference, the Federal Reserve tracks the charge-offs by loan category here.
Banks have two main risks: interest rate risks and credit risks. Since banks mostly borrow short and lend long, they are exposed to increases in short term interest rates, and this would lead to lower NIMs. The credit risk is that too many of those assets will go bad (more on credit risks in the next post).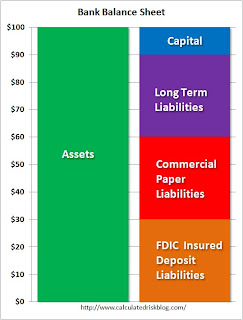 Not all liabilities are the same. The second diagram shows three categories of liabilities: 1) Long term bank debt, 2) commercial paper (called CP, this is less than 270 days duration, and usually much shorter), and 3) FDIC insured deposits.
Not all liabilities are the same. The second diagram shows three categories of liabilities: 1) Long term bank debt, 2) commercial paper (called CP, this is less than 270 days duration, and usually much shorter), and 3) FDIC insured deposits.
Each category has advantages and disadvantages.
Commercial paper is usually the lowest interest rate, but it is the shortest duration and has the highest interest risk. Usually the bank pays the highest interest rate on long term debt, but there is no interest risk for the duration of the security. Most banks have a mix of liabilities.
Now imagine the bank starts reporting higher than expected credit losses - or at least depositors believe the bank will start reporting huge loses.  Here the bank has lost $5 billion, and the capital has been cut in half.
Here the bank has lost $5 billion, and the capital has been cut in half.
Fearing further losses, the commercial paper (CP) investors run for the hills and refuse to reinvest again when their short term paper matures.
The FDIC insured depositors run (or amble) towards the hills too. A classic bank run.
The long term debt holders are stuck. They can sell in the market, but at a lower price - and that doesn't impact the bank's balance sheet (OK, there are some accounting issues here that I will ignore).
To stop the bank run, the FDIC stepped up and increased the guarantee on FDIC insured assets to $250 thousand. But this did nothing for the commercial paper investors.  Next the Fed steps in and replaces the commercial paper liability as it matures.
Next the Fed steps in and replaces the commercial paper liability as it matures.
If this was just a panic, and the bank was actually fine, the commercial paper investors would return (or the bank could sell more long term debt), and the Fed would be replaced by private debt.
However this is not just a liquidity crisis, and the Fed is still providing liquidity to the banks.
This doesn't work long term because the Fed requires the banks to over collateralize any money borrowed from the Fed. As the long term debt starts to mature, those investors will follow the commercial paper investors to the hills - and the Fed will have to provide more and more liquidity. And eventually there will not be enough collateral to borrow from the Fed. Here is an example of the Collateral Margins Table for the discount window.
Next I'll discuss the solvency issues (not as easy to fix).
Krugman Worries about L-Shaped Recession
by Calculated Risk on 4/26/2009 10:15:00 AM
From the Cincinnati Enquirer: Nobel-winning economist speaks at UC (ht Jonathan)
The country may experience some economic growth in the latter half of this year, but don't expect the rate of job losses to abate anytime soon, noted economist and recent Nobel Prize laureate Paul Krugman told an audience of economists and area business leaders Friday at the University of Cincinnati.And from a separate interview with the Enquirer:
...
"There are two kinds of recessions that are bad - those that take place because of financial crises, and those that are synchronized around the world," he said. "In both cases, the recessions tend to last longer and be deeper. Right now, we've got both going on."
Q: What will it take to pull out of this crisis?
Krugman: I'm in the camp that really worries about the L-shaped recession. We level off but we don't get the recovery. We hope it isn't, but it has all the markings of it. This looks like the kind of slump that has all the markings of where normal recovery forces are very, very weak.
It's hard to see where recovery comes from. Almost always the way a country recovers from a financial crisis is with an export boom. The problem is that we have a global crisis this time. So who are we going to export to, unless we find another planet to take our stuff?
Economist: A Glimmer of Hope?
by Calculated Risk on 4/26/2009 01:15:00 AM
The Economist cover story is titled A glimmer of hope? and cautions: "The worst thing for the world economy would be to assume the worst is over" Click on cover for larger image in new window.
Click on cover for larger image in new window.
[W]elcome as it is, optimism contains two traps, one obvious, the other more subtle. The obvious trap is that confidence proves misplaced—that the glimmers of hope are misinterpreted as the beginnings of a strong recovery when all they really show is that the rate of decline is slowing. The subtler trap, particularly for politicians, is that confidence and better news create ruinous complacency. Optimism is one thing, but hubris that the world economy is returning to normal could hinder recovery and block policies to protect against a further plunge into the depths.
emphasis added


