by Calculated Risk on 12/14/2009 12:03:00 PM
Monday, December 14, 2009
FDIC's Bair takes the "Over"
On Saturday I wrote that I'd take the "over" - more bank failures in 2010 than 2009. This is primarily because many FDIC insured banks are overly exposed to Construction & Development (C&D) and Commercial Real Estate (CRE) loans.
FDIC Chairwoman Sheila Bair is also taking the "over".
From CNBC: Worst of Bank Failures Isn't Over Yet: FDIC's Bair
Bank failures will continue to accelerate into next year despite "some encouraging signs" that things are turning around for the battered industry, FDIC Chair Sheila Bair told CNBC.A industry contact told me this weekend that they expect 400 bank failures in 2010.
... Bair did not quantify how bad the failures would get but said the worst isn't over yet for institutions that will suffer even as the economy improves.
"There's a lag generally with bank recovery from the overall economy," she said. "We do think bank failures will continue to go up next year but will peak. Even at higher levels than we have this year, it's still far below where we were during the S&L days."
...
"Even though the insured depository institutions are having their share of problems, it's really much lower than it was during the S&L days simply because most of this occurred outside the insured banks," Bair said.
Amid the problems for the industry, Bair said the Federal Deposit Insurance Corp's financial standing remains solid. She said the FDIC will head into 2010 with about $60 billion in cash reserves.
Refinance Activity and Interest Rates
by Calculated Risk on 12/14/2009 10:35:00 AM
The Mortgage Bankers Association's (MBA) current forecast for refinance activity in 2010 is $693 billion, and falling further in 2011 to $591 billion. The MBA is currently estimating 2009 refinance originations will be $1,246 billion - so they expect activity to fall almost in half.
This gives me an excuse for a graph or two (as if I need one).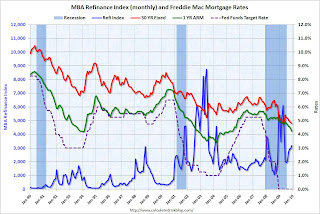 Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Refinance activity picks up when mortgage rates fall (for obvious reasons), and this graph shows the monthly refinance activity (MBA refinance index) and the Freddie Mac 30 year fixed mortgage rate and one year adjustable mortgage rate - and the Fed Funds target rate since Jan 1990.
Mortgage rates would have to fall further in 2010 to get another increase in refinance activity, and with the Fed MBS purchase program scheduled to end by the end of Q1, it seems unlike that rates will fall - unless the program is extended or the economy weakens significantly.
Notice that following the '90/'91 and '01 recessions, the Fed kept lowering the Fed Funds rate because of high unemployment rates. This spurred refinance activity. The second graph shows the weekly MBA refinance activity, and the Ten Year Treasury yield.
The second graph shows the weekly MBA refinance activity, and the Ten Year Treasury yield.
Every time the 10 year yield drops sharply, refinance activity picks up. But notice what happened at the end of 1995. The Ten Year yield dropped, but the increase in refinance activity was muted. This was because mortgage rates didn't fall below the rates of a couple years earlier - and many people had already refinanced at those lower rates. The same thing will happen in 2010 and 2011 - there will only be a surge in refinance activity if rates fall below the rates of 2009.
Citi Reaches Agreement to Repay TARP
by Calculated Risk on 12/14/2009 08:13:00 AM
Press Release from Citigroup: Citigroup, U.S. Government and Regulators Agree to TARP Repayment
From the NY Times: Citigroup Says It Has Reached a Deal to Repay Bailout Funds
Misc: Dubai, Citi, CRE
by Calculated Risk on 12/14/2009 12:33:00 AM
From the WSJ: Abu Dhabi Supplies $10 Billion to Dubai
Dubai's government Monday said it received $10 billion in financing from Abu Dhabi, which will pay part of the debt held by conglomerate Dubai World and its property unit Nakheel.From the NY Times: Citigroup Nears Deal to Return Billions in Bailout Funds
Citigroup was close to a deal on Sunday night to be the last of the big Wall Street banks to exit the government’s bailout program, after trying to persuade regulators that it was sound enough to stand on its own.And on CRE:
Sunday, December 13, 2009
Housing Bust and Mobility
by Calculated Risk on 12/13/2009 10:06:00 PM
A couple more articles on the impact of the housing bust on mobility ...
From Patrick Coolican at the Las Vegas Sun: Mobility bust bad for Vegas
“Vegas is going to be disproportionately affected by the absolute crashing halt of interstate migration,” said Michael Hicks, director of the Center for Business and Economic Research at Ball State University.And a personal tale from Brian Fitzgerald at the WSJ: Confessions of an Underwater Homeowner
About 4.7 million Americans moved from one state to another in 2007 and 2008, according to the Census Bureau. That’s just 55 percent of the total in 1999 and 2000. Geographers and economists think the number will plummet further this year.
...
“People are underwater on their homes and that affects mobility,” said Isabel Sawhill, a Brookings Institution economist.
...
Geographic mobility is what economists call “countercyclical.” When a recession hits, people usually move to where the jobs are. Job-related stasis — staying put in one’s job versus hitting the road in search of a better one — is unique to this recession.
We never considered purposefully defaulting ... Although, if I were laid off and unemployed for more than a few months we might have to. ... if I was offered a job in another city, we wouldn't be able to sell.There is much more in Fitzgerald's story, but this bit on mobility is important - he can't sell, and he can't move to change jobs - and just like most Americans trapped underwater, he is trying to stick it out and hoping for the best.
Worker mobility has always been a significant positive for the U.S. economy, and this decline in mobility is one of the long lasting tragedies of the bubble. As I wrote almost two years ago:
Less worker mobility [due to negative equity] is kind of like arteriosclerosis of the economy. It lowers the overall growth potential.
Perhaps as many as 15 to 20 million households will be saddled with negative equity by 2009. Even if most of these homeowners don't "walk away", there might still be a negative impact on the economy due to less worker mobility.
Large Apartment Developer Files for Bankruptcy
by Calculated Risk on 12/13/2009 06:29:00 PM
From the WSJ: Fairfield Files for Chapter 11
Fairfield, which has built some 64,000 apartments, condominiums and off-campus student-housing units throughout the country, failed amid an inability to refinance debt or sell investment properties.Their main two lenders were Wachovia (now part of Wells Fargo) and Capmark Financial (now in bankruptcy). This is also another hit to a Morgan Stanley real estate fund and others:
The bankruptcy is also a blow to the California State Teacher's Retirement System and a subsidiary of Mitsubishi Corp., both of which invested in Fairfield over the years.
A Fairfield spokeswoman confirmed that investors including the Morgan Stanley fund and CalSTRS would be wiped out by the bankruptcy but said they would continue as joint-venture partners on Fairfield projects.
Summary and a Look Ahead
by Calculated Risk on 12/13/2009 02:36:00 PM
Some key real estate news will be released this week including the Housing Market Index on Tuesday, Housing Starts (November) and the Architecture Billings Index for CRE (both on Wednesday).
In other economic news, the Fed will release Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization (November) on Tuesday, and the FOMC meeting announcement on Wednesday (no change). CPI will be released on Wednesday and the Philly Fed Index on Thursday.
And a summary of last week ...
From the BLS: Job Openings and Labor Turnover Summary The following graph shows job openings (yellow line), hires (blue Line), Quits (green bars) and Layoff, Discharges and other (red bars) from the JOLTS. Red and green added together equals total separations.
 Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.Notice that hires (blue line) and separations (red and green together) are pretty close each month. When the blue line is above total separations, the economy is adding net jobs, when the blue line is below total separations, the economy is losing net jobs.
According to the JOLTS report, there were 3.966 million hires in October, and 4.203 million separations, or 237 thousand net jobs lost. With job openings and hires near record lows, this suggests the current labor problem is mostly a lack of new jobs although layoffs and discharges were still elevated in October.
The Census Bureau reported: "The ... total October exports of $136.8 billion and imports of $169.8 billion resulted in a goods and services deficit of $32.9 billion, down from $35.7 billion in September, revised."
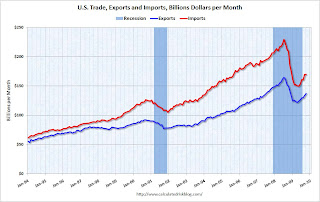 This graph shows the monthly U.S. exports and imports in dollars through October 2009.
This graph shows the monthly U.S. exports and imports in dollars through October 2009.Imports and exports both increased in October. On a year-over-year basis, exports are off 9% and imports are off 19%.
Import oil prices decreased slightly to $67.39 in October - and oil import volumes dropped sharply in October. The decline in oil imports was the major contributor to decrease in the trade deficit.
 The Treasury reported 31,382 HAMP permanent modifications as of the end November.
The Treasury reported 31,382 HAMP permanent modifications as of the end November. Here is the link at Treasury. See here for a list of reports.
The rules to include a borrower in a trial modification program vary by servicer - and that makes that number essentially meaningless. The number that matters is the permanent mods, and although early, it appears the program will fall short of the original goal.
The Fed released the Q3 2009 Flow of Funds report this week: Flow of Funds.
According to the Fed, household net worth is now off $11.9 Trillion from the peak in 2007, but up $4.9 trillion from the trough earlier this year.
 This is the Households and Nonprofit net worth as a percent of GDP.
This is the Households and Nonprofit net worth as a percent of GDP.This includes real estate and financial assets (stocks, bonds, pension reserves, deposits, etc) net of liabilities (mostly mortgages). Note that this does NOT include public debt obligations.
This really shows the recent stock and real estate bubbles.
Also, the following Mortgage Equity Withdrawal estimate is calculated from the Fed's Flow of Funds data and the BEA supplement data on single family structure investment. (See: Q3 2009: Mortgage Equity Extraction Strongly Negative)
 This graph shows the net equity extraction, or mortgage equity withdrawal (MEW), results, using the Flow of Funds (and BEA data) compared to the Kennedy-Greenspan method.
This graph shows the net equity extraction, or mortgage equity withdrawal (MEW), results, using the Flow of Funds (and BEA data) compared to the Kennedy-Greenspan method. For Q3 2009, the Net Equity Extraction was minus $91 billion, or negative 3.3% of Disposable Personal Income (DPI). This is not seasonally adjusted.
On a monthly basis, retail sales increased 1.3% from October to November (seasonally adjusted), and sales are up 1.9% from November 2008.
 This graph shows retail sales since 1992. This is monthly retail sales, seasonally adjusted (total and ex-gasoline).
This graph shows retail sales since 1992. This is monthly retail sales, seasonally adjusted (total and ex-gasoline).This shows that retail sales fell off a cliff in late 2008, and appear to have bottomed, but at a much lower level.
The red line is for retail sales ex-gasoline and this shows there might be a little pickup in final demand.
"In summary, it is encouraging to find that, despite the rapid growth of mortgage debt, only a small fraction of households across the country have loan-to-value ratios greater than 90 percent. Thus, the vast majority of homeowners have a sizable equity cushion with which to absorb a potential decline in house prices."
Alan Greenspan, Sept, 2005
Best wishes to all.
Volcker Cautions on Complacency
by Calculated Risk on 12/13/2009 11:39:00 AM
From Der Spiegel: Interview with US Economic Recovery Advisory Board Chair Paul Volcker (ht jb)
Volcker: ... We had a quarter of increased growth but I don't think we are out of the woods.And on the banks:
SPIEGEL: You expect a backlash?
Volcker: The recovery is quite slow and I expect it to continue to be pretty slow and restrained for a variety of reasons and the possibility of a relapse can't be entirely discounted. I'm not predicting it but I think we have to be careful.
SPIEGEL: What is the difference between this deep recession and all the other recessions we have seen since World War II?
Volcker: What complicates this situation, as compared to the ordinary garden variety recession, is that we have this financial collapse on top of an economic disequilibrium. Too much consumption and too little investment, too many imports and too few exports. We have not been on a sustainable economic track and that has to be changed. But those changes don't come overnight, they don't come in a quarter, they don't come in a year. You can begin them but that is a process that takes time. If we don't make that adjustment and if we again pump up consumption, we will just walk into another crisis.
...
Volcker: ... We have not yet achieved self-reinforcing recovery. We are heavily dependent upon government support so far. We are on a government support system, both in the financial markets and in the economy.
emphasis added
Volcker: It's amazing how quickly some people want to forget about the trouble and go back to business as usual. We face a real challenge in dealing with that feeling that the crisis is over. ...There is much more in the interview.
SPIEGEL: You have been clear about your ideas. Do you really believe we have to break up the big banks in order to create a more sustainable financial system?
Volcker: Well, breaking them up is difficult. I would prefer to say, let's just slice them up. I don't want them to get heavily involved in capital market activities so my view is: Hedge funds, no. Equity funds, no. Proprietary trading, no. Trading in commodities, no. And that in itself would reduce the size of the big banks. So you get some reduction in size. Equally important, you make them more manageable and easier to deal with if they do get in trouble.
WaMu Freedom of Information Request Denied
by Calculated Risk on 12/13/2009 09:27:00 AM
 Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Kirsten Grind provides some of the responses to the Puget Sound Business Journal's requests for information: The fight for WaMu documents (ht Spatch)
The Puget Sound Business Journal for months has asked the Office of Thrift Supervision (OTS), the federal agency that regulated Washington Mutual, to release internal communications between WaMu's regulators.In her article last week, Kirsten asks: Why Did They Close WaMu?. From the piece:
The newspaper made its requests under the U.S. Freedom of Information Act, the decades-old law that requires federal agencies to disclose public documents.
Of particular interest were internal emails, which could help explain why regulators seized the bank in September 2008 even though WaMu appeared to meet regulatory standards for operating banks, despite its burden of bad loans. (You can read the second installment of our six-month investigation about that decision here. The first in the series, about the bank's final days is here.)
On Wednesday, an OTS official told the Business Journal in an email: “After careful review, I have determined that your request, as it pertains to the above-referenced documents, is denied in full.”
[D]ocuments and interviews with former WaMu employees show that regulators closed WaMu even though it had liquidity and capital that were well above the levels at which a bank might normally be threatened with closure.It appears that WaMu employees considered the untapped FHLB and Fed lines of credit of over $14 billion as part of WaMu's $29 billion in net liquidity - and unmentioned (but likely) is that the Seattle FHLB and the Fed were probably about ready to pull those lines - and the FDIC probably knew that was about to happen and closed WaMu. Of course we don't know from the FOIA documents!
Typically, a bank is in danger of being seized if its net liquidity dips below 5 percent of total assets, according to banking experts and former regulators. On the day regulators shut WaMu, the bank had $29 billion in net liquidity—about 9.4 percent of assets, and nearly twice the closure threshold. The figure was provided by a former senior WaMu manager who closely tracked the bank’s liquidity at the time. It was confirmed by a former top WaMu executive who had full knowledge of the bank’s liquidity position.
“With the cash it had, WaMu should never have been seized,” said a senior banking regulator familiar with the matter.
...
Other documents also support the view that WaMu had sufficient liquidity to stay open. The last liquidity report from inside WaMu shows that on September 11 the bank could borrow $6.2 billion from the Federal Home Loan Banks in Seattle and San Francisco. It could borrow an additional $8.2 billion from the Federal Reserve Bank, a line that it hadn’t accessed at the time of its seizure, according to two people familiar with the matter.
But this would be just like a homeowner with an unused HELOC. Just when the homeowner is about to use the HELOC, the bank reduces or eliminates the line, and the homeowner's "liquidity" vanishes. Funny thing about liquidity - it can be there one day, and gone the next.
Saturday, December 12, 2009
Jim the Realtor: McMansion Foreclosures Coming
by Calculated Risk on 12/12/2009 10:48:00 PM
Jim shows several more homes in foreclosure in a nice area of north county coastal San Diego.
FDIC Bank Failure Update
by Calculated Risk on 12/12/2009 07:37:00 PM
Here is a graph of bank failures, by number of institutions and assets, from the December Congressional Oversight Panel’s Troubled Asset Relief Program report. (ht Catherine Rampell):  Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.
From the report (page 45):
Figure 11 shows numbers of failed banks, and total assets of failed banks since 1970. It shows that, although the number of failed banks was significantly higher in the late 1980s than it is now, the aggregate assets of failed banks during the current crisis far outweighs those from the 1980s. At the high point in 1988 and 1989, 763 banks failed, with total assets of $309 billion.167 Compare this to 149 banks failing in 2008 and 2009, with total assets of $473 billion.168Note: This is in 2005 dollars and this includes the failure of WaMu in 2008 with $307 billion in assets that didn't impact the DIF.
The second graph shows bank failures by week in 2009.
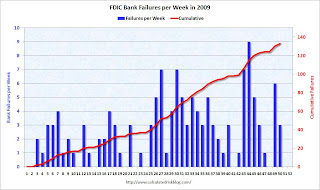 Note: Week 1 on graph ended Jan 2nd.
Note: Week 1 on graph ended Jan 2nd.There have been 133 bank failures this year, and there are only two more weeks left to close banks in 2009 (Dec 18th and maybe Dec 24th). This will set the over-under line for 2010 - will there be more bank failures in 2010 than in 2009?
I'll take the over (more failures in 2010 than in 2009).
Refinancing with Negative Equity
by Calculated Risk on 12/12/2009 03:37:00 PM
From David Streitfeld in the NY Times: Rates Are Low, but Banks Balk at Refinancing (ht Dave)
On refinancing with negative equity:
Mark Belvedere bought a condominium in a San Francisco suburb in early 2004 and refinanced it in 2005. He now owes $235,000 on a property that would sell for barely half that today.Unfortunately David Streitfeld doesn't provide any further information on Belvedere's loan. If the loan was held by a bank, then it might make sense for the bank to refinance the loan (this lowers the bank's risk of default). However Belvedere's "lender" might be a servicing company and the loan may have been securitized. Then it is impossible to refinance because the current holders of the note would be paid off, and no new lender would make a loan greater than the value of the collateral.
Mr. Belvedere said he would be willing to live with all that lost equity if he could refinance his loan from a variable rate, which could eventually go as high as 12 percent, into a 30-year fixed term.
His lender said no, citing the diminished value of the property. “It makes no sense and is so frustrating,” Mr. Belvedere said. “I’m ready and willing to pay the mortgage for the next 30 years, but they act like they’d rather have me walk away.”
As Streitfeld notes, the GSEs have a program called Home Affordable Refinance Program (HARP) that will allow lenders to refinance loans upto 125% of the property value. But this is only for loans the GSEs already holds or insures (and because refinancing lowers the risk of default). This wouldn't help Belvedere because he owes almost twice what his property is worth.
Housing Inventory: A Local Observation
by Calculated Risk on 12/12/2009 01:04:00 PM
"For Sale" signs are sprouting up all over my neighborhood again. In fact it is hard to find a block without one or two homes for sale. This is a very high number, especially for December.
My neighborhood may be unusual (fairly high priced SoCal area), but I suspect many homeowners have heard about an "improving market" and are testing the water.
This is one of the key categories of "shadow inventory" that we've discussed before:
Note: Homes in the foreclosure process listed in the MLS as "short sales" are not shadow inventory.
Inventory is usually the best metric to follow for the housing market - and according to recent releases inventory is declining for both new and existing homes - however shadow inventory clouds this picture.
Distressed Sales: Sacramento Market as an Example
by Calculated Risk on 12/12/2009 08:52:00 AM
Note: The Sacramento Association of REALTORS® is breaking out monthly resales by equity sales (conventional resales), and distressed sales (Short sales and REO sales). I'm following this series as an example to see changes in the mix in a former bubble area.  Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Here is the November data.
They started breaking out REO sales last year, but this is only the sixth monthly report with short sales. About 63 percent of all resales (single family homes and condos) were distressed sales in November.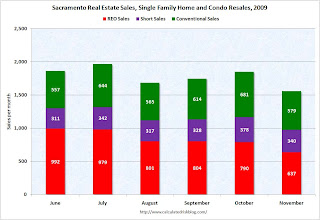 The second graph shows the mix for the last six months. It will be interesting to see if foreclosure resales pick up early next year when the early trial modifications period is over.
The second graph shows the mix for the last six months. It will be interesting to see if foreclosure resales pick up early next year when the early trial modifications period is over.
Total sales in November were off 16.1% compared to November 2008; the sixth month in a row with declining YoY sales.
On financing, over half the sales were either all cash (26.4%) or FHA loans (31.4%), suggesting most of the activity in distressed former bubble areas like Sacramento is first-time home buyers using government-insured FHA loans (and taking advantage of the tax credit), and investors paying cash.
This is a local market still in severe distress.
Friday, December 11, 2009
Volcker: "Not time for business as usual"
by Calculated Risk on 12/11/2009 11:38:00 PM
From Bloomberg: Volcker Says ‘Basic Structure’ of Economy to Impede U.S. Growth
“We have another economic problem which is mixed up in this of too much consumption, too much spending relative to our capacity to invest and to export,” [said Former Federal Reserve Chairman Paul Volcker] “It’s involved with the financial crisis but in a way it’s more difficult than the financial crisis because it reflects the basic structure of the economy.”
...
“It’s likely that economic growth is going to be pretty sluggish for a while.”
Click image for video or click for Bloomberg Video |
Unofficial Problem Bank List, Dec 11, 2009
by Calculated Risk on 12/11/2009 09:09:00 PM
This is an unofficial list of Problem Banks compiled only from public sources.
NOTE: This was compiled prior to the bank failures today.
Changes and comments from surferdude808:
Last week’s closings by the FDIC contributed to a decline in the number of institutions and assets on the Unofficial Problem Bank List.The list is compiled from regulator press releases or from public news sources (see Enforcement Action Type link for source). The FDIC data is released monthly with a delay, and the Fed and OTC data is more timely. The OCC data is a little lagged. Credit: surferdude808.
The list includes 539 institutions with aggregate assets of $298.1 billion down from 542 and $310 billion last week. There were 6 failures last Friday that had combined assets of $12.8 billion, which mostly came from the collapse of AmTrust Bank ($11.4 billion). There was one other removal from the list as the OCC terminated its Supervisory Agreement against Beach First National Bank.
This week there are 4 additions, which include Saehan Bank, Los Angeles, CA ($829 million); Phoenixville Federal Bank and Trust, Phoenixville, PA ($381 million); Pierce Commercial Bank, Tacoma, WA ($267 million); and Bank of Shorewood, Shorewood, IL ($141 million).
Note: The FDIC announced there were 552 bank on the official Problem Bank list at the end of Q3. The difference is a mostly a matter of timing - some enforcement actions haven't been announced yet, and others may be pending.
See description below table for Class and Cert (and a link to FDIC ID system).
For a full screen version of the table click here.
The table is wide - use scroll bars to see all information!
NOTE: Columns are sortable - click on column header (Assets, State, Bank Name, Date, etc.)
Class: from FDIC
The FDIC assigns classification codes indicating an institution's charter type (commercial bank, savings bank, or savings association), its chartering agent (state or federal government), its Federal Reserve membership status (member or nonmember), and its primary federal regulator (state-chartered institutions are subject to both federal and state supervision). These codes are:Cert: This is the certificate number assigned by the FDIC used to identify institutions and for the issuance of insurance certificates. Click on the number and the Institution Directory (ID) system "will provide the last demographic and financial data filed by the selected institution".N National chartered commercial bank supervised by the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency SM State charter Fed member commercial bank supervised by the Federal Reserve NM State charter Fed nonmember commercial bank supervised by the FDIC SA State or federal charter savings association supervised by the Office of Thrift Supervision SB State charter savings bank supervised by the FDIC
Bank Failure #132&133: Arizona and Kansas
by Calculated Risk on 12/11/2009 07:16:00 PM
Note: since I get questions now and then - the Haiku was started long ago and is kind of a tradition.
AKA Giant Cash Sinkhole
We can't climb out of
Prairie bank failure
Solution for Solutions:
Arvest to invest
by Soylent Green is People
From the FDIC: Enterprise Bank & Trust, Clayton, Missouri, Assumes All of the Deposits of Valley Capital Bank, National Association, Mesa, Arizona
Valley Capital Bank, National Association, Mesa, Arizona, was closed today by the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, which appointed the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) as receiver. ...From the FDIC: Arvest Bank, Fayetteville, Arkansas, Assumes All of the Deposits of SolutionsBank, Overland Park, Kansas
As of September 30, 2009, Valley Capital Bank had total assets of approximately $40.3 million and total deposits of approximately $41.3 million. ...
The FDIC estimates that the cost to the Deposit Insurance Fund (DIF) will be $7.4 million. ... Valley Capital Bank is the 132nd FDIC-insured institution to fail in the nation this year, and the forth in Arizona. The last FDIC-insured institution closed in the state was Bank USA, National Association, Phoenix, on October 30, 2009.
SolutionsBank, Overland Park, Kansas, was closed today by the Office of the State Bank Commissioner of Kansas, which appointed the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) as receiver. ...Less than $300 million hit to the DIF so far today ...
As of September 30, 2009, SolutionsBank had total assets of $511.1 million and total deposits of approximately $421.3 million. ...
The FDIC estimates that the cost to the Deposit Insurance Fund (DIF) will be $122.1 million. ... SolutionsBank is the 133rd FDIC-insured institution to fail in the nation this year, and the third in Kansas. The last FDIC-insured institution closed in the state was First National Bank of Anthony, Anthony, on June 19, 2009.
Bank Failure #131: Republic Federal Bank, National Association, Miami, Florida
by Calculated Risk on 12/11/2009 05:16:00 PM
Palm trees, warm ocean waters
Plus one toasted bank
by Soylent Green is People
From the FDIC: 1st United Bank, Boca Raton, Florida, Assumes All of the Deposits of Republic Federal Bank, National Association, Miami, Florida
Republic Federal Bank, National Association, Miami, Florida, was closed today by the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), which appointed the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) as receiver. ...An early failure ...
As of September 30, 2009, Republic Federal Bank, N.A. had total assets of approximately $433.0 million and total deposits of approximately $352.7 million. ...
The FDIC estimates that the cost to the Deposit Insurance Fund (DIF) will be $122.6 million. ... Republic Federal Bank, N.A. is the 131st FDIC-insured institution to fail in the nation this year, and the 13th in Florida. The last FDIC-insured institution closed in the state was Commerce Bank of Southwest Florida, Fort Myers, on November 20, 2009.
San Francisco Bank: "Not-so-smart" CRE Loans
by Calculated Risk on 12/11/2009 04:00:00 PM
Since it is Friday, here are a couple of articles from San Francisco Magazine on some "not-so-smart" apartment loans ... the first on the lender, the second on the borrower.
From David Johnson: When smart money said "no more," not-so-smart Marin bank loaned the Lembis $41 million. (ht Eric)
The Lembi real-estate implosion (see “War of Values,” December 2009) is on the verge of claiming another casualty: little Tamalpais Bank of San Rafael, which lent $41 million to the Lembi family and has now declared virtually its entire portfolio of commercial mortgages to be in default.And from Danelle Morton: War of values
... Walter and Frank Lembi, the father and son behind the CitiApartments rental behemoth, used more than $1 billion in financing from international investment banks and purchased more than 170 San Francisco apartment buildings between 2003 and 2008, bringing the total number of buildings they owned to 300 ...
Tamalpais Bank made most of the Lembi loans between December 2007 and April 2008. ... by this past September, the Lembis had defaulted on all except one of their loans, leaving Tamalpais Bank with a $38 million hole in its portfolio. The size of the loans was equivalent to more than 75 percent of the bank’s total capital.
“Lending that much of the bank’s capital to a single borrower is inherently reckless, imprudent, and simply unsafe and unsound,” said Richard Newsom, a retired San Francisco bank regulator. “Originating such a huge concentration of credit to one borrower in that period is beyond unsafe and unsound, because the commercial real-estate market was already starting to crack at that time.”
emphasis added
Since 2003, the [Lembi] family, through its various corporate entities, had acquired more than 170 properties—close to $1 billion in real estate—on top of the 130 or so they’d already owned. This briefly made them the largest private landlord in a city where 65 percent of residents are tenants.This is similar to the strategy of the buyers of Peter Cooper Village and Stuyvesant Town in New York; the plan was to somehow remove the rent controlled tenants and increase the rents significantly. It worked about the same.
There seemed to be no pattern to their acquisitions. They bought everything from grande dames, like the Park Lane on Nob Hill, to ratty dumps in the Tenderloin.
...
The Lembis were primarily interested in properties built before 1979: In other words, buildings covered by rent control. The reason is spelled out in a confidential document prepared by the investment bank Credit Suisse in winter 2008. The document focuses on the group of 24 properties that included the Carlomagno buildings. It shows, unit by unit, how the Lembis planned to replace 85 percent of the tenants. The family had set aside $9 million for “relocation costs,” and another $13 million for renovations. Once the apartments were fixed up, the document states, CitiApartments planned to raise rents by an average of 59 percent.
House Approves Bank Reform
by Calculated Risk on 12/11/2009 02:33:00 PM
Note: Mortgage cram downs were defeated.
From CNBC: What's In the House Financial Services Reform Bill
From the NY Times: House Votes to Tighten Regulation of Wall Street


