by Calculated Risk on 11/09/2010 01:44:00 PM
Tuesday, November 09, 2010
Ireland: A Side Show
UPDATE: Two days after this post, I posted Ireland: Bank funding problems?
Ireland is fully funded until mid-2011, however I've heard this morning that certain European investors are no longer willing to provide Irish banks with overnight funding. This could lead to a serious liquidity problem for the Irish banks - and some investors believe that Ireland may need to borrow from the IMF or the EFSF to support the banks.Original post:
I've been posting on Ireland recently because the 10-year bond yield is approaching 8% (some analysts think Ireland will use the European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF) above 8%). The Ireland 10-year yield hit a record 7.94% today.
To be clear: Ireland is not Greece. There is no short term liquidity issue; Ireland does not need to borrow until mid-2011 and rates could fall before then.
The increase in yields is being driven by investor fears of a permanent
crisis-resolution mechanism that will include possible haircuts for private investors.
Here are some excerpts from a proposal from the think-tank Bruegel about a permanent
crisis-resolution mechanism (Via the WSJ Making Default A Real Possibility):
We propose in this paper the creation of a European Crisis Resolution Mechanism (ECRM) consisting of two pillars:This is similar to some of the recent German proposals.
A procedure to initiate and conduct negotiations between a sovereign debtor with unsustainable debt and its creditors leading to, and enforcing, an agreement on how to reduce the present value of the debtor’s future obligations in order to re-establish the sustainability of its public finances. This would require a special court to deal with such cases. The European Court of Justice is the natural institution for this purpose and a special chamber could be created within it for that purpose.
Rules for the provision of financial assistance to euro-area countries as an element in resolving the crisis. Should a euro-area country be found insolvent, the provision of financial aid should be conditional on the achievement of an agreement between the debtor and the creditors reestablishing solvency. The task of supplying financial assistance could be given to the EFSF provided that it is made permanent and an institution of the European Union. Lending by the permanent EFSF could also be provided, under appropriate conditions, to euro area countries facing temporary liquidity problems, as currently foreseen by the temporary EFSF.
Right now this is a side show (but still interesting).
BLS: Job Openings decrease slightly in September, Low Labor Turnover
by Calculated Risk on 11/09/2010 10:23:00 AM
Note: The temporary decennial Census hiring and layoffs distorted this series over the summer months.
From the BLS: Job Openings and Labor Turnover Summary
The number of job openings in September was 2.9 million, which was little changed from August. Although the month-to-month change is small, the number of job openings in September was 25 percent higher than the number at the most recent series trough in July 2009.Note: The difference between JOLTS hires and separations is similar to the CES (payroll survey) net jobs headline numbers. The CES (Current Employment Statistics, payroll survey) is for positions, the CPS (Current Population Survey, commonly called the household survey) is for people.
The following graph shows job openings (yellow line), hires (purple), Layoff, Discharges and other (red column), and Quits (light blue column) from the JOLTS.
Unfortunately this is a new series and only started in December 2000.
 Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.Notice that hires (purple) and total separations (red and blue columns stacked) are pretty close each month. When the purple line is above the two stacked columns, the economy is adding net jobs - when it is below the columns, the economy is losing jobs.
In September, about 4.19 million people lost (or left) their jobs, and 4.19 million were hired (this is the labor turnover in the economy) for no change in total jobs.
Note: I think this graph makes a key point: The change in net jobs each month is small compared to the overall labor turnover. Over 4 million jobs were lost in September (seasonally adjusted) and over 4 million people were hired!
Although job openings declined slightly in September, it appears job openings are still trending up. However overall labor turnover is still low.
Ceridian-UCLA: Diesel Fuel index declines in October, "Signals Weaker Holiday Season"
by Calculated Risk on 11/09/2010 09:00:00 AM
This is the new UCLA Anderson Forecast and Ceridian Corporation index using real-time diesel fuel consumption data: Pulse of Commerce IndexTM
 Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.
This graph shows the index since January 1999.
This is a new index, and doesn't have much of a track record in real time, although the data suggests the recovery has had a "time out" since May.
Press Release: Over the Road Trucked Shipping Decline Signals Weaker Holiday Season, Reports Latest Ceridian-UCLA Pulse of Commerce Index™
The Ceridian-UCLA Pulse of Commerce Index™ (PCI), a real-time measure of the flow of goods to U.S. factories, retailers, and consumers, fell 0.6 percent in October following a decline of 0.5 percent in September and a decline of 1.0 percent in August. The three consecutive month decline is the first since January 2009, when the U.S. was still deep in recession. The negative month-over-month trajectory for October, typically a peak month for America’s trucking industry, may also prelude a disappointing holiday season, indicating retailer wariness about future sales prospects.I'm not confident in using this index to forecast GDP growth, although it does appear to track Industrial Production over time (with plenty of noise).
“The October data begins the fourth quarter on a down note. October is also an especially important siren for the holiday season,” said Ed Leamer, chief PCI economist and director of the UCLA Anderson Forecast.
...
“We have had a recovery ‘time out,’” summarized Leamer. “Since May’s peak, trucking has receded 8.3 percent. Fortunately, the full stew of economic information does not appear to foretell a double dip in the coming. Rather, the economic malaise that set-in this summer is still very much with us.”
With the three-to-one relationship between the PCI and GDP growth in recessions and recoveries, the 4.1 percent annualized growth figure translates to 1.3 percent forecasted growth for GDP. PCI results need to reach 10 to 15 percent year-over-year growth for a truly healthy job market. The declines in the PCI also suggest further slowing in the Federal Reserve's monthly Industrial Production (IP) index (to be released later this month), and anticipate a month-over-month IP decrease of 0.16 percent.
...
The Ceridian-UCLA Pulse of Commerce Index™ is based on real-time diesel fuel consumption data for over the road trucking ...
NFIB: Small Business Optimism improves slightly
by Calculated Risk on 11/09/2010 08:14:00 AM
From National Federation of Independent Business (NFIB): Small Business Optimism improves slightly
Optimism rose again in October, but the index remains stuck in the recession zone established over the past two years, not a good reading even with a 2.7 point improvement over September. This is still a recession level reading based on Index values since 1973. However, job creation plans did turn positive and job reductions ceased.Note: Small businesses have a larger percentage of real estate and retail related companies than the overall economy.
 Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.The first graph shows the small business optimism index since 1986. Although the index increased to 91.7 in October (highest since May), it is still at recessionary level according to NFIB Chief Economist Bill Dunkelberg.
 The second graph shows the net hiring plans over the next three months.
The second graph shows the net hiring plans over the next three months.Hiring plans have turned slightly positive again. According to NFIB: "Average employment growth per firm was 0 in October, one of the best performances in years. ... Over the next three months, eight percent plan to increase employment (unchanged), and 13 percent plan to reduce their workforce (down three points), yielding a seasonally adjusted net one percent of owners planning to create new jobs, a four point gain from September."
 And the third graph shows the percent of small businesses saying "poor sales" is their biggest problem.
And the third graph shows the percent of small businesses saying "poor sales" is their biggest problem.Usually small business owners complain about taxes and regulations (that usually means business is good!), but now their self reported biggest problem is lack of demand.
Monday, November 08, 2010
More Ireland
by Calculated Risk on 11/08/2010 09:58:00 PM
The WSJ has some interesting facts on the Ireland residential housing market: Ireland's Next Blow: Mortgages
More than 36,000 borrowers, representing 4.6% of Irish mortgage loans, were at least 90 days behind on their loans as of June 30, according to Ireland's financial regulator. ... nearly 200,000 Irish mortgages—about one of every four outstanding home loans—is expected to be "underwater" by the end of the year.As a comparison, the Q2 CoreLogic report showed 11 million American mortgages, or 23 percent of households with mortgages, were underwater - about the same percentage as in Ireland. In the U.S. about 4.3% of mortgages are more than 90 days delinquent, and another 3.8% are in the foreclosure process.
The Ireland 10-year bond yield hit a record 7.86% today. Ireland will not have to borrow until next year, but if the 10-year yield moves above 8% or so, then it is likely that Ireland would use the European Financial Stability Fund (EFSF).
AAR: October 2010 Rail Traffic Continues Mixed Progress
by Calculated Risk on 11/08/2010 05:06:00 PM
From the Association of American Railroads: October 2010 Rail Traffic Continues Mixed Progress. The AAR reports carload traffic in October 2010 was up 8.7% compared to October 2009, however carload traffic was still 7.9% lower than in October 2008. Intermodal traffic (using intermodal or shipping containers) is up 10.4% over October 2009 and up 1.2% over October 2008.
"Last week the government announced that GDP grew roughly two percent in the third quarter of 2010. Rail traffic in October suggests that similarly moderate growth is continuing into the fourth quarter," said AAR Senior Vice President John T. Gray.
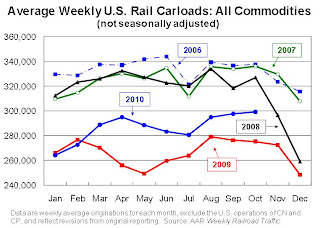 Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.This graph shows U.S. average weekly rail carloads (NSA). Traffic increased in 15 of 19 major commodity categories year-over-year.
From AAR:
• U.S. freight railroads originated 1,196,432 carloads in October 2010, an average of 299,108 carloads per week. That’s up 8.7% from October 2009 and down 7.9% from October 2008 on a non-seasonally adjusted basisAs the first graph shows, rail carload traffic collapsed in November 2008, and now, a year into the recovery, carload traffic has only recovered half way. However intermodal has performed better ...

• On a non-seasonally adjusted basis, October is usually the highest intermodal month of the year for U.S. railroads. That’s the case again in 2010This is consistent with a sluggish recovery.
• Well over half of U.S. intermodal traffic consists of imports or exports, and growth in international trade is a major factor behind higher intermodal traffic so far this year. In the first nine months of 2010, import TEUs (twenty-foot equivalent units) at six of the largest U.S. ports — Los Angeles, Long Beach, Savannah, New York & New Jersey, Seattle, and Norfolk — rose 19.9% in aggregate compared with the first nine months of 2009. Export TEUs at the same ports were up 15.5% in aggregate.excerpts with permission
Note: The Ceridian-UCLA diesel fuel index for October will be released tomorrow.
Fed: Banks expect tight lending standards for foreseeable future
by Calculated Risk on 11/08/2010 02:23:00 PM
In general banks have stopped tightening standards (they are already very tight), and demand has stopped falling (there is little demand for loans).
From the Federal Reserve The October 2010 Senior Loan Officer Opinion Survey on Bank Lending Practices
The October survey indicated that, on net, banks eased standards and terms over the previous three months on some categories of loans to households and businesses. ... However, substantial fractions of banks reported in response to a set of special questions that standards for many categories of loans would not return to their longer-run averages for the foreseeable future.Here is the full report.
...
Domestic survey respondents reported easing standards and most terms on [commercial and industrial] C&I loans to firms of all sizes. ... Demand declined, on net, for C&I loans ...
Most respondents reported no change in their bank's standards for approving [commercial real estate] CRE loans. ...
[A] special question asked banks whether their current level of lending standards remained tighter than the average level over the past decade and, if so, when they expected that standards would return to their long-run norms, assuming that economic activity progressed according to consensus forecasts. For all loan categories, substantial fractions of respondents thought that their bank's lending standards would not return to their long-run norms until after 2012 or would remain tighter than longer-run average levels for the foreseeable future.
NY Fed: Continued Decline in Consumer Debt
by Calculated Risk on 11/08/2010 11:14:00 AM
This is a new quarterly report from the NY Fed ... an interesting finding is that consumers are actively reducing their debt - the decline in debt isn't just because of defaults.
From the NY Fed: Q3 Report on Household Debt and Credit Shows Continued Decline in Consumer Debt
The Federal Reserve Bank of New York today released its Quarterly Report on Household Debt and Credit for the third quarter of 2010, which shows that consumer debt continues its downward trend of the previous seven quarters, though the pace of decline has slowed recently. Since its peak in the third quarter of 2008, nearly $1 trillion has been shaved from outstanding consumer debts.Here is the Q3 report: Quarterly Report on Household Debt and Credit
Additionally, this quarter’s supplemental report addresses for the first time the question of how this decline has been achieved and notes a sharp reversal in household cash flow from debt, indicating a decrease in available funds for consumption. According to newly available data through year end 2009, the payoff of debt by consumers reduced their cash flow by about $150 billion, whereas between 2000 and 2007, borrowing had contributed more than $300 billion annually to consumers’ cash flow.
Excluding the effects of defaults and charge-offs, available data show that non-mortgage debt fell for the first time since at least 2000. Also, net mortgage debt paydowns, which began in 2008, reached nearly $140 billion by year end 2009. These unique findings suggest that consumers have been actively reducing their debts, and not just by defaulting.
“Consumer debt is declining but only part of the reduction is attributable to defaults and charge-offs,” said Donghoon Lee, senior economist in the Research and Statistics Group at the New York Fed. “Americans are borrowing less and paying off more debt than in the recent past. This change, which we continue to study carefully, can be a result of both tightening credit standards and voluntary changes in saving behavior.”
And a supplemental report: Have Consumers Become More Frugal?
So are consumers becoming more frugal? Yes. Holding aside defaults, they are indeed reducing their debts at a pace not seen over the last ten years. A remaining issue is whether this frugality is a result of borrowers being forced to pay down debt as credit standards tightened, or a more voluntary change in saving behavior.And some data and graphs.
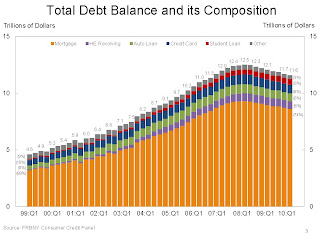 Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.From the NY Fed:
Aggregate consumer debt continued to decline in the second quarter, continuing its trend of the previous six quarters. As of June 30, 2010, total consumer indebtedness was $11.7 trillion, a reduction of $812 billion (6.5%) from its peak level at the close of 2008Q3, and $178 billion (1.5%) below its March 31, 2010 level. Household mortgage indebtedness has declined 6.4%, and home equity lines of credit (HELOCs) have fallen 4.4% since their respective peaks in 2008Q3 and 2009Q1. Excluding mortgage and HELOC balances, consumer indebtedness fell 1.5% in the quarter and, after having fallen for six consecutive quarters, stands at $2.31 trillion, 8.4% below its 2008Q4 peak.There are a number of credit graphs at the NY Fed site.
Ireland Update: "Relying on the kindness of strangers"
by Calculated Risk on 11/08/2010 08:49:00 AM
The yield on the Ireland 10-year bond hit a record 7.75% this morning.
From Bloomberg: Irish Fight to End Bond `Buyers Strike' as EU Examines Budget
EU Economic and Monetary Affairs Commissioner Olli Rehn arrives in Dublin today for a two-day visit ... Ireland has the funds to avert the need for an immediate rescue, its cash may run out in the middle of next year unless it can raise money from the bond market in 2011.And a long piece from Professor Morgan Kelly (Ireland's "Doctor Doom"): If you thought the bank bailout was bad, wait until the mortgage defaults hit home. He is definitely pessimistic, and concludes:
...
Erik Nielsen, chief European economist at Goldman Sachs Group Inc., said Ireland may need help from the European Stability Fund and the IMF in Washington in early 2011.
“This is starting to feel like a tsunami of new concerns,” Nielsen said “There is a considerable probability that the alphabet soup will get involved in financing Ireland and Portugal early next year.”
Ireland faced a painful choice between imposing a resolution on banks that were too big to save or becoming insolvent, and, for whatever reason, chose the latter. Sovereign nations get to make policy choices, and we are no longer a sovereign nation in any meaningful sense of that term.
From here on, for better or worse, we can only rely on the kindness of strangers.
Sunday, November 07, 2010
NY Times on Irish Bond Yields
by Calculated Risk on 11/07/2010 10:23:00 PM
From Landon Thomas at the NY Times: Irish Debt Woes Revive Concern About Europe
The yield on Ireland’s 10-year bond climbed to 7.6 percent on Friday ... Its debt woes have stoked fear that it might even need to follow Greece and request a bailout from the European Union and the International Monetary Fund.Ireland has until next June to make progress. If Ireland does need a bailout next year, it will probably come from the European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF) - and at rates of around 8%.
...
For the moment, at least, that outcome seems improbable. Unlike Greece earlier this year, Ireland has enough cash on hand to allow it to finance government operations through June 2011.
Earlier:


