by Calculated Risk on 9/10/2009 11:39:00 AM
Thursday, September 10, 2009
Census Bureau: Real Median Household Income Fell 3.6%
From the Census Bureau:
The U.S. Census Bureau announced today that real median household income in the United States fell 3.6 percent between 2007 and 2008, from$52,163 to $50,303. This breaks a string of three years of annual income increases and coincides with the recession that started in December 2007.Here are some interesting stats on income: Annual Social and Economic (ASEC) Supplement
The nation’s official poverty rate in 2008 was 13.2 percent, up from 12.5 percent in 2007. There were 39.8 million people in poverty in 2008, up from 37.3 million in 2007.
Meanwhile, the number of people without health insurance coverage rose from 45.7 million in 2007 to 46.3 million in 2008, while the percentage remained unchanged at15.4 percent.
...
•Income inequality was statistically unchanged between 2007 and 2008, as measured by shares of aggregate household income by quintiles and the Gini index. The Gini index was 0.466 in 2008.
Note: for the house price to household income chart I graph every quarter, I assumed a "2% increase in household [nominal] median income for 2008 and flat for 2009". That was too optimistic.
Report: Treasury to Announce Short Sale Incentives this Month
by Calculated Risk on 9/10/2009 11:02:00 AM
From Diana Golobay at Housing Wire: Federal Incentives Coming for Short Sales, Deeds-in-Lieu
US Treasury Department sources confirmed to HousingWire the Treasury expects to issue details on the short sale and deed-in-lieu program later this month.This program is aimed at borrowers who would be "generally eligible for a MHA modification", but are probably too far underwater ... or owe too much.
...
[Federal Housing Administration (FHA) commissioner David Stevens said, in prepared remarks, at a House Financial Services subcommittee hearing yesterday:] “Because we know that the MHA program will not reach every at-risk homeowner or prevent all foreclosures, on May 14th the Administration announced the Foreclosure Alternatives program that will provide incentives for, and encourage, servicers and borrowers to pursue short sales and deeds-in-lieu (DIL) of foreclosure in cases where the borrower is generally eligible for a MHA modification but does not qualify or is unable to complete the process.”
He said the program will simplify the process of pursuing short sales and deeds-in-lieu, which will encourage more servicers and borrowers to participate in the program. The program will standardize the process, documentation and short performance timeframes.
“These options eliminate the need for potentially lengthy and expensive foreclosure proceedings, preserve the physical condition and value of the property by reducing the time a property is vacant, and allows the homeowners to transition with dignity to more affordable housing,” Stevens added.
emphasis added
Trade Deficit Increases in July
by Calculated Risk on 9/10/2009 08:46:00 AM
The Census Bureau reports:
The ... total July exports of $127.6 billion and imports of $159.6 billion resulted in a goods and services deficit of $32.0 billion, up from $27.5 billion in June, revised.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.The first graph shows the monthly U.S. exports and imports in dollars through July 2009.
Imports were up again in July, and exports also increased. On a year-over-year basis, exports are off 22% and imports are off 30%.
The second graph shows the U.S. trade deficit, with and without petroleum, through July.
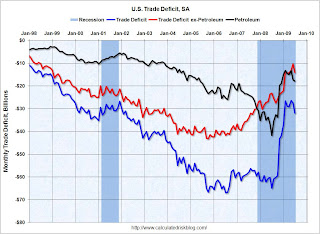 The blue line is the total deficit, and the black line is the petroleum deficit, and the red line is the trade deficit ex-petroleum products.
The blue line is the total deficit, and the black line is the petroleum deficit, and the red line is the trade deficit ex-petroleum products.Import oil prices increased to $62.48 in July - up about 50% from the prices in February (at $39.22) - and the fifth monthly increase in a row. Import oil prices will probably rise further in August.
It appears the cliff diving for U.S. trade might be over, although recent port data shows some weakness in traffic.
Weekly Unemployment Claims Decline
by Calculated Risk on 9/10/2009 08:31:00 AM
The DOL reports weekly unemployment insurance claims decreased to 550,000:
In the week ending Sept. 5, the advance figure for seasonally adjusted initial claims was 550,000, a decrease of 26,000 from the previous week's revised figure of 576,000. The 4-week moving average was 570,000, a decrease of 2,750 from the previous week's revised average of 572,750.
...
The advance number for seasonally adjusted insured unemployment during the week ending Aug. 29 was 6,088,000, a decrease of 159,000 from the preceding week's revised level of 6,247,000.
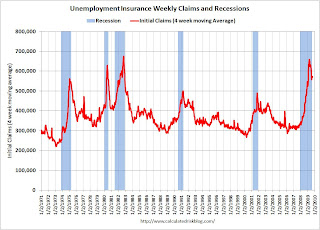 Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.This graph shows the 4-week moving average of weekly claims since 1971.
The four-week average of weekly unemployment claims decreased this week by 1,250 to 570,000, and is now 88,750 below the peak in April.
It appears that initial weekly claims have peaked for this cycle. However it seem that weekly claims are stuck at a very high level; weekly claims have been in the high 500 thousands for 10 weeks. This indicates continuing weakness in the job market. The four-week average of initial weekly claims will probably have to fall below 400,000 before the total employment stops falling.
Wednesday, September 09, 2009
Corus Bank: "The Great Enabler of Condo Madness"
by Calculated Risk on 9/09/2009 09:12:00 PM
From Eric Dash at the NY Times: In Florida, Vestiges of the Boom
On the corner of Flamingo Road and Pink Flamingo Lane ... a soaring monument to the great condominium bust bakes under the Florida sun.This article touches on several key points - the speculative activities of Corus, the slow response of their primary regulator, the FDIC trying to split the bank in two to sell the banking operations (not worth much) separately from the "monuments to madness" condo towers (also not worth much), the coming losses from C&D and CRE loans for other banks, the coming hit from Corus to the Deposit Insurance Fund (DIF) and more ...
The Tao Sawgrass ... built on the western fringes of Fort Lauderdale with easy money from the now tottering condo king of American finance: Corus Bancshares of Chicago. Only about 50 of the 396 units have been sold.
... The primary regulator of Corus, the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, failed to sound the alarm until Corus was deeply troubled. ... Corus will go down as the great enabler of condo madness, and its travails are a harbinger of the pain yet to come in the troubled world of commercial real estate.
...regulators are moving to cleave the bank in two and sell its banking operations and condominium loans separately. The hope is to clinch a deal by the end of the month.
Also, this article suggests Corus might have until the end of the month. However the bids for assets were due last Thursday, and I think it is likely that Corus will be seized this week.
Obama on Health Care
by Calculated Risk on 9/09/2009 08:05:00 PM
YouTube live feed (ht bANK fAILURE) or Link Here for large image.
Note: Embed removed. Here is the text for the speech.
A comment on the Deficit and National Debt
by Calculated Risk on 9/09/2009 07:21:00 PM
There seems to more and more concern about the deficit and the increases in the National Debt. It is definitely scary, and I've been writing about this issue for a number of years.
Back in late 2000 and in 2001 (I started this blog in January 2005) I focused on the deficit - and the long term fiscal damage I felt the Bush policies would cause.
President Bush argued in February 2001 that his fiscal policy "returns ... the surplus to the American taxpayers". In his 2001 testimony to Congress, then Fed Chairman Alan Greenspan supported President Bush by offering projections of "an on-budget surplus of almost $500 billion ... in fiscal year 2010". The National Debt would soon be retired and the Boomer's retirements secure. Greenspan offered a projection of "an implicit on-budget surplus under baseline assumptions well past 2030 despite the budgetary pressures from the aging of the baby-boom generation, especially on the major health programs."
Mr Bush also said in February 2001: "After paying the bills, my plan reduces the national debt, and fast. So fast, in fact, that economists worry that we're going to run out of debt to retire. That would be a good worry to have."
I disagreed strongly with President Bush and Mr. Greenspan's projections. I argued the surpluses were a mirage, and the tax policies would create a significant structural deficit.
I became even more adamant about the Bush structural deficits in 2004 and 2005, when it became obvious that the small improvement in the annual deficit was because of the housing bubble. I wrote in March 2005 about why I was so concerned about the housing bubble:
If we slide into a global recession, we have limited tools available to stimulate the economy. Interest rates are already very low (although the Fed has recently put some arrows back into the quiver), and we are already running general fund budget deficits of close to 6% of GDP.In 2006, Professor Samwick (who served as Chief Economist on the Staff of President Bush's Council of Economic Advisers) wrote: First Things First
CR writes:Today I believe some people are getting upset about the wrong thing at the wrong time. As Samwick noted, during a recession the deficits will increase - from falling tax revenues, automatic stabilizers and stimulus spending. Maybe some people disagree with the stimulus package, but that isn't going to change (except additions like extending unemployment benefits again).Everyone should agree that the most immediate fiscal problem is the structural General Fund deficit. Excluding future health care costs, the structural deficit is around 4% to 4.5% of GDP. This serious problem has been caused almost exclusively by Bush's policies. And imagine if the economy slows next year, as many people expect, adding a cyclical deficit on top of the huge Bush structural deficit.CR is correct in his diagnosis of the immediacy and the size of the problems of the General Fund deficit. As I have discussed in earlier posts ... the appropriate target for the General Fund deficit is for it to average to zero over a business cycle. A corollary to that is that the General Fund should be in surplus during the non-recessionary parts of that business cycle. (A slightly weaker target that I would also accept is that the Debt/GDP ratio not trend upward over time.)
So isn't it reasonable to suggest that Mr. Bush and the GOP fix the structural deficit first, before addressing other long-term issues? Of course.
Eliminating the recessionary deficit requires the economy to recover, and unfortunately the recovery will most likely be choppy and sluggish, but eventually a recovery will happen. Eliminating the structural deficit will be much more difficult and will require hard choices, but now is not the time.
The time to concerned about the structural deficit was in 2001 through 2006, and hopefully again starting in 2011 or 2012.
Market and StuyTown Update
by Calculated Risk on 9/09/2009 04:08:00 PM
Since I haven't posted this in some time ... Click on graph for larger image in new window.
This graph is from Doug Short of dshort.com (financial planner): "Four Bad Bears".
Note that the Great Depression crash is based on the DOW; the three others are for the S&P 500.
And on StuyTown from the NY Times: Buyers of Huge Manhattan Complex Face Default Risk (ht Ann)
[T]he buyers [of Stuyvesant Town and Peter Cooper Village in Manhattan] are running out of time and money. Jerry and Rob Speyer and their partner, BlackRock Realty, who together paid $5.4 billion ... have nearly exhausted an additional $890 million set aside for apartment renovations, landscaping and interest payments. Rents are down 25 percent from their peak.At that valuation - about two-thirds off the total $6.3 billion price - the equity is wiped out, the mezzanine debt is wiped out, and the first mortgage will take a significant haircut.
Real estate analysts say that the partnership’s money will run out as soon as December and that the owners are at “high risk” of default on $4.4 billion in loans.
...
A recent report from Realpoint, a credit rating agency, estimates that the property has a value today of only $2.13 billion.
...
At Stuyvesant Town, there is a $3 billion first mortgage, or commercial mortgage-backed security, and a $1.4 billion second loan, known as “mezzanine debt” held by SL Green, the government of Singapore and others.
Finally, there is $1.9 billion in equity put up by Tishman Speyer, BlackRock and their investors.
Fed's Beige Book: Economic Activity Stabilizing
by Calculated Risk on 9/09/2009 02:00:00 PM
From the Fed: Beige Book
Reports from the 12 Federal Reserve Districts indicate that economic activity continued to stabilize in July and August. Relative to the last report, Dallas indicated that economic activity had firmed, while Boston, Cleveland, Philadelphia, Richmond, and San Francisco mentioned signs of improvement. Atlanta, Chicago, Kansas City, Minneapolis, and New York generally described economic activity as stable or showing signs of stabilization; St. Louis remarked that the pace of decline appeared to be moderating. Most Districts noted that the outlook for economic activity among their business contacts remained cautiously positive.And on real estate:
The majority of Districts reported flat retail sales.
emphasis added
Residential real estate markets remained weak, but signs of improvement continued to be noted. Chicago, Richmond, Boston, and San Francisco observed an uptick in sales over the last six weeks, while sales in the Philadelphia District were described as steady. ... Most Districts noted that demand remained stronger at the low-end of the housing market. Boston, Cleveland, Dallas, Kansas City, Richmond, and New York indicated that the first-time home buyer tax incentive was spurring sales. However, Philadelphia did note an upturn in sales at the high-end of the market. Reports on house prices generally indicated ongoing downward pressures ...Stabilization is not new growth. Just more beige shoots ...
Reports on commercial real estate markets indicated that demand for space remained weak and that construction continued to decline in all Districts. Atlanta, Philadelphia, Richmond, and San Francisco reported that vacancy rates increased, while rates held steady in the Boston and Kansas City Districts and were mixed in New York. ... Commercial rents declined according to Boston, Chicago, New York, Philadelphia, and Richmond. Rent concessions were reported in the Richmond and San Francisco markets, and Richmond noted that some landlords had postponed property improvements in an effort to conserve cash. Construction remained at very low levels, with modest improvements noted in public construction in the Chicago, Cleveland, and Minneapolis Districts.
Mortgage Cram Downs: The Return
by Calculated Risk on 9/09/2009 12:10:00 PM
From Ryan Grim at the HuffPost: Cramdown Is Back: Banks Against Homeowners, Round 2 (ht Atrios)
House Financial Services Committee Chairman Barney Frank (D-Mass.) tells the Huffington Post he plans to revive the effort to give bankruptcy judges the authority to renegotiate home mortgages -- by making it part of this fall's much-anticipated financial regulatory reform bill.For a history of mortgage Cram Downs, and why they are needed, see Tanta's Just Say Yes To Cram Downs . Some excerpts:
...
On Tuesday, Frank was asked by HuffPost if he had plans to readdress cramdown. "Yes, as I will announce tomorrow, and I told this to bankers, given the slow pace of modifications, for whatever reason: they're not putting enough people on it, they're not taking it seriously, there are legal obstacles. As of now my intention would be to include the bankruptcy on primary residences in the reg reform."
The prohibition of court-ordered modifications for mortgages on principal residences was created in 1978; between 1978 and 1993 most bankruptcy courts interpreted the law to mean that while interest-rate reduction or term-extension modifications were not allowed, home mortgages could still be crammed down.There is much more in Tanta's post.
In 1993, with Nobleman v. American Savings Bank, the Supreme Court held that the prohibition on modifications of principal-residence mortgage loans also included cram downs. The result is that borrowers who are upside down and who have toxic, high-rate mortgages are simply, in practical terms, unable to maintain their homes in Chapter 13.
...
I am fully in favor of removing restrictions on modifications of mortgage loans in Chapter 13, but not necessarily because that helps current borrowers out of a jam. I'm in favor of it because I think it will be part of a range of regulatory and legal changes that will help prevent future borrowers from getting into a lot of jams, which is to say that it will, contra MBA, actually help "stabilize" the residential mortgage market in the long term. Any industry that wants special treatment under the law because of the socially vital nature of its services needs to offer socially viable services, and since the industry has displayed no ability or willingness to quit partying on its own, then treat it like any other partier under BK law.
Cram downs are in important step: as Ryan Grim notes in the HuffPost article, the mortgage modification programs are all "carrot" and the cram downs will provide a "stick", and more importantly, as Tanta noted, the cram downs will bring discipline to the mortgage industry.


