by Calculated Risk on 3/05/2009 01:31:00 PM
Thursday, March 05, 2009
UK: BoE Cuts Rate to 0.5%, Begins Quantitative Easing
From The Times: Bank to 'print' £75bn of new money as it cuts rate
The Bank of England ... confirmed it is beginning a strategy of so-called “quantitative easing”.With quantitative easing, the Fed (or the BoE in this case) prints money to buy treasuries (gilts) or other assets. The goal is to expand the monetary base.
...
The MPC ordered another half-point cut in base rate from an existing 1 per cent that was already the lowest in the Bank’s 314-year history to a new all-time low of 0.5 per cent.
...
The MPC’s decision to press on rapidly with QE, signalled a fortnight ago in minutes of its last meeting, means that it will now begin buying from commercial banks a range of corporate bonds (businesses’ IOUs) and Treasury gilt-edged stock or “gilts” (Government IOUs).
But as Krugman noted last year, the results might be disappointing: The humbling of the Fed (wonkish).
[T]he Bank of Japan tried that, under the name “quantitative easing;” basically, the money just piled up in bank vaults. To see why, think of it this way: once T-bills have a near-zero interest rate, cash becomes a competitive store of value, even if it doesn’t have any other advantages. As a result, monetary base and T-bills — the two sides of the Fed’s balance sheet — become perfect substitutes. In that case, if the Fed expands its balance sheet, it’s basically taking away with one hand what it’s giving with the other: more monetary base is out there, but less short-term debt, and since these things are perfect substitutes, there’s no market impact. That’s why the liquidity trap makes conventional monetary policy impotent.Note: Krugman's comments apply when the T-bill (or other assets) have a near-zero rate. So it depends on what assets the BoE buys.
More on MBA National Delinquency Survey
by Calculated Risk on 3/05/2009 01:05:00 PM
Here is the press release from the Mortgage Bankers Association (MBA): Delinquencies Continue to Climb in Latest MBA National Delinquency Survey
The delinquency rate for mortgage loans on one-to-four-unit residential properties rose to a seasonally adjusted rate of 7.88 percent of all loans outstanding as of the end of the fourth quarter of 2008, up 89 basis points from the third quarter of 2008, and up 206 basis points from one year ago, according to the Mortgage Bankers Association’s (MBA) National Delinquency Survey.The initial resets are behind us for the 2-28 subprime ARMs, but still ahead of us for the 5/1 ARMs (fixed for 5 years and then adjust monthly). I do agree the impact of the resets is overstated (especially now since the various indices used for ARMs are very low), but there will still be a significant impact when certain NegAm loans recast (like Option ARMs). For the difference between "reset" and "recast" see Tanta's: Reset Vs. Recast, Or Why Charts Don't Match
The delinquency rate breaks the record set last quarter and the quarter-to-quarter jump is the also the largest. The records are based on MBA data dating back to 1972.
The delinquency rate includes loans that are at least one payment past due but does not include loans somewhere in the process of foreclosure. The percentage of loans in the foreclosure process at the end of the fourth quarter was 3.30 percent, an increase of 33 basis points from the third quarter of 2008 and 126 basis points from one year ago. The combined percent of loans in foreclosure and at least one payment past due was 11.18 percent on a seasonally adjusted basis and 11.93 percent on a non-seasonally adjusted basis. Both of these numbers are the highest ever recorded in the MBA delinquency survey.
...
“Subprime ARM loans and prime ARM loans, which include Alt-A and pay option ARMs, continue to dominate the delinquency numbers. Nationwide, 48 percent of subprime ARMs were at least one payment past due and in Florida over 60 percent of subprime ARMs were at least one payment past due.
“We will continue to see, however, a shift away from delinquencies tied to the structure and underwriting quality of loans to mortgage delinquencies caused by job and income losses. For example, the 30-day delinquency rate for subprime ARMs continues to fall and is at its lowest point since the first quarter of 2007. Absent a sudden increase in short-term rates, this trend should continue because the last 2-28 subprime ARMs (fixed payment for two years and adjustable for the next 28 years) were written in the first half of 2007. The problem with initial resets is largely behind us, although the impact of the resets was generally overstated.
emphasis added
"Reset" refers to a rate change. "Recast" refers to a payment change.
Daily Show: CNBC Gives Financial Advice
by Calculated Risk on 3/05/2009 12:12:00 PM
Oh my ... (ht Spatch)
Report: Record 5.4 Million U.S. Homeowners Delinquent or in Foreclosure
by Calculated Risk on 3/05/2009 10:58:00 AM
From the WSJ: Delinquent Mortgages Hit Record Level
A record 5.4 million U.S. homeowners with a mortgage, or nearly 12%, were either behind on payments or in foreclosure at the end of last year, according to [the Mortgage Bankers Association] ...I haven't seen the actual report yet, and I'm especially interested in increases by loan category.
The percentage of loans at least 30 days past due rose to a record 7.88%, up from 6.99% in the third quarter and 5.82% a year earlier -- the biggest quarterly jump for delinquencies since the survey began in 1972.
The percentage of loans somewhere in the foreclosure process was 3.30% in the fourth quarter, up from 2.97% in the third quarter ...
The sharpest increases in loans 90-days past due were in Louisiana, New York, Georgia, Texas and Mississippi ...
The Stress Test "19"
by Calculated Risk on 3/05/2009 09:56:00 AM
In the Treasury White Paper on the Capital Assistance Program, the Treasury announced that the 19 largest bank are current undergoing stress tests:
Examinations will be conducted across the 19 banking organization with assets in excess of $100 billion, as measured according to the data reported for 2008Q4 in the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System Consolidated Financial Statements for Bank Holding Companies.Paul Kiel at ProPublica has compiled a list of the likely 19 banks by total assets: GMAC, MetLife Among Banks Undergoing Stress Tests
| Name | Total Assets (Billions) |
|---|---|
| 1. JPMorgan Chase | 2,175 |
| 2. Citigroup | 1,947 |
| 3. Bank of America (1) | 1,822 |
| 4. Wells Fargo | 1,310 |
| 5. Goldman Sachs | 885 |
| 6. Morgan Stanley | 659 |
| 7. MetLife | 502 |
| 8. PNC Financial Services | 291 |
| 9. U.S. Bancorp | 267 |
| 10. Bank of New York Mellon | 238 |
| 11. GMAC | 189 |
| 12. SunTrust | 189 |
| 13. State Street | 177 |
| 14. Capital One Financial Corp. | 166 |
| 15. BB&T | 152 |
| 16. Regions Financial Corp. | 146 |
| 17. American Express | 126 |
| 18. Fifth Third Bancorp | 120 |
| 19. KeyCorp | 105 |
This shows that the assets are concentrated in just a few large banks.
(1) Note: Data as of Q4 2008. Merrill is not included in the BofA asset numbers. IF added, BofA would have almost $2.5 trillion in assets (ht Evan).
Initial Jobless Claims: Slight Decrease
by Calculated Risk on 3/05/2009 08:30:00 AM
Note: Weekly claims is historically a noisy series. So, for initial claims, most analysts use the 4-week moving average - and that increased again this week.
The DOL reports on weekly unemployment insurance claims:
In the week ending Feb. 28, the advance figure for seasonally adjusted initial claims was 639,000, a decrease of 31,000 from the previous week's revised figure of 670,000. The 4-week moving average was 641,750, an increase of 2,000 from the previous week's revised average of 639,750.
...
The advance number for seasonally adjusted insured unemployment during the week ending Feb. 21 was 5,106,000, a decrease of 14,000 from the preceding week's revised level of 5,120,000. The 4-week moving average was 5,011,000, an increase of 76,750 from the preceding week's revised average of 4,934,250.
 Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.The first graph shows weekly claims and continued claims since 1971.
The four week moving average is at 641,750 the highest since 1982.
Continued claims are now at 5.11 million - just below the record set last week - and above the previous all time peak of 4.71 million in 1982.
 The second graph shows the 4-week average of initial weekly unemployment claims (blue, right scale), and total insured unemployed (red, left scale), both as a percent of covered employment.
The second graph shows the 4-week average of initial weekly unemployment claims (blue, right scale), and total insured unemployed (red, left scale), both as a percent of covered employment.This normalizes the data for changes in insured employment.
Another weak initial claims report ...
Wednesday, March 04, 2009
Late Night Futures
by Calculated Risk on 3/04/2009 11:59:00 PM
By popular request, an open thread and a few sources for futures and the foreign markets. Hopefully the comments are working better ...
Bloomberg Futures.
CBOT mini-sized Dow
CME Globex Flash Quotes
Futures from barchart.com
And the Asian markets.
And a graph of the Asian markets.
Best to all.
CRE: Investment in Hotels, Offices and Malls
by Calculated Risk on 3/04/2009 09:30:00 PM
There was a strong downward revision in non-residential structure investment in the Q4 GDP report. The CRE investment bust is here - and will get much worse based on the Fed's recent Senior Loan Officer Opinion Survey and the Architecture Billings Index. Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.
This graph shows investment in lodging (based on data from the BEA) as a percent of GDP. The recent boom in lodging investment has been stunning. Lodging investment is now at 0.33% of GDP - slightly below the all time high set in Q3 2008 - and preparing to cliff dive!
Note: prior to 1997, the BEA included Lodging in a category with a few other buildings. This earlier data was normalized using 1997 data, and is an approximation.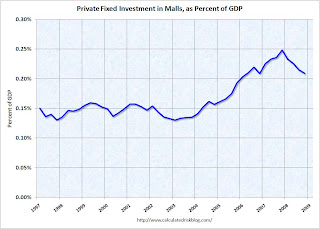 Investment in multimerchandise shopping structures (malls) decreased in Q4 2008 to .21% of GDP, after peaking in Q4 2007 at .25% of GDP. This is a pretty steep decline, but now it appears that new mall construction is about to almost stop.
Investment in multimerchandise shopping structures (malls) decreased in Q4 2008 to .21% of GDP, after peaking in Q4 2007 at .25% of GDP. This is a pretty steep decline, but now it appears that new mall construction is about to almost stop.
As David Simon, Chief Executive Officer or Simon Property Group, the largest U.S. shopping mall owner said a few weeks ago:
"The new development business is dead for a decade. Maybe it’s eight years. Maybe it’s not completely dead. Maybe I’m over-dramatizing it for effect."
 The third graph shows office investment as a percent of GDP since 1972. Office investment decreased slightly in Q4 2008. With the office vacancy rate rising sharply, office investment will probably decline all this year.
The third graph shows office investment as a percent of GDP since 1972. Office investment decreased slightly in Q4 2008. With the office vacancy rate rising sharply, office investment will probably decline all this year.Note: In 1997, the Bureau of Economic Analysis changed the office category. In the earlier years, offices included medical offices. After '97, medical offices were not included (The BEA presented the data both ways in '97).
Investment in all three categories - malls, lodging and offices - will decline sharply in 2009.
Fed's Lockhart on Real Estate
by Calculated Risk on 3/04/2009 08:04:00 PM
From Atlanta Fed President Dennis Lockhart: On Real Estate and Other Risks to the Economic Outlook A few excerpts. First on the rental market:
I should also comment on the weakening multifamily residential real estate picture. No two rental markets are exactly alike. But to generalize, those markets trending the worst probably share one or more characteristics. They had excessive condo construction or condo conversion activity. Such markets are seeing unsold units return as rentals. They had very high home price appreciation in the years 2004—07 with large amounts of speculative house construction activity. Today, in several markets, houses compete with apartments as rentals. And they have been experiencing high and rising foreclosure rates.Although Lockhart mentioned that houses are competing with apartments as rentals, he doesn't mention that this is happening for two reasons: 1) homeowners who can't sell their homes (or are "waiting for a better market") are renting their homes, and 2) many REOs are being purchased by cash flow investors as rentals helping to increase rental supply and push down rents.
And on Commercial real estate (CRE):
While historically smaller than residential real estate, commercial real estate (or nonresidential structures) accounts for a not-insignificant portion of the American economy—at least 4 percent of GDP directly and perhaps more, depending on estimates. ...This is good data. Although the CRE bust will be significant, it will not be as large an impact as the residential bust.
There are currently some $2.5 trillion of commercial property loans on the balance sheets of financial institutions and in commercial mortgage-backed securities (CMBS) markets. In contrast, residential mortgage debt amounts to about $11 trillion.
Some 25 percent of commercial real estate debt is securitized, compared with 60 percent of outstanding home mortgage debt. The volume of CMBS has more than doubled since 2003, a bit faster than the growth of overall commercial real estate debt.
There are several subsectors of commercial real estate: retail, office, hotel, and industrial. All are facing problems.This gives me an excuse, in the next post, to update the graphs of office, mall and hotel investment based on the revisions to Q4 GDP.
There is a growing imbalance of retail space for several reasons. A lot of new retail space was added in areas that saw a high level of home construction, much of which has not been absorbed.
This imbalance is aggravated by general weakness in the retail industry. Established retail centers are seeing rising vacancy rates. When an anchor tenant leaves a shopping center, or overall occupancy falls below a threshold level, other tenants are often free to cancel their leases. Industry data indicate that abandoned retail store expansions and store closings have reached levels not seen since the recession and real estate slump of 1991–92.
The hotel subsector is facing excess supply in the face of soft demand. Occupancy rates declined about 8 percentage points in the fourth quarter of 2008, according to industry sources. Summer tourism was hurt by high gas prices, and now business travel is declining as companies scale back in a weak economy.
Also, with the decline in the economy and rising unemployment, office and industrial vacancies have been rising. In virtually all segments of commercial real estate, there is downward pressure on property values because of new construction coming on stream—construction started before the recession fully set in—coupled with the effects of the economic downturn.
Interestingly, the only property type currently withstanding downward pressures is warehouse. This seems to be, perversely, at least partly because of the back-up of inventories resulting from weak consumer spending and adverse retail and manufacturing conditions.
Mortgage Modification and 2nd Mortgages
by Calculated Risk on 3/04/2009 06:19:00 PM
I'm back from my civic duty, and starting to read the newly released details of the Mortgage Modification Plan. The second mortgage sections are interesting.
This first reference to 2nd liens seems to be part of Home Affordable Refinance Program (Part I of the plan).
From the Making Home Affordable, Updated Detailed Program Description Fact Sheet
Second Liens: While eligible loan modifications will not require any participation by second lien holders, the program will include additional incentives to extinguish second liens on loans modified under the program, in order to reduce the overall indebtedness of the borrower and improve loan performance. Servicers will be eligible to receive compensation when they contact second lien holders and extinguish valid junior liens (according to a schedule to be specified by the Treasury Department, depending in part on combined loan to value). Servicers will be reimbursed for the release according to the specified schedule, and will also receive an extra $250 for obtaining a release of a valid second lien.So the 2nd lien holder will have a choice: do nothing, or take some unspecified compensation to extinguish the 2nd.
Then there is this section that seems to be in Part II: Home Affordable Modification Program Housing Counselor Q&As:
What if the borrower has a second mortgage and would like to apply for a Home Affordable Modification?Is that saying they will pay the 2nd holder up to $1000 under Part II?
Under the Home Affordable Modification program, junior lien holders will be required to subordinate to the modified loan. However, through the Home Affordable Modification an incentive payment of up to $1,000 is available to pay off junior lien holders. Servicers are eligible to receive an additional $500 incentive payment for efforts made to extinguish second liens on loans modified under this program.
Note: Part I is the section allowing homeowner with Fannie and Freddie held mortgages to refinance upto 105% LTV. This section makes sense since this lowers Fannie and Freddie's risk on loans they already own or guarantee. Under Part II the lender must bring the total monthly payments on mortgages to 38% of the borrowers gross income, and then the U.S. will match dollar for dollar from 38% down to 31% debt-to-income ratio for the borrower.


