by Calculated Risk on 1/06/2008 03:07:00 PM
Sunday, January 06, 2008
Recession: Mild or Severe?
Professor Nouriel Roubini suggests the debate has shifted from whether there will be a recession following the housing bust, to the severity of the recession. Roubini argues the recession will be severe:
“As argued here before, at this point the debate is not about soft land or hard landing; rather it is about how hard the hard landing will be. … This author’s assessment is … of a … severe and painful recession – lasting at least four quarters...”Others think it is still possible for the economy to avoid recession, but even then it will probably feel like one. As Goldman Sachs noted last week:
“the economy [may] skirt a technical recession, but in many respects this distinction may feel like an academic one.”This raises the question: What is the difference between a mild and a severe recession? Looking back at the last ten recessions, perhaps we can define a severe recession as lasting a year or more, with unemployment rising above 8%, and real GDP falling 2.5% or more from peak to trough.
By that definition, the U.S. has had two severe recession in the last 60 years:
1) Nov-73 to Mar-75:
Duration: 16 months2) Jul-81 to Nov-82:
Peak unemployment: 9%
Real GDP declined 3.1%
Duration: 16 monthsWe could use other measures for employment, such as the change in the unemployment rate (from expansion trough to recession peak) or the year-over-year change in total employment.
Peak unemployment: 10.8%
Real GDP declined 2.9%
This graph shows the unemployment rate and the year-over-year change in employment vs. recessions for the last 60 years.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.Back in the '40s and '50s, it was common for the YoY total employment to decline by significantly more than 2%. This was because of the large swings in manufacturing employment. Now a YoY decline of 2% would be severe.
Also the recession with the highest unemployment rates started from pretty high levels ('70s and early '80s). So maybe the change in unemployment, from expansion trough to contraction peak, would be a better measure to gauge the severity of a recession than the absolute unemployment rate.

The second graph shows manufacturing and construction employment as a percent of total employment. The smaller percentage of manufacturing employment - compared to the '40 and '50s - is one of the reasons the economy hasn't experienced the large swings in employment characteristic of recession in those earlier periods.
Construction employment could fall back to 4.5% of total employment, with the loss of over 1 million construction jobs, but manufacturing probably won't see sharp layoffs like earlier periods. Note that Bernard Markstein, director of forecasting at the National Association of Home Builders, recently suggested the loss of 1 million construction jobs was possible.
If we assume the loss of 1 million construction jobs, 0.5 million retail jobs, and another 0.5 million jobs elsewhere, the unemployment rate would only rise to 6.3% (probably less because the participation rate would fall). And under most definitions that probably isn't a severe recession.
Perhaps other areas of the economy will shed more jobs and Roubini will be proven correct, but my expectation right now is for a recession, but not severe (the unemployment rate will stay below 8%). I also expect that the eventual recovery will be sluggish, especially for employment. For housing related industries, the depression will continue for some time.
CRE: More on Macklowe
by Calculated Risk on 1/06/2008 12:39:00 AM
From the NY Times: Harry Macklowe’s $6.4 Billion Bill.
This is a story we've been following because it appears Macklowe bought at the top, and he has a large bill coming due next month for a highly leveraged transaction:
[Macklowe] has a $6.4 billion debt payment coming due next month in connection with his purchase of seven ... Midtown Manhattan office buildings a year ago. When he bought those buildings from Equity Office Properties, he ... used only $50 million of his own money to do so; he borrowed $7 billion to finance the rest of the purchase.According to the WSJ, Macklowe paid $6.8 billion for these seven properties, and borrowed a total of $7.6 billion! The NY Times also mentions a couple of other deals in possible trouble:
The Kushner Companies ... plunged into the Manhattan real estate market in 2006, paying $1.8 billion for 666 Fifth Avenue, at 53rd Street. The cash flow from 666 Fifth represents only about two-thirds of the amount needed to service the debt on the building — a shortfall of about $5 million a month — according to Real Capital Analytics, a research company in New York.
In Los Angeles, the developer Robert F. Maguire III may be forced to sell his publicly traded company, Maguire Properties, after buying a portfolio of buildings from the Blackstone Group just before the subprime credit crisis sent many of his tenants into bankruptcy.
Saturday, January 05, 2008
The Economist on Commercial Property
by Calculated Risk on 1/05/2008 09:55:00 PM
From the Economist: Dominoes on the skyline
FROM up high, London is a picture of vigorous renewal. In just about every direction, construction cranes point contemplatively to the skies. They also point to the great boom that has taken place in commercial property in recent years. The collapse of that boom, which now threatens to slash the values of these gleaming office towers and destroy the savings of millions, may pose almost as great a threat to Britain's banking system as the subprime crisis that has been roiling financial markets since late in 2007.The CRE slowdown was very predictable, but I doubt it will "pose almost as great a threat to Britain's banking system as the subprime crisis" because CRE wasn't as overbuilt as residential.
... with the impeccably bad timing the industry is known for, construction boomed just as the market was peaking. CB Richard Ellis, a consultancy, reckons that new offices are being built in London at their fastest rate in nearly two decades. Most of the ones going up this year have yet to find tenants (see chart), and not all will ...
For 2008 I Nominate "Bongwater"
by Tanta on 1/05/2008 01:41:00 PM
Via sterlingirl: AP
Subprime was chosen as 2007's word of the year.
Jingle Liens
by Tanta on 1/05/2008 07:45:00 AM
Hat tip to Disempowered Paper Pusher (the backbone of our industry!) for this excellent BusinessWeek piece on homes abandoned by both borrower and lender, "Dirty Deeds."
An anecdote with all the right motifs:
In 1998, Elizabeth M. Manuel obtained a $34,500 mortgage on the property from IMC Mortgage (since acquired by Citibank). By 2002, the loan had been sold into a securitization trust administered by Chase Manhattan (now JPMorgan Chase) as trustee. It also went into default, and Chase began foreclosure proceedings. In a court filing, Manuel (who could not be located for comment) said she left the home while the foreclosure action was pending. More than five years later, though, the title remains in her name. The house, although still standing, has become a fire-gutted wreck.Besides amusing myself by trying to figure out just what documents I'd have to give Judge Boyko to prove standing to foreclose in this case, I am of course deeply impressed by the social acceptability of "just walking away."
In May 2007, Nowak issued a default judgment against Chase for $9,000. But these cases can be notoriously difficult to untangle. Thomas A. Kelly, a spokesman for the bank, notes that Chase sold its trustee business to the Bank of New York Mellon (BK) in October, 2006, and couldn't locate anyone at Chase able to comment. But he reiterates the industry view that Chase can't be held responsible for maintaining a property it never owned. He acknowledges that if a home didn't seem worth taking as collateral, the bank may have made a decision to "just walk away."
My guess is that Chase never completed the foreclosure precisely because it never wanted to held accountable for taxes, insurance, and maintenance on a nearly worthless property; the "tangle" of securitization and trustee swaps and so on undoubtedly contributes to the mess but at some level that's smoke. So the city of Buffalo is working out a new process to tie those properties around the lenders' necks precisely to forestall this game. It will certainly be interesting to see whether it catches on elsewhere.
Reading things like this also always makes me think of the endless complaining you get over FHA appraisal and property inspection practices. Every time you're tempted to think those are silly and bureaucratic--delaying closing for another 30 days while an attic window pane is repaired--and in need of "modernization," remember these properties that were decrepit at the time they were first mortgaged by those modernized conventional subprime lenders, nearly worthless at the point the borrower could no longer carry the payments, and then nothing more than urban blight after years of the lender refusing to take title. FHA, for all its flaws, never walks away from title.
Friday, January 04, 2008
Vancouver 2010
by Calculated Risk on 1/04/2008 10:30:00 PM
Off topic: It's hard to believe the Torino Winter Olympic games were almost two years ago!
Back then, I posted a few times about figure skater Sasha Cohen (a family friend). I still occasionally receive news clippings from readers, and questions about Sasha, so here is an update: Sasha has not skated competitively since March 2006, and she is also not competing this winter. She is currently performing in Japan, and then is touring the U.S. with Stars on Ice through April.
The following video is from the Stars on Ice tour. It is completely different and simply amazing. Sasha also skates two solo performances during the show.
I'm frequently asked: Will she try a competitive comeback? The answer - not too cryptically - is in the post title.
Fed Funds: Market Expects 50bps Rate Cut
by Calculated Risk on 1/04/2008 05:27:00 PM
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.
Source: Cleveland Fed, Fed Funds Rate Predictions
The market expectations are now for a 50 bps rate cut on January 30th.
Meanwhile, the Fed has expanded the Term Auction Facility (TAF) in January:
The Federal Reserve will conduct two auctions of 28-day credit through its Term Auction Facility (TAF) in January. It will offer $30 billion in the auction to be held on Monday, January 14 and $30 billion in the auction to be held on Monday, January 28.
...
The Federal Reserve intends to conduct biweekly TAF auctions for as long as necessary to address elevated pressures in short-term funding markets. Decisions regarding auctions in February will be announced by Friday, February 1.
Glassman: "Real estate excesses will vanish by spring 2008"
by Calculated Risk on 1/04/2008 02:21:00 PM
A few days ago, the WSJ asked: Will Home Prices Hit Bottom by June?. The WSJ's Greg Ip provided a link to a research report by James Glassman, economist at J.P. Morgan Chase. (no relation to James K. Glassman, co-author of “Dow 36,000″)
"The correction of housing prices is well under way. Given the present trends in income and house prices, real estate excesses of the past five years will have vanished by spring 2008.And Glassman references this figure:
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph is incorrect. The author is comparing gross income per household vs. the S&P / Case-Shiller house price index.
The repeat sales index determines the average change in a house price. The gross income could be distorted by a few individuals with extraordinary income gains.
The average change in a house price could be distorted too, if the most expensive homes appreciated at a much faster rate than other homes. But this doesn't appear to be an issue.
Instead of using the gross income per household, the author should use the median household income gain for homeowners (probably the top 2/3 of households).
This is a simple error, but it leads to a very wrong conclusion. The real estate excesses will not vanish by spring 2008.
Besides the graph is very funny - the housing bubble of the late '80s is graphed as the normal price range. And the subsequent housing bust is graphed as housing being undervalued. That was a very painful bust for many builders and homeowners, and that bubble / bust was small compared to the current bubble.
S&P may cut $6.42 Billion in CDOs
by Calculated Risk on 1/04/2008 12:24:00 PM
From Reuters: S&P may cut $6.42 bln CDOs affecting 149 tranches
Standard & Poor's may cut the rating on $6.42 billion of collateralized debt obligations (CDOs) following downgrades to billions of dollars worth of second-lien residential mortgage-backed securities last month.
S&P said the action affects 149 tranches from 43 U.S. cash flow and hybrid CDOs of asset-backed securities.
December Employment Report
by Calculated Risk on 1/04/2008 08:31:00 AM
Update: This graph shows the unemployment rate and the year-over-year change in employment vs. recessions.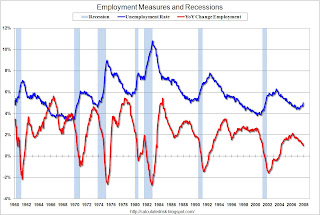 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.
The rise in unemployment, from a cycle low of 4.4% to 5.0% will set off alarm bells.
Also concerning is the YoY change in employment is less than 1%, also suggesting a recession.
Employment numbers can be heavily revised, but this report will definitely get attention.
Original Post: From the BLS: Employment Situation Summary
The unemployment rate rose to 5.0 percent in December, while nonfarm payroll employment was essentially unchanged (+18,000), the Bureau of Labor Statistics of the U.S. Department of Labor reported today. Job growth in several service-providing industries, including professional and technical services, health care, and food services, was largely offset by job losses in construction and manufacturing. Average hourly earnings rose by 7 cents, or 0.4 percent.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.Residential construction employment declined 28,500 in December, and including downward revisions to previous months, is down 293.1 thousand, or about 8.5%, from the peak in March 2006. (compared to housing starts off almost 50%).
Note the scale doesn't start from zero: this is to better show the change in employment.
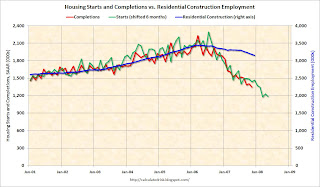 This second graph shows starts, completions and residential construction employment. (starts are shifted 6 months into the future). Completions and residential construction employment were highly correlated, and Completions typically lag Starts by about 6 months.
This second graph shows starts, completions and residential construction employment. (starts are shifted 6 months into the future). Completions and residential construction employment were highly correlated, and Completions typically lag Starts by about 6 months.This suggests residential construction employment could fall significantly from current levels.
Overall this is a very weak report, and the unemployment rate rising to 5% will set off recession arguments.


