by Calculated Risk on 2/26/2015 12:18:00 PM
Thursday, February 26, 2015
Key Measures Show Low Inflation in January
The Cleveland Fed released the median CPI and the trimmed-mean CPI this morning:
According to the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland, the median Consumer Price Index rose 0.2% (1.9% annualized rate) in January. The 16% trimmed-mean Consumer Price Index rose 0.1% (1.3% annualized rate) during the month. The median CPI and 16% trimmed-mean CPI are measures of core inflation calculated by the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland based on data released in the Bureau of Labor Statistics’ (BLS) monthly CPI report.Note: The Cleveland Fed has the median CPI details for January here. Motor fuel declined at a 92% annualized rate in January, following a 69% annualized rate decline in December, a 55% annualized rate decline in November, and a 31% annualized rate decline in October. However motor fuel will add to inflation in February.
Earlier today, the BLS reported that the seasonally adjusted CPI for all urban consumers fell 0.7% (−7.8% annualized rate) in January. The CPI less food and energy rose 0.2% (2.2% annualized rate) on a seasonally adjusted basis.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows the year-over-year change for these four key measures of inflation. On a year-over-year basis, the median CPI rose 2.2%, the trimmed-mean CPI rose 1.8%, and the CPI less food and energy rose 1.6%. Core PCE is for December and increased 1.3% year-over-year.
On a monthly basis, median CPI was at 1.9% annualized, trimmed-mean CPI was at 1.3% annualized, and core CPI was at 2.2% annualized.
On a year-over-year basis these measures suggest inflation remains below the Fed's target of 2% (median CPI is slightly above 2%).
The key question for the Fed is if these key measures will move back towards 2%.
Kansas City Fed: Regional Manufacturing Activity Expanded "Slightly" in February, Weaker Energy Sector
by Calculated Risk on 2/26/2015 11:36:00 AM
From the Kansas City Fed: Tenth District Manufacturing Activity Rose Just Slightly
The Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City released the February Manufacturing Survey today. According to Chad Wilkerson, vice president and economist at the Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City, the survey revealed that Tenth District manufacturing activity rose just slightly from the previous month, but producers expected activity to pick up moderately in the months ahead.We are seeing some impact from lower oil prices - however, overall, lower prices is a positive for the economy.
“We saw a further slowing in growth this month, driven in part by weaker factory activity in our energy states”, said Wilkerson. “The raw materials prices index also fell for the first time in over five years.”
The month-over-month composite index was 1 in February, down from 3 in January and 8 in December. The composite index is an average of the production, new orders, employment, supplier delivery time, and raw materials inventory indexes. The overall slower growth was mostly attributable to large declines in primary metals and computer and electronics production. Looking across District states, the weakest activity was in Colorado, Oklahoma, and New Mexico. In contrast, production activity in the fabricated metals and machinery industries both increased moderately. ... the new orders index inched lower from 5 to 3, and the employment index fell for the second straight month.
emphasis added
Weekly Initial Unemployment Claims increased to 313,000
by Calculated Risk on 2/26/2015 08:30:00 AM
The DOL reported:
In the week ending February 21, the advance figure for seasonally adjusted initial claims was 313,000, an increase of 31,000 from the previous week's revised level. The previous week's level was revised down by 1,000 from 283,000 to 282,000. The 4-week moving average was 294,500, an increase of 11,500 from the previous week's revised average. The previous week's average was revised down by 250 from 283,250 to 283,000.The previous week was revised down to 282,000.
There were no special factors impacting this week's initial claims.
The following graph shows the 4-week moving average of weekly claims since January 2000.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.The dashed line on the graph is the current 4-week average. The four-week average of weekly unemployment claims increased to 294,500.
This was above the consensus forecast of 290,000, and the low level of the 4-week average suggests few layoffs.
Wednesday, February 25, 2015
Thursday: CPI, Unemployment Claims, Durable Goods
by Calculated Risk on 2/25/2015 08:45:00 PM
First, from the ATA: ATA Truck Tonnage Index Jumped 1.2% in January
American Trucking Associations’ advanced seasonally adjusted For-Hire Truck Tonnage Index increased 1.2% in January, following a revised gain of 0.1% during the previous month. In January, the index equaled 135.7 (2000=100), an all-time high.Thursday:
Compared with January 2014, the SA index increased 6.6%, which was the largest year-over-year gain in over a year.
...
ATA recently revised the seasonally adjusted index back five years as part of its annual revision. For all of 2014, tonnage was up 3.7%, slightly better than the 3.4% originally reported. In 2013, the index increased 5.5%.
“Truck tonnage continued to improve in January, marking the fourth straight gain totaling 3.5%,” said ATA Chief Economist Bob Costello. “Last year was slightly better for truck tonnage than we originally thought and I am expecting that momentum to continue in 2015.”
emphasis added
• At 8:30 AM ET, the initial weekly unemployment claims report will be released. The consensus is for claims to increase to 290 thousand from 283 thousand.
• Also at 8:30 AM, the Consumer Price Index for January. The consensus is for a 0.6% decrease in CPI, and for core CPI to increase 0.1%.
• Also at 8:30 AM: Durable Goods Orders for January from the Census Bureau. The consensus is for a 1.7% increase in durable goods orders.
• At 9:00 AM, FHFA House Price Index for December 2014. This was originally a GSE only repeat sales, however there is also an expanded index. The consensus is for a 0.5% increase.
• At 11:00 AM: the Kansas City Fed manufacturing survey for February.
MBA: Mortgage Delinquency and Foreclosure Rates Decrease in Q4, Lowest since 2007
by Calculated Risk on 2/25/2015 05:42:00 PM
Earlier from the MBA: Mortgage Delinquencies Continue to Decrease in Fourth Quarter
The delinquency rate for mortgage loans on one-to-four-unit residential properties decreased to a seasonally adjusted rate of 5.68 percent of all loans outstanding at the end of the fourth quarter of 2014. This was the lowest level since the third quarter of 2007. The delinquency rate decreased 17 basis points from the previous quarter, and 71 basis points from one year ago, according to the Mortgage Bankers Association’s (MBA) National Delinquency Survey.
The delinquency rate includes loans that are at least one payment past due but does not include loans in the process of foreclosure. The percentage of loans in the foreclosure process at the end of the fourth quarter was 2.27 percent, down 12 basis points from the third quarter and 59 basis points lower than the same quarter one year ago. This was the lowest foreclosure inventory rate seen since the fourth quarter of 2007.
...
“Delinquency rates and the percentage of loans in foreclosure decreased for another quarter and were at their lowest levels since 2007,” said Marina Walsh, MBA’s Vice President of Industry Analysis. “We are now back to pre-crisis levels for most measures.”
Walsh continued: “The foreclosure inventory rate has decreased every quarter since the second quarter of 2012, and is now at the lowest level since the fourth quarter of 2007. Foreclosure starts ticked up two basis points, after being flat last quarter, largely due to state-level fluctuations in the speed of the foreclosure process. Compared to the same quarter last year, foreclosure starts are down eight basis points.
“At the state level, 45 states saw a decline in their foreclosure inventory rates over the quarter, although judicial states continue to account for a disproportionately high share. Fewer than half the states had an increase in non-seasonally adjusted 30 day delinquencies, which is highly seasonal and usually increases in the fourth quarter. Foreclosure starts increased in 28 states, but this has become more volatile, with recent state-level mediation requirements and changing laws, as well as servicer procedures, dictating the changes from quarter to quarter.
“States that utilize a judicial foreclosure process continue to have a foreclosure inventory rate that is roughly three times that of non-judicial states. For states where the judicial process is more frequently used, 3.79 percent of loans were in the foreclosure process, compared to 1.23 percent in non-judicial states. States that utilize both judicial and non-judicial foreclosure processes had a foreclosure inventory rate closer that of to the non-judicial states at 1.43 percent.
“Legacy loans continue to account for the bulk of all troubled mortgages. Within loans that were seriously delinquent (either more than 90 days delinquent or in the foreclosure process), 73 percent of those loans were originated in 2007 and earlier. More recent loan cohorts, specifically loans originated in 2012 and later, continue to exhibit low serious delinquency rates.
“We expect the improvement in mortgage performance to continue due to the improving economy and a strengthening job market, and the improved credit quality of recent vintages.”
emphasis added
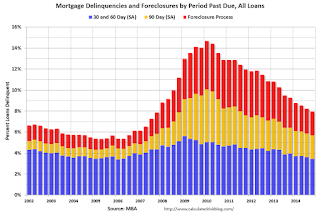 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows the percent of loans delinquent by days past due.
The percent of loans 30 and 60 days delinquent are back to normal levels.
The 90 day bucket peaked in Q1 2010, and is about 70% of the way back to normal.
The percent of loans in the foreclosure process also peaked in 2010 and and is about two-thirds of the way back to normal.
So it has taken about 4 years to reduce the backlog of seriously delinquent and in-foreclosure loans by two-thirds, so a rough guess is that serious delinquencies and foreclosure inventory will be back to normal in a couple more years. Most other measures are already back to normal (still working through the backlog of bubble legacy loans).


