by Calculated Risk on 11/16/2012 09:15:00 AM
Friday, November 16, 2012
Industrial Production decreased 0.4% in October due to Hurricane Sandy, Capacity Utilization decreased
From the Fed: Industrial production and Capacity Utilization
Industrial production declined 0.4 percent in October after having increased 0.2 percent in September. Hurricane Sandy, which held down production in the Northeast region at the end of October, is estimated to have reduced the rate of change in total output by nearly 1 percentage point. The largest estimated storm-related effects included reductions in the output of utilities, of chemicals, of food, of transportation equipment, and of computers and electronic products. In October, the index for manufacturing decreased 0.9 percent; excluding storm-related effects, factory output was roughly unchanged from September. The output of utilities edged down 0.1 percent in October, and production at mines advanced 1.5 percent. At 96.6 percent of its 2007 average, total industrial production in October was 1.7 percent above its year-earlier level. Capacity utilization for total industry decreased 0.4 percentage point to 77.8 percent, a rate 2.5 percentage points below its long-run (1972--2011) average.
emphasis added
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows Capacity Utilization. This series is up 10.9 percentage points from the record low set in June 2009 (the series starts in 1967).
Capacity utilization at 77.8% is still 2.5 percentage points below its average from 1972 to 2010 and below the pre-recession level of 80.6% in December 2007.
Note: y-axis doesn't start at zero to better show the change.
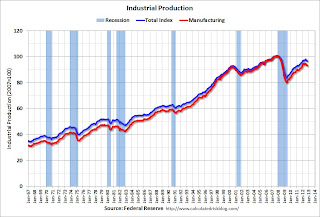 The second graph shows industrial production since 1967.
The second graph shows industrial production since 1967.Industrial production decreased in October to 96.6. This is 15% above the recession low, but still 4.1% below the pre-recession peak.
IP was slightly below expectations due to the impact of Hurricane Sandy. We will probably see some bounce back over the next couple of months.
Thursday, November 15, 2012
Friday: Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization
by Calculated Risk on 11/15/2012 09:18:00 PM
Note: The report linked to in 2012 FHA Actuarial Review Released: Negative $13.5 Billion economic value appears to have been taken down (maybe released early by mistake). Nick Timiraos at the WSJ writes: Report: FHA to Exhaust Capital Reserves
[T]he latest forecasts show that while the FHA currently has reserves of $30.4 billion, it expects to lose $46.7 billion on the loans it has guaranteed, resulting in a $16.3 billion deficit.Friday:
...
"If [the FHA] were a private company, it would be declared insolvent and probably put under conservatorship like Fannie and Freddie," said Thomas Lawler, an independent housing economist in Leesburg, Va.
...
Overall, the FHA insured nearly 739,000 loans that were 90 days or more past due or in foreclosure at the end of September, an increase of more than 100,000 loans from a year ago. That represents about 9.6% of all insured loans.
Most of the agency's losses stem from loans made between 2007 and 2009, as the housing bust deepened. Loans made since 2010 are expected to be very profitable.
• At 9:15 AM ET, the Fed will release Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization for October. The consensus is for 0.2% increase in Industrial Production in October, and for Capacity Utilization to increase to 78.4%.
Another question for the November economic prediction contest (Note: You can now use Facebook, Twitter, or OpenID to log in).
2012 FHA Actuarial Review Released: Negative $13.5 Billion economic value
by Calculated Risk on 11/15/2012 06:08:00 PM
From HUD: Actuarial Review of the Mutual Mortgage Insurance Fund. Excerpts:
Based on our stochastic simulation analysis, we estimate that the economic value of the Fund as of the end of FY 2012 is negative $13.48 billion. This represents a $14.67 billion drop from the $1.19 billion estimated economic value as of the end of FY 2011.Update: A few comments from Tom Lawler:
...
We project that there is approximately a 5 percent chance that the Fund’s capital resources could turn negative during the next 7 years. We also estimate that under the most pessimistic economic scenario, the economic value could stay negative until at least FY 2019.
The latest review concluded that the “economic value” of the FHA MMIF (ex HECMs) – defined as the sum of the MMIFs existing capital resources plus the present value of the current books of business, was NEGATIVE $13.478 billion at the end of FY 2012. Stated another way, the present value of expected future cash flows on outstanding business – a sizable negative $39.052 billion – outstrips the MMIF’s current capital resources (of $25.574 billion) by $13.478 billion. The FY actuarial review of FHA’s HECM business concluded that the “economic value” of the current FHA HECM book was NEGATIVE $2.799 billion at the end of FY 2012.
In last year’s actuarial review the “economic value” of the FHA MMIF (ex HECMs) at the end of FY 2011 was +$1.193 billion, and the projected economic value of the MMIF at the end of FY 2012 (under the “base case) scenario) was a POSITIVE $9.351 billion. In recent years, however, these “projections,” based on “reasonable” benign projections, have been ridiculously optimistic.
Contrary to what at least one press report said, the actuarial “unsoundness” of the FHA MMIF is NOT the result of mortgage loans insured at or near the peak of the housing bubble. The “honkingly big” losses (in dollars) are concentrated in the FY 2008 and FY 2009 “books (October 2007 – October 2009) – that is, loans insured in the first few years AFTER the peak in the housing bubble, when “private capital” for risky loans dried up and FHA experienced a surge in market share, AND took on a lot of very risky (by any standard) mortgages, a significant % of which should not have been made.
The “walk-forward” of the FY 2012’s economic value from a projection of positive $9.351 billion a year ago to negative $13.478 billion today is a little hard to follow or understand. On the positive side, the money FHA extorted from lenders in the mortgage settlement added about $1.1 billion, and higher-than-projected 2011-12 volumes, actual performance, and different-than-projected portfolio composition added about $3.8 billion. On the negative side, various model changes, especially in the loss severity model, took out about $11.0 billion; lower interest rate assumptions took out $8.4 billion; just slightly lower home price assumptions (beyond 2012) took out a surprisingly large $10.5.
Key Measures show low inflation in October
by Calculated Risk on 11/15/2012 03:57:00 PM
The Cleveland Fed released the median CPI and the trimmed-mean CPI this morning:
According to the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland, the median Consumer Price Index rose 0.2% (2.3% annualized rate) in October. The 16% trimmed-mean Consumer Price Index increased 0.1% (1.7% annualized rate) during the month. The median CPI and 16% trimmed-mean CPI are measures of core inflation calculated by the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland based on data released in the Bureau of Labor Statistics' (BLS) monthly CPI report.Note: The Cleveland Fed has the median CPI details for October here.
Earlier today, the BLS reported that the seasonally adjusted CPI for all urban consumers rose 0.1% (1.8% annualized rate) in October. The CPI less food and energy increased 0.2% (2.2% annualized rate) on a seasonally adjusted basis.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows the year-over-year change for these four key measures of inflation. On a year-over-year basis, the median CPI rose 2.2%, the trimmed-mean CPI rose 1.9%, the CPI rose 2.2%, and the CPI less food and energy rose 2.0%. Core PCE is for September and increased 1.7% year-over-year.
On a monthly basis, two of these measure were above the Fed's target; median CPI was at 2.3% annualized, core CPI increased 2.2% annualized. However trimmed-mean CPI was at 1.7% annualized, and core PCE for September increased 1.4% annualized. These measures suggest inflation is close to the Fed's target of 2% on a year-over-year basis.
The Fed's focus will probably be on core PCE and core CPI, and both are at or below the Fed's target on year-over-year basis.
Bernanke suggests Mortgage Lending Standards are "Overly Tight", "Pendulum has swung too far"
by Calculated Risk on 11/15/2012 01:20:00 PM
From Fed Chairman Ben Bernanke: Challenges in Housing and Mortgage Markets. Excerpt:
Although the decline in the number of willing and qualified potential homebuyers explains some of the contraction in mortgage lending of the past few years, I believe that tight credit nevertheless remains an important factor as well. The Federal Reserve's Senior Loan Officer Opinion Survey on Bank Lending Practices indicates that lenders began tightening mortgage credit standards in 2007 and have not significantly eased standards since. Terms and standards have tightened most for borrowers with lower credit scores and with less money available for a down payment. For example, in April nearly 60 percent of lenders reported that they would be much less likely, relative to 2006, to originate a conforming home-purchase mortgage to a borrower with a 10 percent down payment and a credit score of 620--a traditional marker for those with weaker credit histories. As a result, the share of home-purchase borrowers with credit scores below 620 has fallen from about 17 percent of borrowers at the end of 2006 to about 5 percent more recently. Lenders also appear to have pulled back on offering these borrowers loans insured by the Federal Housing Administration (FHA).Clearly Bernanke and the Fed are concerned that credit isn't flowing to a large segment of the population.
When lenders were asked why they have originated fewer mortgages, they cited a variety of concerns, starting with worries about the economy, the outlook for house prices, and their existing real estate loan exposures. They also mention increases in servicing costs and the risk of being required by government-sponsored enterprises (GSEs) to repurchase delinquent loans (so-called putback risk). Other concerns include the reduced availability of private mortgage insurance for conventional loans and some program-specific issues for FHA loans as reasons for tighter standards. Also, some evidence suggests that mortgage originations for new purchases may be constrained because of processing capacity, as high levels of refinancing have drawn on the same personnel who would otherwise be available for handling loans for purchase. Importantly, however, restrictive mortgage lending conditions do not seem to be linked to any insufficiency of bank capital or to a general unwillingness to lend.
Certainly, some tightening of credit standards was an appropriate response to the lax lending conditions that prevailed in the years leading up to the peak in house prices. Mortgage loans that were poorly underwritten or inappropriate for the borrower's circumstances ultimately had devastating consequences for many families and communities, as well as for the financial institutions themselves and the broader economy. However, it seems likely at this point that the pendulum has swung too far the other way, and that overly tight lending standards may now be preventing creditworthy borrowers from buying homes, thereby slowing the revival in housing and impeding the economic recovery.
emphasis added


