by Calculated Risk on 8/06/2007 12:18:00 AM
Monday, August 06, 2007
More on Bear Stearns Mess
From the WSJ: How Bear Stearns Mess Cost Executive His Job
On Wednesday James Cayne, the 73-year-old chief executive of Bear Stearns Cos., summoned his top lieutenant to his smoky, dimly lit office in midtown Manhattan.The article has some new details on the Bear Stearns hedge funds:
...
He told Mr. Spector he had lost confidence in him. "I think it's in the best interests of the firm for you to resign," Mr. Cayne told Mr. Spector ...
By mid-June, the enhanced-leverage fund had missed margin calls -- requests for additional cash and collateral -- from lenders including Merrill Lynch & Co. and J.P. Morgan Chase & Co. The lenders wanted to be made whole.
Some Wall Street executives were pressuring Bear Stearns to stop the bleeding. Initially, the firm's executive committee balked. ... On the afternoon of June 14, J.P. Morgan's investment banking co-chief, Steven Black, and his top risk officer had a tense phone call with Mr. Spector, in which the lender urged Bear Stearns to give the fund some emergency credit, participants in the call say.
Calling the J.P. Morgan executives "naïve," Mr. Spector said Bear Stearns was the resident expert in the mortgage business, recalls one participant, and that the lenders should back off.
Early that evening, J.P. Morgan sent an in-house lawyer to Bear Stearns's headquarters with an official default notice. But a Bear Stearns receptionist told the lawyer that the firm was closed for business, and that the documents couldn't be accepted, people familiar with the matter say.
The blow to Bear Stearns's reputation, however, caused the firm to reverse course. Late the following week, after hearing a presentation from Bear Stearns's in-house mortgage team suggesting that the older fund might still contain value, the firm's executive committee authorized a secured loan to the less-leveraged fund of up to $3.2 billion. The fund ended up borrowing $1.6 billion, which it didn't repay entirely, leaving Bear Stearns's loan officers to seize the collateral remaining in Mr. Cioffi's fund. Bear Stearns could lose much of the $1.3 billion the fund still owes it, public filings indicate.
Sunday, August 05, 2007
SFAS 140: Like A Bridge Over Troubled Bong Water
by Anonymous on 8/05/2007 10:25:00 AM
(Look. I have to keep up with my betters in the MMI basket of Big Paid Media Foolishness. Besides, you made me read the New York Post again. Don't do that.)
Horror item from that staid publication, NYP:
Defaults are ripping through the entire mortgage bond industry at the fastest pace in years.Either the SEC is up to something I don't know about--sure, it could happen--or the Post writer has managed one of the more fearfully tendentious descriptions of an accounting rule interpretation in living memory. It would be easier to decide this had the Post writer supplied something like "detail." I am going to assume he means the recent clarification on SFAS 140 treatment of loan modifications. If he means something else, now would be a good time to act like a reporter instead of Emily Latella.
Investors hold about $6.5 trillion in mortgage bonds, the world's largest such fixed-income market, says the Securities Industry Financial Markets Association.
Meanwhile, Securities and Exchange Commission chief Chris Cox said the SEC is coming up with new, more flexible accounting rule interpretations that companies and others could use to avoid declaring their mortgage securities in default.
Of course it's not just the NYP writer whose knickers got thoroughly knotted over this. Jonathan Weil at Bloomberg became downright hysterical on the subject in "Subprime Mess Fueled by Crack Cocaine Accounting":
On May 30, the board said it will look hard at eliminating the concept of off-balance-sheet trusts -- called qualifying special purpose entities, or QSPEs -- from Statement 140 entirely. The likely effect: Lenders no longer could record sales on transfers of loans or other financial assets to securitization trusts in which they have continuing involvement.The issue here is the "Q Election," and this is a problem Lewis Ranieri raised the alarm about several months ago. When a mortgage securitization is structured as an off-balance sheet sale (for which gains on sale may be taken) rather than an on-balance sheet financing, SFAS 140 requires that the transaction (the sale of the pool of mortgage loans) to the qualifying trust entity or QSPE be a "true sale." One of the conditions of a true sale is that the seller not retain control over the assets being sold. The point of this is to avoid sham sale transactions (like the famous Enron Nigerian barges).
Instead, the transactions would be treated as secured borrowings, and the assets would stay on the lender's balance sheet, though possibly in a way that would show the specific liabilities to which they're linked. . . .
While that wouldn't get rid of gain-on-sale, it would be much more difficult for lenders to record immediate profits, unless they sold their loans to independent third parties lock, stock and barrel. Such a change would affect any company that securitizes loans or accounts receivable, including credit-card companies and many manufacturers.
If it weren't for QSPEs, the securitization industry might look very different today. That's partly because mortgage lenders might not have lent so much money to people with poor credit, if the rules hadn't let them front-load their profits and show smaller balance sheets to investors.
Adding to the complexity, gain-on-sale calculations are based on lots of estimates and guesswork about future events, such as customer defaults, prepayments and interest rates. Things like these normally are impossible for mere mortals to predict consistently. Yet the absence of any right answers also makes it difficult for outsiders to challenge the numbers. Armed with that insight, practitioners of gain-on-sale accounting can create profits through sheer optimism. . . .
Time and again, gain-on-sale has proved its power to addict, from the crashes at FirstPlus Financial Group Inc. and Mercury Finance Co. back in 1998, to the 2007 wave of collapses led by New Century Financial Corp. Take one puff, and it feels euphoric. To keep getting the same high, however, you must take bigger and bigger hits. Before long, you may end up in Chapter 11 rehab.
Statement 140 had envisioned QSPEs as ``brain-dead'' entities akin to wind-up toys, meaning they aren't supposed to exercise judgment or discretion. Any actions they take -- such as responding to a customer's default -- are supposed to be automatic responses to circumstances clearly spelled out in the documents that created the trusts. If lenders remain involved in servicing a QSPE's mortgages, they're supposed to take limited roles, like collecting borrowers' payments or executing foreclosures if needed.
In practice, servicing has taken a much broader role, and FASB officials say the QSPE concept has proven unworkable. At a June 22 meeting with FASB members, the Mortgage Bankers Association presented a paper taking the position that Statement 140 permits QSPEs to grant ``concessions to debtors experiencing financial difficulty'' on the grounds that this, too, is part of servicing activities.
The trouble with mortgage loans is that they must be serviced, and securitized mortgage loans are frequently serviced by the originator, under the terms of a servicing agreement with the QSPE. SFAS 140 has always allowed "normal servicing activity" by the originator without endangering the true sale status of the transaction, as long as the servicing activity does not exceed the terms of the servicing agreement. If the servicing agreement says that the servicer can modify loans that are currently in default, then the servicer can do that without jeopardizing the Q-status of the securitization (that is, without forcing the whole deal back onto the originator's balance sheet and taking back the gain on sale that was originally booked when the transaction closed).
The trouble arose when servicers began modifying--or began recommending that they be allowed to modify--loans that are in a "reasonably foreseeable danger of default," but not yet defaulted. The problem is that the "in default" standard is pretty clear: a mortgagor has missed one or more payments, this can be established by reference to the remittance reports, and so modification can be justified as a work-out of a loan that is not performing. When you begin to contemplate modifications of loans that are actually still performing today, but that you believe will stop performing if you don't do something about them, you can cross into murky territory: are you "servicing" the pool or "managing" it?
Lew Ranieri, Tanta, and about eleventy-jillion other mortgage market participants would say that as long as you are verifying your facts, and proceeding in the same way you would if the loan were defaulted, you are "servicing" the pool. We say this because the lines have never been as clear and simple as those hysterics at the NYP or Bloomberg seem to think. Since approximately several months after the first mortgage loan was serviced by the first mortgage lender, someone has called up and said "I just got laid off today. I want to keep making my house payment, but I'm going to have some trouble for the next couple of months. Is there anything you can do to help me?" Since about ten minutes after that, servicers have contacted the borrower's employer to verify the layoff story, ordered a new credit report to make sure this isn't someone on a debt-binge, reviewed the past payment history and current value of the property, and said "OK, we can put you in forbearance for three months, then if you start making payments again we'll modfiy your loan to add the three past-due payments to the balance and bring you current again."
What's "new" these days is all those stupid 2/28 ARMs everybody made, counting on the borrowers to refinance or sell the property before the adjustment blew their capacity to repay out of the bong water. Now that we're hip-deep in actual defaults of these loans, we're realizing that we'll be ear-deep in them unless servicers take a proactive stance, and start calling up those borrowers who haven't reset yet but are about to. The point of that is to find out whether they understand that they're about to adjust, whether they know how bad it could be (many borrowers, unlike, say, Bloomberg columnists, don't really follow LIBOR every day), and to find out what they're going to do about it if they can't manage the new payment. Nobody I know of is just blindly offering modifications to these folks; quite honestly, a huge percentage of them can't get anywhere with a mod. They are being counseled to list the property now, while there's some chance they can sell with their credit records intact. But clearly, in some cases, a modification is going to be offered to a borrower who isn't in default yet.
When I first read Weil's frothing about "wind-up toys," I remember remarking to my computer monitor, "that's the most profoundly retarded thing I've read in weeks." With the passage of time my opinion has changed somewhat; I shouldn't be that unfair to the profoundly retarded, who as a class are not, as far as I know, agitating for skinning consumers just so that investors in mortgage-backed securities and financial sector stocks don't have to understand anything more complicated than "I got mine, screw you." So let me apologize to everyone on the short bus.
Do you really want to live in a world in which mortgage servicers--I'm talking mortgages, kids, the loan for the roof over the family's heads here, not your basic yacht financing--work on the "collect payments or foreclose, no judgement exercised" basis? You like doing business with outfits like that? You happy calling up the customer service line and getting some untrained bored squirrel on the other side who tells you nothing can be done if you're not late, but that nothing can be done if you are late? You like paying .25-.50 extra in interest every month so that your mortgage servicer can act like Major Major? You think it's not bad enough that we made 100% loans to people, giving them little incentive to repay the debt, we should make it worse by giving them no hope if they try to pay it? You think people who are asking for forbearance should be told just to walk away?
Oh, I suppose, if you're some perfect righteous Bloomberg columnist investor type, you'd never ever have such a problem and you don't give a rat's patootie about the unwashed masses who might need "judgement exercised" instead of Catch-22. You're free to feel that way, but as far as I'm concerned you're not free to pretend like this is some conspiracy on the part of some crackheads to mess with your NAV. There are huge, massive, deeply important public policy issues around home mortgage lending, which makes it a little bit of a problem to treat mortgages like any other "financial asset." We have entire neighborhoods and communities falling apart because of the Wall Streetization of mortgage finance, and now that someone's trying to deal with the mess, it's not a good time to suggest that we pile on the punishments just so you can figure out how to read a balance sheet.
What, exactly, did those Krazy Kommies at the SEC say?
Currently, the Commission's staff does not believe that additional interpretive guidance is necessary in order to clarify the application of FAS 140 to the contemplated types of securitized mortgage loan work-out activities. Rather, after considering the information gathered at the FASB educational forum and information we have received from other sources, there appears to be general agreement in practice regarding the application of FAS 140 to these fact patterns. Specifically, there appears to be a consensus in practice, and it is our view, that entering into loan restructuring or modification activities (consistent with the nature of activities permitted when a default has occurred) when default is reasonably foreseeable does not preclude continued off balance sheet treatment under FAS 140.Translation: we asked the accountants who have actually had exposure to the mortgage industry before, and they said "What? We've always done that." This is "hiding default" or "crack-cocaine accounting" only to those folks who thought that investing in mortgages was just like buying pork bellies. Not.
The time to have gotten fired up about the real issues around off balance sheet securitization--the great "de-linking" of risk that was openly advertised as the benefit to the investor of all of this--was back when those 2/28s were being originated. We here at Calculated Risk were on it back then, and being dismissed as "bubbleheads." Absolutely nobody, as far as I know, is happy with any of the bad choices we now have since we've gone into cleanup mode. But this desperate attempt to keep the moral hazard in place, whether it's Cramer begging for a rate cut or bond investors demanding that FASB shoot the wounded, sink the lifeboats, and close the gates of mercy to protect the interests of the AAA crowd, is a little hard to take.
Sit down, boys and girls. There has always been an "information asymmetry" issue with mortgage-backeds. The originator has always known more than you know. The servicer has always known more than you know. The auditors have always known more about the balance sheet ingredients than you have. This problem did not arise a couple of months ago when the ABX tanked.
It has also always been the case that the party on the other side of that cash-flow is Joe and Jane Homeowner. Taxpayer, voter, citizen, parent, child, grannie and gramps, your neighbor. This is a group of folks it's a bit hard to demonize. We've been trying, with this "it's all subprime and all subprime borrowers are deadbeats" meme, but except for a few dead-ender holdouts, that dog is no longer barking. No one will be less surprised than I to find many politicians doing the wrong thing here, out of a misguided sense that something must be done, and seen to be done. Possibly someone will do something sane and useful.
But if you are surprised that this is now, fully and inescapably, a political issue, and it's homeowners against Wall Street, then you never realized that it's about mortgages. After Social Security, this is the closest thing to a Third Rail that there is. They call it the "American Dream" for a reason. If you thought this was just a socially-neutral "asset class" you could simply suck dry forever, a little wind-up toy that would never fight back, you're Part. Of. The. Problem. And I for one raise my mechanical pencil, as lama says, in salute to all the nerds at FASB who are ignoring you.
Home Builder Myths Meet Reality
by Calculated Risk on 8/05/2007 01:04:00 AM
"We can earn our way through any economic cycle, except one like the Great Depression."
Donald Tomnitz, CEO, D.R. Horton, Dec 1, 2005
D.R. Horton Inc, the largest U.S. home builder, on [July 26, 2007] reported its first quarterly loss as a public company ...From the WSJ: Home Myths Meet Reality
Reuters, July 26, 2007
It wasn't supposed to happen like this. Today's home builders were thought to be better-capitalized, savvier and more geographically diverse than many of their predecessors in the last downturn, in the early 1990s. While many are expected to weather the slump, concern is mounting about the balance sheets of a growing number of companies.The article discusses a few more challenges for home builders, but unmentioned are two key points:
...
What's going wrong? An array of business assumptions that both builders and housing analysts propagated have turned out to be misguided.
...
One big assumption had to do with their cash flow: The common wisdom among some analysts was that builders would turn into "cash machines" in the event of a housing downturn, because they would pare construction and land buying.
In reality, most builders haven't been able to stockpile as much cash as expected. That is partly because they have had to keep building large housing developments, even though demand dropped off sharply.
...
Also eating into that cash flow: the sharp drop in sales and home prices.
First, the home builders are still building too many housing units because that is the only way they can liquidate land and pay down debt. This overbuilding will extend the duration of the slump in new home construction.
Second, there is way too much home building capacity in the U.S., and competition will be fierce until enough home builders exit the business.
Meanwhile, with the growing credit crunch, bankers might be quick to call loans:
Until recently, many analysts believed banks would be forgiving of the builders. But it now looks as if some companies could run into trouble with their banks.
That is because some builders' net worth is eroding so quickly -- as they write down the value of land -- that some may be getting close to tripping contractual agreements ...
Saturday, August 04, 2007
Bonus: Saturday Poll Rocking
by Anonymous on 8/04/2007 10:21:00 AM
For those of you who missed it yesterday: on the top left side of the page you may take the Calculated Risk rate-cut poll. We promise to pass on the results to our Overlords at the Federal Reserve. (If they take Cramer's calls, they'll bloody well take ours.)
Here's something to get you into the mood:
Saturday Rock Blogging: All The Pain Money Can Buy
by Anonymous on 8/04/2007 08:19:00 AM
This is for all of my friends in the mortgage business, especially Hoover and her Merry Band of Traders. Sorry I'm not in the trenches with you for this one. Kinda. Well, not really.
Freddie Mac's Syron on Mortgage Woes
by Calculated Risk on 8/04/2007 12:59:00 AM
From the NY Times: Markets Fall as Lender Woes Keep Mounting
Richard F. Syron, chief executive of Freddie Mac, the large buyer of mortgages created by Congress in the 1970s, said yesterday that the speed and severity of the tighter credit terms are surprising, but perhaps necessary given the excesses in the market in recent years.
In a telephone interview from Washington, he was wary of the calls by some mortgage industry officials that Freddie Mac and its cousin, Fannie Mae, step in to buy loans and securities that private investors will no longer purchase. Mr. Syron noted that his company was operating under an agreement with its regulator that limited the size of its portfolio.
“There are some loans that are in difficulty” because credit pools are drying up, Mr. Syron said. “There are other loans that probably should never have been made and providing more liquidity will make that situation worse in the long term.”
Friday, August 03, 2007
American Home Mortgage to file for bankruptcy
by Calculated Risk on 8/03/2007 10:01:00 PM
From Newsday: American Home Mortgage to file for bankruptcy, Strauss sells off shares
American Home is in the process of filing for bankruptcy, senior vice president Tim Neer told about 200 now-former employees around 10:15 a.m. Friday.
...
Later Friday, it was revealed in a filing that founder and chief executive Michael Strauss had sold off almost 3 million shares of company stock on Wednesday for $1.17 a share. The same day he reaped almost $3.5 million, employees had been told in a conference call to stay positive and keep processing loan applications.
Should the Fed cut rates on Tuesday?
by Calculated Risk on 8/03/2007 09:17:00 PM
Our first poll: It is very unlikely that the Fed will cut rates on Tuesday, but should they?
Here are the current Fed Funds Rate Predictions from the Cleveland Fed.
Some economists are suggesting the Fed will move to a neutral bias on Tuesday, from their current view:
"... the Committee's predominant policy concern remains the risk that inflation will fail to moderate as expected."Perhaps some people would like to use the comments here to discuss the merits of a Fed rate cut.
Cramer Goes Crazy
by Calculated Risk on 8/03/2007 04:51:00 PM
Cramer: Bernanke, Wake Up
Update: Of course Cramer is wrong. This is a classic credit crunch with rapidly increasing nonprice rationing. Cutting the rate would help a few homeowners, but it is the tightening lending standards for both mortgages and corporate credit (especially junk rated bonds) that are causing the credit crunch.
Cerberus Closes Chrysler, JPMorgan Owns Pier
by Calculated Risk on 8/03/2007 03:59:00 PM
From Bloomberg: DaimlerChrysler Closes Sale of Chrysler to Cerberus
Banks led by JPMorgan Chase & Co. are taking on the remaining $10 billion.The other Chrysler pier owners are Goldman Sachs Group, Bear Stearns, Morgan Stanley and Citigroup. The impact of these "hung" bridge loans on the growing credit crunch is significant.
Note: a bridge loan is supposed to be temporary financing while the banks syndicate the debt. When the debt can't be sold, the bridge loan becomes a "pier loan" - a bridge to nowhere - and ties up the capital of the investment banks.
Fannie and Freddie Limiting the Bailout
by Anonymous on 8/03/2007 02:30:00 PM
Mike Perry, chief executive of mortgage lender IndyMac Bancorp said on Thursday that he got a phone call this week from U.S. Sen. Christopher Dodd, D-Conn., who asked whether Congress can help the U.S. mortgage industry in any way.
"I also have talked to the Chairman of Fannie Mae this morning and have traded calls with the Chairman of Freddie Mac," Perry wrote in a company blog. "Fannie Mae's Chairman (is) telling me that they are 'prepared to step up and help the industry'."
Fannie and Freddie have a Federal charter that requires them to provide liquidity and stability to the mortgage market. However, those organizations made it clear on Friday that any help will be limited.
"Congress is very focused on this issue," Doug Duvall, a spokesman at Freddie Mac, said. "There's a squeeze in the market right now and lenders are tightening their standards. But having a little more prudent underwriting isn't a bad thing. It's important to keep people in their homes and to make sure they buy homes they can afford."
Freddie has pledged to invest $20 billion in new subprime mortgage products, however those loans have to meet much stricter underwriting standards.
Brian Faith, a Fannie Mae spokesman, said the company is "playing an active but prudent role in the effort to stabilize the secondary market."
Fannie has so far refinanced $5.4 billion of formerly subprime mortgages, bought $450 million of state HFA rescue packages and modified terms on more than 20,000 loans, he noted.
"We will continue to work with our lender customers to provide additional liquidity where we can to help stabilize and support the market," Faith added.
However, another person close to Freddie Mac who didn't want to be identified stressed that Fannie and Freddie aren't just going to buy up non-conforming loans to bail out troubled players in the secondary market.
MMI: Intraday Volatility
by Anonymous on 8/03/2007 12:21:00 PM
Bloomberg wipes up the floor with WSJ today. I hope you weren't having lunch.
Credit Brothel Raided, Even Piano Player Not Safe: Mark Gilbert
By Mark Gilbert
Aug. 3 (Bloomberg) -- As the financial-liquidity police raid the credit-market brothel, even the piano player faces arrest. The malaise enveloping global markets is becoming increasingly indiscriminate in choosing its victims. . . .
At least 70 U.S. mortgage companies have shut, gone bust or sold themselves since the start of last year, according to Bloomberg data. As Dennis Gartman, economist and editor of the Suffolk, Virginia-based Gartman Letter, is fond of saying in his research reports, there's never only one cockroach.
Cockroach Counting
What investors have to decide, especially those still confident about the outlook for stocks, is how many cockroaches they are willing to endure before deciding the credit market is cracked, derivatives are doomed, and the economy imperiled.
The credit bordello has enjoyed some wild times in the past few years, luring customers into the room at the back where the exotica are displayed. As the raid ensnares more and more of the regulars, newcomers are likely to become increasingly wary of the derivatives market's wares. And when the piano player is led off to jail, the music stops.
Andrew Davidson on the Securitization Food Chain
by Anonymous on 8/03/2007 08:19:00 AM
Andrew Davidson & Co. generally produces thoughtful stuff; they are a well-known provider of pricing and risk analytics models to the mortgage and securitization industry. This essay attempts to get at the problem of "degrees of separation" of risk in the current industry model, and it arrives at the conclusion that having larger capital stakes at the origination points--skin in the game--would probably help.
In aid of which argument the following graphical illustration is provided:
Every time I look at something like this, I confess, I am less struck by the question "Where's the capital stake?" than I am by the question "How many mouths can a homeowner feed?" Davidson, just as a for instance, provides high-quality software and consulting services. They aren't free. And this chart doesn't even show you the points were the mortgage insurers enter, where due-diligence firms get paid to look at loans, where banks with a trust department serve as document custodians for these securities (for a fee), or all of the other for-profit businesses that have grown up around not just mortgage lending as such, but secondary-market mortgage lending. Tax service contracts, for instance: in a thrift-style lend-and-hold model, you don't need to pay a vendor to track property tax bills for you; you need that if the servicing rights to the loan are going to change hands six times prior to maturity. Every loan needs a "flood hazard determination" to assure that the home isn't in a flood plain, but now you pay incrementally more to get a "transferrable" one. A company called MERS, Inc. exists solely to replace the old-fashioned assignment of mortgages in the old-fashioned county land records with an "electronic registration," the entire demand for which is a function of secondary market sales of loans.
Somebody is paying for all this, and it would be you, the homeowner. You pay part of it in your interest rate; you pay a lot of it in fees and closing costs and prepayment penalties. There's an argument that increasing technological innovation (like MERS, or those transferrable tax service contracts) does make it cheaper for all this to go on, and that you benefit by having "access" to secondary market lenders, who can now afford to take your risk. I'm not interested in arguing that today.
I simply want to point out that "due diligence" is not missing from the chart above, at certain points, because no one thought it necessary. It was missing because subprime borrowers cannot buy overpriced homes and still pay a high enough interest rate that we can afford to have Clayton look at every loan in the deal. Well, not if some fund manager is going to take 2 and 20 we can't.
I've listened to more investor conference calls than I should have, life being as short as it is, and I can tell you that I rarely hear anyone ask if enough money is being spent on "inefficiency" to assure that operational risk is being priced correctly. The usual political response by industry lobbyists to increased regulations is always that the costs of it will be passed on to you, the consumer. It is worth you, the consumer, asking what costs you're already covering.
July Employment Report
by Calculated Risk on 8/03/2007 08:18:00 AM
The BLS reports: U.S. nonfarm payrolls rose by 92,000 in June. The unemployment rate was up slightly at 4.6% in July. 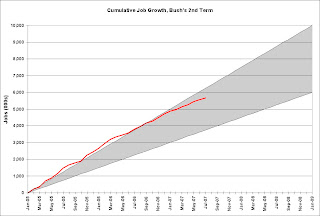 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.
Here is the cumulative nonfarm job growth for Bush's 2nd term. The gray area represents the expected job growth (from 6 million to 10 million jobs over the four year term). Job growth has been solid for the last 2 1/2 years and is near the top of the expected range.
Residential construction employment was flat in July, and including downward revisions to previous months, is down 141.2 thousand, or about 4.1%, from the peak in March 2006. (compare to housing starts off 30%).
Note the scale doesn't start from zero: this is to better show the change in employment.
The ADP report wasn't close to the BLS report this month. ADP estimated private employment grew by only 48K in July, and the BLS reported private employment grew by 120K.
MMI: Gamma Deltas the Alphas With a Beta
by Anonymous on 8/03/2007 07:46:00 AM
Well, it sounds better in Greek. Via Seeking Alpha, I present The Slatin Report:
Led by seismic subprime holdings, the roiling debt markets are casting a pall over the entire real estate sector. And so they should: published reports put the total number of unsold loans sitting in financial institutions' warehouses waiting to be resold at around $260 billion in the US and another $200 billion in Europe. And with investment spigots turning off across the US, that money is going to sit for a while. . . .
Yes, it's quiet out there. Too quiet.
Thursday, August 02, 2007
More on 'Major Changes' in Home Lending
by Calculated Risk on 8/02/2007 06:49:00 PM
Bloomberg covers the IndyMac CEO's letter to employees, and mentions the following lenders: IndyMac, Rivals Make `Major Changes' in Home Lending
National City ... the 16th-largest home lender last year ... In its Aug. 1 notice ... said it won't buy loans that can't be resold to Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac, the two largest mortgage buyers, unless the borrowers' income and assets are fully documented.I expect the impact on home sales, from these 'major changes' in home lending, to show up first in the Census Bureau's August New Home sales report (released in September), but not show up in the NAR's existing home sales report until the September report (released in October).
... Wachovia, the seventh largest home lender, discontinued making Alt A mortgages through brokers because ``it's becoming more difficult to sell these mortgages in the secondary market as the financial markets continue to tighten,'' spokeswoman Christy Phillips-Brown said.
... Wells Fargo & Co., the second-biggest lender, said last week that it would no longer make subprime home loans through brokers, while continuing to make them in a retail channel.
... SunTrust Banks Inc., the 14th largest home lender, has ``pretty much gotten out of Alt A'' for now, said Sterling Edmunds, who heads its mortgage unit.
AHM Throws in the Towel
by Anonymous on 8/02/2007 04:14:00 PM
American Home Mortgage Investment Corp. will be closing its doors Friday, after several attempts to sell of all or some of its divisions to rival lenders went up in smoke this week, numerous employees said.
Employees said they were contacted by senior management through the course of the day and told that none of their strategic options for remaining open had panned out.
Thanks, Gamma.
Even More on Alt-A
by Anonymous on 8/02/2007 03:28:00 PM
Several of you have asked about the size of the Alt-A market. Here are some charts from Credit Suisse you may find informative.
Hat tip "Clyde"!
More on Alt-A
by Calculated Risk on 8/02/2007 12:53:00 PM
I've seen several unconfirmed reports of Alt-A products being discontinued at various lenders. Mathew Padilla has a follow-up on the Wells Fargo Alt-A story: Wells Fargo scales back Alt-A loans
I'm hearing similar reports regarding the discontinuation of products from IndyMac, WaMu and Wachovia. Note: none of these stories have been confirmed.
As I mentioned in the comments, it appears August rhymes with February. In February standards started to be tightened for many subprime products - or the products were eliminated completely. Now the same appears to be happening for Alt-A.
UPDATE: IndyMac comments (hat tip Brian) Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.
IndyMac CEO says mortgage markets "panicked and illiquid"
IndyMac CEO says AAA private MBS bonds are difficult to trade.
IndyMac CEO says disruption "broader and more serious" than past.
From IMB report:
... here is a copy of an email CEO Mike Perry sent out to all Indymac employees yesterday on this subject:
Unfortunately, the private secondary markets (excluding the GSEs and Ginnie Mae) continue to remain very panicked and illiquid. By way of example, it is currently difficult, at present, to trade even the AAA bond on any private MBS transaction. In addition, to give you an idea as to how unprecedented this market has become…I received a call from U.S. Senator Dodd this morning who seeking an understanding of “what is really going on and how can I and Congress help?” I also have talked to the Chairman of Fannie Mae this morning and have traded calls with the Chairman of Freddie Mac (Fannie Mae’s Chairman telling me that they are “prepared to step up and help the industry”).
Unlike past private secondary mortgage market disruptions, which have lasted a few weeks or so…our industry and Indymac have to be prudent and assume that this present disruption, which appears broader and more serious, might take longer to correct itself. As a result, we have seen just since yesterday, many major mortgage lenders announce additional product cutbacks…some leaving subprime, Alt-a, and other products altogether or restricting some products to only their own retail channel (and possibly wholesale) and significant, additional price widening.
While we have very strong liquidity, a good amount of excess capital and there are no realistic scenarios that I can foresee that would impair Indymac’s viability (thanks to our Federal Thrift structure), as I said on the earnings conference call yesterday…we cannot continue to fund $80 to $100 billion of loans through a $33 billion balance sheet….unless we know we can sell a significant portion of these loans into the secondary market…and right now, other than the GSEs and Ginnie Mae….the private secondary market is not functioning.
As a result, Indymac like all major lenders, will continue to widen its pricing and tighten product and underwriting guidelines to ensure that a much great percentage of our production qualifies for sale to the GSEs or through a GNMA security (we sold 40% to the GSEs in the 2nd quarter, up from 30% in Q107 and 19% in 2006, and we want to get it up to at least 60% asap). We are hopeful that private AAA MBS bonds begin to trade soon…and have encouraged the GSEs to step in and provide additional liquidity to the secondary markets (their primary role) for both these private securities and other loans.
While this is an abrupt and uncomfortable change, it is a change that all of our competitors are making just as abruptly, if not more abruptly…so it should not result in one mortgage company having a competitive advantage over another. The reality is I have a lot of confidence in our industry’s mortgage originators (and in particular Indymac’s customers and retail loan officers)….to quickly move as many borrowers as possible to this more full doc, conforming loan environment. I remain hopeful that these very major changes which are clearly negative for our and industry’s loan volumes…will be largely offset for Indymac by the fact that we have fewer players left in the business….we are certainly seeing it play out this way so far this week.
More specific details on products and channels will follow in the next few days. Thanks. Mike
P.S. We will still originate product that cannot be sold to the GSEs…just less of it and we will have to assume we retain it in portfolio (until the AAA private MBS market recovers).
LAT on Hedge Funds
by Anonymous on 8/02/2007 11:36:00 AM
Kimono firmly closed, we learn:
Some hedge funds that have suffered losses on investments are closing the gate on clients who want to pull money out, a move that could further undermine confidence in already shaky financial markets.Hordes of well-heeled investors? Is that the opposite of a select group of unwashed masses?
Temporarily barring withdrawals, though legal, also could damage the image of the hedge fund industry, which in recent years has attracted hordes of well-heeled investors seeking high returns. The industry has mushroomed to 9,700 funds with $1.7 trillion in assets.
"Psychologically, separating people from their money is generally considered to be a hostile way to behave," said Ron Geffner, a partner at New York law firm Sadis & Goldberg.



