by Calculated Risk on 5/29/2019 07:00:00 AM
Wednesday, May 29, 2019
MBA: Mortgage Applications Decreased in Latest Weekly Survey
From the MBA: Mortgage Applications Decrease in Latest MBA Weekly Survey
Mortgage applications decreased 3.3 percent from one week earlier, according to data from the Mortgage Bankers Association’s (MBA) Weekly Mortgage Applications Survey for the week ending May 24, 2019.
... The Refinance Index decreased 6 percent from the previous week. The seasonally adjusted Purchase Index decreased 1 percent from one week earlier. The unadjusted Purchase Index decreased 3 percent compared with the previous week and was 7 percent higher than the same week one year ago.
...
“Concerns over European economic growth and ongoing uncertainty about a trade war with China were some of the main factors that kept mortgage rates low last week. Even with lower rates on three of the five surveyed loan types, refinance activity fell 6 percent, essentially reversing an 8 percent increase the week before,” said Joel Kan, MBA’s Associate Vice President of Economic and Industry Forecasting. “Purchase applications decreased for the third straight week, but remained more than 7 percent higher than a year ago. It is possible that the trade dispute is causing potential homeowners to hold off on buying, with the fear that further escalation – or the lack of resolution – may have adverse impacts on the economy and housing market.”
...
The average contract interest rate for 30-year fixed-rate mortgages with conforming loan balances ($484,350 or less) remained unchanged from 4.33 percent, with points decreasing to 0.42 from 0.43 (including the origination fee) for 80 percent loan-to-value ratio (LTV) loans.
emphasis added
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.The first graph shows the refinance index since 1990.
Once mortgage rates fell more than 50 bps from the highs of last year, a number of recent buyers were able to refinance. But it would take another significant decrease in rates to see a further increase in refinance activity.
 The second graph shows the MBA mortgage purchase index
The second graph shows the MBA mortgage purchase indexAccording to the MBA, purchase activity is up 7% year-over-year.
Tuesday, May 28, 2019
Wednesday: Richmond Fed Mfg Survey
by Calculated Risk on 5/28/2019 09:34:00 PM
From Matthew Graham at Mortgage News Daily: Mortgage Rates Are Great, But They Could Be Greater
The world of mortgage rate analysis is both simple and complicated. On a simple note, rates are near long-term lows and they'll generally continue to follow the broader market for interest rates (which is largely based on US Treasuries, domestically). …Wednesday:
The biggest issue--and the one that's most difficult to explain in simple terms--is that mortgages have not been doing a good job of keeping pace with Treasury yields lately. [30YR FIXED - 4.0% - 4.125%]
emphasis added
• At 7:00 AM ET, The Mortgage Bankers Association (MBA) will release the results for the mortgage purchase applications index.
• At 10:00 AM, Richmond Fed Survey of Manufacturing Activity for May. This is the last of regional manufacturing surveys for May.
Real House Prices and Price-to-Rent Ratio in March
by Calculated Risk on 5/28/2019 03:49:00 PM
Here is the earlier post on Case-Shiller: Case-Shiller: National House Price Index increased 3.7% year-over-year in March
It has been over eleven years since the bubble peak. In the Case-Shiller release this morning, the seasonally adjusted National Index (SA), was reported as being 12.6% above the previous bubble peak. However, in real terms, the National index (SA) is still about 7.9% below the bubble peak (and historically there has been an upward slope to real house prices). The composite 20, in real terms, is still 14.7% below the bubble peak.
The year-over-year increase in prices has slowed to 3.7% nationally, and I expect price growth will slow a little more.
Usually people graph nominal house prices, but it is also important to look at prices in real terms (inflation adjusted). Case-Shiller and others report nominal house prices. As an example, if a house price was $200,000 in January 2000, the price would be close to $287,000 today adjusted for inflation (43%). That is why the second graph below is important - this shows "real" prices (adjusted for inflation).
Nominal House Prices

In nominal terms, the Case-Shiller National index (SA)and the Case-Shiller Composite 20 Index (SA) are both at new all times highs (above the bubble peak).
Real House Prices
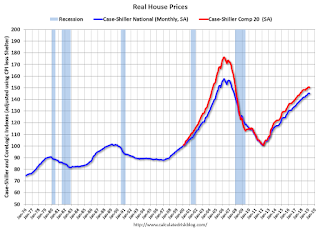
In real terms, the National index is back to January 2005 levels, and the Composite 20 index is back to June 2004.
In real terms, house prices are at 2004/2005 levels.
Price-to-Rent
In October 2004, Fed economist John Krainer and researcher Chishen Wei wrote a Fed letter on price to rent ratios: House Prices and Fundamental Value. Kainer and Wei presented a price-to-rent ratio using the OFHEO house price index and the Owners' Equivalent Rent (OER) from the BLS.

This graph shows the price to rent ratio (January 2000 = 1.0).
On a price-to-rent basis, the Case-Shiller National index is back to February 2004 levels, and the Composite 20 index is back to October 2003 levels.
In real terms, prices are back to late 2004 levels, and the price-to-rent ratio is back to late 2003, early 2004.
Update: A few comments on the Seasonal Pattern for House Prices
by Calculated Risk on 5/28/2019 12:09:00 PM
CR Note: This is a repeat of earlier posts with updated graphs.
A few key points:
1) There is a clear seasonal pattern for house prices.
2) The surge in distressed sales during the housing bust distorted the seasonal pattern.
3) Even though distressed sales are down significantly, the seasonal factor is based on several years of data - and the factor is now overstating the seasonal change (second graph below).
4) Still the seasonal index is probably a better indicator of actual price movements than the Not Seasonally Adjusted (NSA) index.
For in depth description of these issues, see former Trulia chief economist Jed Kolko's article "Let’s Improve, Not Ignore, Seasonal Adjustment of Housing Data"
Note: I was one of several people to question the change in the seasonal factor (here is a post in 2009) - and this led to S&P Case-Shiller questioning the seasonal factor too (from April 2010). I still use the seasonal factor (I think it is better than using the NSA data).
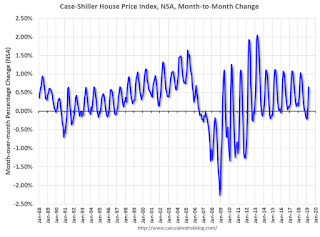
This graph shows the month-to-month change in the NSA Case-Shiller National index since 1987 (through March 2019). The seasonal pattern was smaller back in the '90s and early '00s, and increased once the bubble burst.
The seasonal swings have declined since the bubble.

The swings in the seasonal factors has started to decrease, and I expect that over the next several years - as recent history is included in the factors - the seasonal factors will move back towards more normal levels.
However, as Kolko noted, there will be a lag with the seasonal factor since it is based on several years of recent data.
Dallas Fed: "Texas Manufacturing Expansion Continues but Pace Slows"
by Calculated Risk on 5/28/2019 10:36:00 AM
From the Dallas Fed: Texas Manufacturing Expansion Continues but Pace Slows
Texas factory activity continued to expand in May, albeit at a slower pace, according to business executives responding to the Texas Manufacturing Outlook Survey. The production index, a key measure of state manufacturing conditions, fell six points to 6.3, indicating output growth decelerated from April.This was the worst reading for the general activity index since 2016.
Most other measures of manufacturing activity also suggested slower expansion in May. The survey’s demand indicators fell but remained positive: The new orders index slipped seven points to 2.4, and the growth rate of orders index moved down from 5.2 to 1.1. The capacity utilization index fell to 7.7 from a seven-month high of 15.6 in April. Meanwhile, the shipments index edged up to 7.6.
Perceptions of broader business conditions exhibited some weakness in May. The general business activity index turned negative and reached a year-to-date low of -5.3. The company outlook index dipped into negative territory for the first time this year, coming in at -1.7. The index measuring uncertainty regarding companies’ outlooks jumped nine points to 16.1, its highest reading since last September. More than a quarter of firms said uncertainty increased this month.
Labor market measures suggested stronger employment growth and longer workweeks in May. The employment index rebounded from its April dip, rising seven points to 11.6.
emphasis added
Case-Shiller: National House Price Index increased 3.7% year-over-year in March
by Calculated Risk on 5/28/2019 09:10:00 AM
S&P/Case-Shiller released the monthly Home Price Indices for March ("March" is a 3 month average of January, February and March prices).
This release includes prices for 20 individual cities, two composite indices (for 10 cities and 20 cities) and the monthly National index.
Note: Case-Shiller reports Not Seasonally Adjusted (NSA), I use the SA data for the graphs.
From S&P: S&P CoreLogic Case-Shiller Index Shows Annual Home Price Gains Continue to Weaken
The S&P CoreLogic Case-Shiller U.S. National Home Price NSA Index, covering all nine U.S. census divisions, reported a 3.7% annual gain in March, down from 3.9% in the previous month. The 10-City Composite annual increase came in at 2.3%, down from 2.5% in the previous month. The 20-City Composite posted a 2.7% year-over-year gain, down from 3.0% in the previous month.
Las Vegas, Phoenix and Tampa reported the highest year-over-year gains among the 20 cities. In March, Las Vegas led the way with an 8.2% year-over-year price increase, followed by Phoenix with a 6.1% increase, and Tampa with a 5.3% increase. Four of the 20 cities reported greater price increases in the year ending March 2019 versus the year ending February 2019.
...
Before seasonal adjustment, the National Index posted a month-over-month increase of 0.6% in March. The 10-City and 20-City Composites both reported 0.7% increases for the month. After seasonal adjustment, the National Index recorded a 0.3% month-over-month increase in March. The 10-City and 20-City Composites both posted 0.1% month-over-month increases. In March, 19 of 20 cities reported increases before seasonal adjustment, while 14 of 20 cities reported increases after seasonal adjustment.
“Home price gains continue to slow,” says David M. Blitzer, Managing Director and Chairman of the Index Committee at S&P Dow Jones Indices. “The patterns seen in the last year or more continue: year-over-year price gains in most cities are consistently shrinking. Double-digit annual gains have vanished. The largest annual gain was 8.2% in Las Vegas; one year ago, Seattle had a 13% gain. In this report, Seattle prices are up only 1.6%. The 20-City Composite dropped from 6.7% to 2.7% annual gains over the last year as well. The shift to smaller price increases is broad-based and not limited to one or two cities where large price increases collapsed.
emphasis added
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image. The first graph shows the nominal seasonally adjusted Composite 10, Composite 20 and National indices (the Composite 20 was started in January 2000).
The Composite 10 index is up slightly from the bubble peak, and up 0.1% in March (SA).
The Composite 20 index is 4.2% above the bubble peak, and up 0.1% (SA) in March.
The National index is 12.6% above the bubble peak (SA), and up 0.3% (SA) in March. The National index is up 52.3% from the post-bubble low set in December 2011 (SA).
 The second graph shows the Year over year change in all three indices.
The second graph shows the Year over year change in all three indices.The Composite 10 SA is up 2.3% compared to March 2018. The Composite 20 SA is up 2.6% year-over-year.
The National index SA is up 3.7% year-over-year.
Note: According to the data, prices increased in 15 of 20 cities month-over-month seasonally adjusted.
I'll have more later.
Tuesday: Case-Shiller House Prices
by Calculated Risk on 5/28/2019 12:11:00 AM
Tuesday:
• At 9:00 AM, S&P/Case-Shiller House Price Index for March. The consensus is for a 2.5% year-over-year increase in the Comp 20 index for March.
• At 9:00 AM, FHFA House Price Index for March 2019. This was originally a GSE only repeat sales, however there is also an expanded index.
• At 10:30 AM, Dallas Fed Survey of Manufacturing Activity for May.
Monday, May 27, 2019
The War on Data Continues
by Calculated Risk on 5/27/2019 10:33:00 AM
Three years ago I wrote: The War on Data
Unfortunately the war on data has continued unabated, as Catherine Rampell noted last week in the WaPo: The Trump administration’s war on statistics isn’t slowing down
Don’t like the numbers? Invent new numbers instead.There are no "alternative facts", and this war on data should concern everyone - ignoring or misrepresenting data leads to irresponsible comments and poor policy decisions.
Or make it harder to collect trustworthy numbers next time.
Or just put the squeeze on the number crunchers themselves.
Slowly but surely, the Trump administration has been chipping away at the independence and integrity of our federal statistical agencies, whose data is critical to keeping our democracy functioning and our economy healthy.
…
Presumably the Trump administration has calculated that doctoring statistical models, skewing survey results and trying to strong-arm statisticians will serve its near-term political interests. In the long term, however, sowing distrust in government data only reduces the ability of policymakers, businesses and voters to make informed decisions.
Sunday, May 26, 2019
Hotels: Occupancy Rate Increased Year-over-year
by Calculated Risk on 5/26/2019 10:14:00 AM
From HotelNewsNow.com: STR: US hotel results for week ending 18 May
The U.S. hotel industry reported positive year-over-year results in the three key performance metrics during the week of 12-18 May 2019, according to data from STR.The following graph shows the seasonal pattern for the hotel occupancy rate using the four week average.
In comparison with the week of 13-19 May 2018, the industry recorded the following:
• Occupancy: +0.8% to 70.8%
• Average daily rate (ADR): +1.4% to US$134.36
• Revenue per available room (RevPAR): +2.2% to US$95.13
emphasis added
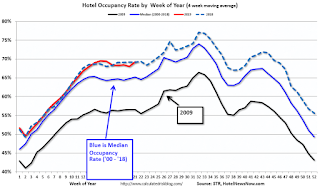 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.The red line is for 2019, dash light blue is 2018, blue is the median, and black is for 2009 (the worst year probably since the Great Depression for hotels).
A decent start for 2019, close - to-date - compared to the previous 4 years.
Seasonally, the occupancy rate will mostly move sideways for several more weeks, and then increase during the Summer travel season.
Data Source: STR, Courtesy of HotelNewsNow.com
Saturday, May 25, 2019
Schedule for Week of May 26, 2019
by Calculated Risk on 5/25/2019 08:11:00 AM
The key reports this week are the second estimate of Q1 GDP, Case-Shiller house prices, and Personal Income and Outlays for April.
For manufacturing, the May Dallas and Richmond Fed manufacturing surveys will be released.
All US markets will be closed in observance of Memorial Day.
 9:00 AM: S&P/Case-Shiller House Price Index for March.
9:00 AM: S&P/Case-Shiller House Price Index for March.This graph shows the year-over-year change in the seasonally adjusted National Index, Composite 10 and Composite 20 indexes through the most recent report (the Composite 20 was started in January 2000).
The consensus is for a 2.5% year-over-year increase in the Comp 20 index for March.
9:00 AM: FHFA House Price Index for March 2019. This was originally a GSE only repeat sales, however there is also an expanded index.
10:30 AM: Dallas Fed Survey of Manufacturing Activity for May.
7:00 AM ET: The Mortgage Bankers Association (MBA) will release the results for the mortgage purchase applications index.
10:00 AM: Richmond Fed Survey of Manufacturing Activity for May. This is the last of regional manufacturing surveys for May.
8:30 AM: The initial weekly unemployment claims report will be released. The consensus is for 215 thousand initial claims, up from 211 thousand last week.
8:30 AM: Gross Domestic Product, 1st quarter 2019 (Second estimate). The consensus is that real GDP increased 3.0% annualized in Q2, down from the advance estimate of 3.2%.
10:00 AM: Pending Home Sales Index for April. The consensus is for a 0.3% increase in the index.
8:30 AM ET: Personal Income and Outlays, April 2019. The consensus is for a 0.3% increase in personal income, and for a 0.2% increase in personal spending. And for the Core PCE price index to increase 0.2%.
9:45 AM: Chicago Purchasing Managers Index for May.
10:00 AM: University of Michigan's Consumer sentiment index (Final for May). The consensus is for a reading of 101.0.


