by Calculated Risk on 3/14/2014 07:31:00 PM
Friday, March 14, 2014
Kolko: Where Do Housing “Leading Indicators” Lead Us?
CR Note: This is from Trulia chief economist Jed Kolko:
How well do leading indicators predict housing activity? In theory they should if housing construction and home purchases follow a logical sequence. When homes are sold, contracts are signed (as measured by NAR’s pending home sales index) before sales close (NAR existing home sales); also, many buyers apply for mortgages (MBA purchase applications index) before a sale closes. Also, when new homes are built, they get permits (Census new home permits) before construction begins (Census new home starts); and roughly two-thirds of new home sales happen when homes are under construction or completed, rather than before they’re started.
But lots of factors can erode the link between leading indicators and the activities they foreshadow. Some homes inevitably fail to follow the standard paths: some sales under contract may fail to close, some permitted units might not get built, and – especially now – homes can be purchased with cash and therefore skip the mortgage-application step altogether. Unanticipated events can break the link, too: bad weather or a sudden crisis that hurts confidence could delay construction on already-permitted units.
Simple correlations and time-series regressions show empirically how well leading indicators actually predict key housing measures. Because the relationships between indicators can change over time, it’s helpful to focus on the most recent years of data. (The real test is whether leading indicators predict month-over-month changes, not year-over-year changes, since eleven months of a year-over-year change are already known before each monthly release of a year-over-year number.)
Based on national housing measures from 2008 to the present, the leading-indicator crystal ball is generally pretty cloudy, though better for existing home sales than for new home starts or sales.
1. Existing home sales
Existing home sales , which are closings, tend to follow pending home sales by one or two months. Pending sales turn out to be a reasonably good leading indicator of existing sales. The correlation between the month-over-month change (m/m) in existing sales and the m/m change in pending sales from one month earlier is 0.45; the correlation with the pending sales from two months earlier is also 0.45. The correlation between existing sales m/m and the average of the one and two month lags of pending sales m/m is 0.70.
How strong is this relationship? That’s weaker than, say, the very tight relationship between the change in the 30-year fixed rate and the same-month change in the MBA refinance index (correlation = -0.84). But the pending-existing sales relationship is stronger than any of the construction-related measures, as we’ll see next.
Putting that into a simple time-series regression shows that the best predictor of the existing sales m/m change is the simple average of pending sales m/m changes from one and two months earlier. Including the m/m change in the MBA purchase-application index from one and two months earlier improves the prediction of existing sales only minimally. The m/m changes in pending home sales for December and January suggest a 3% m/m drop in existing home sales in February.
2. New home starts
Building permits are a weaker predictor of new-home starts than pending sales are of existing home sales. The correlation between the m/m change in starts and the previous month’s m/m change in permits is 0.45, but permits from more than one month back bear little relation to starts. Rather, the m/m change in starts is partly correlated with the same month’s change in permits. That means that changes in new home starts tend to run, on average, half a month behind changes in new home permits. Since permits data are released in the same monthly Census report as new home starts, the value of permits as a leading indicator is limited.
The historical data suggests that the best guess of this month’s m/m change in starts is 0.6 times last month’s m/m change in permits. Permits fell m/m in January by 5%, pointing to a 3% drop in starts in February. But the relationship isn’t very tight, so even that best guess will often be way off.
3. New home sales
It’s even harder to predict new home sales based on other indicators. The m/m change in new home sales is most strongly correlated with the same month change in new single-family permits . Since the Census releases new home sales data one week after the release of starts and permits data for the same month, this month’s change in permits gives a few-day-ahead hint at the same month’s change in new home sales, but only because of the reporting lag.
Overall, the leading indicators don’t get us that far. Changes in pending home sales predict changes in existing home sales reasonably well, when the changes from one and two months earlier are averaged. But lagged pending home sales probably don’t beat out aggregated data from local realtor/MLS reports (regularly posted here on Calculated Risk) as an early look at existing home sales. On the construction side, building permits are halfway between a leading indicator and a concurrent indicator of starts, and neither is a good leading indicator of changes in new home sales. The modest value of leading indicators means that every month there’s plenty of room for housing-data surprises.
Report: "Blackstone’s Home Buying Binge Ends"
by Calculated Risk on 3/14/2014 04:45:00 PM
An interesting article from John Gittelsohn and Heather Perlberg at Bloomberg: Blackstone’s Home Buying Binge Ends as Prices Surge: Mortgages (ht JR)
Blackstone’s acquisition pace has declined 70 percent from its peak last year, when the private equity firm was spending more than $100 million a week on properties, said Jonathan Gray, global head of real estate for the New York-based firm. After investing $8 billion since April 2012 to buy 43,000 homes in 14 cities, the company has narrowed most of its purchasing to Seattle, Atlanta, Miami, Orlando and Tampa.It appears investors are pulling back in a number of markets (this fits with the data I've been posting).
“The institutional wave has passed,” Gray, who oversees almost $80 billion in property investments, said in a telephone interview. “It’s at a much lower level than it was 12 or 24 months ago.”
...
American Homes 4 Rent (AMH) has slowed its buying in some of its 42 markets, chief executive officer David Singelyn said at a March 5 investor conference in Florida. ... American Residential Properties Inc. (ARPI), a landlord with 6,000 homes, slowed acquisitions by almost half in its latest quarter ending Dec. 31
CoStar: Commercial Real Estate prices increased in January, Distress Sales Declining Rapidly
by Calculated Risk on 3/14/2014 02:02:00 PM
Here is a price index for commercial real estate that I follow.
From CoStar: Commercial Real Estate Prices Remain on Upward Trajectory in January
CRE PRICES BROADLY ADVANCE IN JANUARY DESPITE SEASONAL VOLATILITY: In a pattern repeated over the last several years, the number of repeat property sales in January 2014 fell from the previous several months as trading activity predictably returned to a more normal level following the frenzied pace at year-end. This slowdown in investment activity has typically accompanied a pricing decline in the first quarter. And while the CCRSI Value-Weighted U.S. Composite Index slipped by a slight 0.6% in January 2014, reflecting the slowdown in sales activity among larger properties, the Equal-Weighted U.S. Composite Index, which is more heavily influenced by smaller transactions, remained on an upward trajectory, increasing by 1.0% in January 2014.
...
DISTRESS SALES FALLING RAPIDLY: Despite the slowdown in January 2014, the number of observed trades over the last 12 months increased by 14.3% over the prior 12-month period. Importantly for the pricing indices, the number of distressed sales has declined by 21.8% over that same period. As of January 2014, the percentage of total observed pair counts classified as distress sales fell below 10%, down sharply from a peak of 35% in October 2010. Rising occupancies have helped stabilize NOIs across a growing number of markets leading to a large net reduction in the number of forced sales. This trend has been a positive force for commercial real estate pricing.
emphasis added
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph from CoStar shows the Value-Weighted and Equal-Weighted indexes. CoStar reported that the Value-Weighted index is up 52.2% from the bottom (showing the earlier demand for higher end properties) and up 10.6% year-over-year. However the Equal-Weighted index is only up 20.3% from the bottom, and up 12.2% year-over-year.
Note: These are repeat sales indexes - like Case-Shiller for residential - but this is based on far fewer pairs.
Hotel Occupancy Rate increased 2.1% year-over-year in latest Survey
by Calculated Risk on 3/14/2014 11:05:00 AM
From HotelNewsNow.com: STR: US results for week ending 8 March
The U.S. hotel industry posted positive results in the three key performance measurements during the week of 2-8 March 2014, according to data from STR.Note: ADR: Average Daily Rate, RevPAR: Revenue per Available Room.
In year-over-year measurements, the industry’s occupancy increased 2.1 percent to 64.0 percent. Average daily rate rose 4.8 percent to finish the week at US$114.85. Revenue per available room for the week was up 7.1 percent to finish at US$73.52.
emphasis added
During the same week in 2008, RevPAR was around $65. and ADR was at $108. In 2009, RevPAR and ADR declined sharply, but these metrics are now at new highs.
The 4-week average of the occupancy rate is close to normal levels.
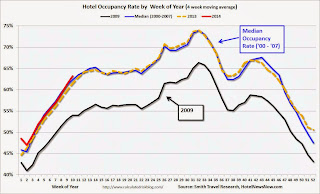
The following graph shows the seasonal pattern for the hotel occupancy rate using the four week average.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.The red line is for 2014 and black is for 2009 - the worst year since the Great Depression for hotels.
Through March 8th, the 4-week average of the occupancy rate is tracking slightly higher than pre-recession levels.
It looks like 2014 should be a solid year for hotels.
Data Source: Smith Travel Research, Courtesy of HotelNewsNow.com
Preliminary March Consumer Sentiment declines to 79.9
by Calculated Risk on 3/14/2014 09:55:00 AM

Click on graph for larger image.
The preliminary Reuters / University of Michigan consumer sentiment index for March was at 79.9, down from 81.6 in February.
This was below the consensus forecast of 81.8. Sentiment has generally been improving following the recession - with plenty of ups and downs - and a big spike down when Congress threatened to "not pay the bills" in 2011, and another smaller spike down last October and November due to the government shutdown.
I expect to see sentiment at post-recession highs very soon.
Thursday, March 13, 2014
Friday: PPI, Consumer Sentiment
by Calculated Risk on 3/13/2014 07:14:00 PM
An important development from the WSJ: Senators Strike Deal on Long-Term Jobless Benefits
Congress has been stalled since extended federal jobless benefits expired on Dec. 28, 2013, taking away financial support from an estimated two million people so far.The key points:
...
Under the agreement reached Thursday, those who had lost benefits in late December would receive retroactive payments.
...
To ensure that the roughly $9.7 billion bill doesn't add to the federal budget deficit, it includes measures designed to generate new revenue.
The deal's fate in the Republican-controlled House of Representatives wasn't immediately clear. House Speaker John Boehner (R., Ohio) had said earlier this year that he would consider renewing the long-term benefits if lawmakers could come up with a plan to offset the cost ...
1) Not having extended benefits with so many suffering is unprecedented and bad policy.
2) The bill is retroactive.
3) The bill is paid for.
4) The bill is bipartisan.
5) But it still needs to pass the House.
Friday:
• At 8:30 AM ET, the Producer Price Index for February from the BLS. The consensus is for a 0.2% increase in prices.
• At 9:55 AM, the Reuter's/University of Michigan's Consumer sentiment index (preliminary for March). The consensus is for a reading of 81.8, up from 81.6 in February.
FNC: House prices increased 9.0% year-over-year in January
by Calculated Risk on 3/13/2014 03:04:00 PM
From FNC: FNC Index: Home Prices of Normal Sales Up 0.4% in January
The latest FNC Residential Price Index™ (RPI) shows U.S. home prices have gotten off to a positive start in 2014, rising a modest 0.4% in January. The index, constructed to gauge the price movement among normal home sales exclusive of distressed properties, indicates home prices of the underlying housing market continue to strengthen as market fundamentals and credit conditions continue to improve.The 100-MSA composite was up 9.0% compared to January2013. The FNC index turned positive on a year-over-year basis in July, 2012.
The index is up 9.0% from a year ago and continues to point to the fastest year-over-year growth to date since the recovery began. Home prices are expected to rise modestly in February as improving signs are emerging in the for-sale market: The for-sale market has strengthened in February and the average seller asking price discount dropped from 5.4% in January to 4.7% in February.
...
Based on recorded sales of non-distressed properties (existing and new homes) in the 100 largest metropolitan areas, the FNC national composite index shows that in January home prices rose at a seasonally unadjusted rate of 0.4%. The two narrower indices (30- and 10- MSA composites) show faster month-over-month price appreciation in the nation’s top housing markets, up 0.6% and 0.8%, respectively. The 30- and 10-MSA composites’ year-over-year trends also show more rapid growth rate in the double digits and, similar to the national index, the fastest year-over-year growth to date since the recovery began.
emphasis added
 Click on graph for larger image.
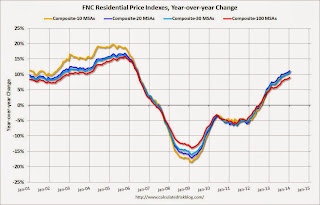
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows the year-over-year change for the FNC Composite 10, 20, 30 and 100 indexes.
Even with the recent increase, the FNC composite 100 index is still off 23.2% from the peak.
I'm expecting the year-over-year change in house prices to slow as more inventory comes on the market - but this index isn't showing a slowdown yet.
DataQuick: February Bay Area Home Sales Slowest Since 2008
by Calculated Risk on 3/13/2014 02:21:00 PM
From DataQuick: Bay Area Home Sales Slowest Since 2008
Bay Area home buyers were kept scrambling last month as a continued lack of inventory contributed heavily to a six-year low in sales. ...And on distressed sales:
A total of 4,963 new and resale houses and condos sold in the nine-county Bay Area last month. That was the lowest for any February since 2008, when 3,989 homes sold. Last month’s sales rose 5.7 percent from 4,696 in January, and fell 8.2 percent from 5,404 in February 2013, according to San Diego-based DataQuick.
Since 1988, when DataQuick’s statistics begin, February sales have ranged from a low of 3,989 in 2008 to a high of 8,901 in 2002. Last month’s sales were 19.9 percent below the average number of February sales – 6,194 – since 1988. Sales haven’t been above average for any month in more than seven years.
“A number of factors can keep a lid on sales. Affordability, for example. Or hard-to-get mortgages. These factors certainly play a role today, but clearly the main culprit is an inadequate supply of homes for sale. It’s going to be fascinating to watch how things play out between now and June. At some point rising home prices will trigger a more significant increase in the number of homes on the market. It’s just a question of when,” said John Walsh, DataQuick president.
Distressed property sales – the combination of foreclosure resales and “short sales” – made up about 12.5 percent of last month’s resale market. That was down from 14.0 percent in January and down from 34.1 percent a year earlier.This decline in sales is due to several factors: limited inventory, higher prices, and fewer distressed sales. With the recent price increases, more inventory should come on the market this year.
Foreclosure resales – homes that had been foreclosed on in the prior 12 months – accounted for 5.4 percent of resales in February, up from a revised 5.2 percent the month before, and down from 13.9 percent a year ago. Foreclosure resales peaked at 52.0 percent in February 2009. The monthly average for foreclosure resales over the past 17 years is 9.9 percent.
Short sales – transactions where the sale price fell short of what was owed on the property – made up an estimated 7.0 percent of Bay Area resales last month. That was down from an estimated 8.8 percent in January and down from 20.2 percent a year earlier.
Lawler: Preliminary Table of Distressed Sales and Cash buyers for Selected Cities in February
by Calculated Risk on 3/13/2014 10:58:00 AM
Economist Tom Lawler sent me the preliminary table below of short sales, foreclosures and cash buyers for several selected cities in February.
From CR: This is just a few markets for February - more to come.
Total "distressed" share is down in all of these markets, mostly because of a sharp decline in short sales.
Foreclosures are down in most of these areas too, although foreclosures are up a little in Las Vegas (there was a state law change that slowed foreclosures dramatically in Nevada at the end of 2011 - so it isn't a surprise that foreclosures are up a little year-over-year).
The All Cash Share (last two columns) is declining year-over-year. As investors pull back, the share of all cash buyers will probably decline.
In general it appears the housing market is slowly moving back to normal.
| Short Sales Share | Foreclosure Sales Share | Total "Distressed" Share | All Cash Share | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feb-14 | Feb-13 | Feb-14 | Feb-13 | Feb-14 | Feb-13 | Feb-14 | Feb-13 | |
| Las Vegas | 14.0% | 37.9% | 12.0% | 10.2% | 26.0% | 48.1% | 46.8% | 59.5% |
| Reno** | 13.0% | 37.0% | 7.0% | 13.0% | 20.0% | 50.0% | ||
| Phoenix | 5.3% | 15.0% | 8.3% | 13.8% | 13.7% | 28.8% | 33.6% | 46.1% |
| Sacramento | 12.3% | 30.3% | 7.0% | 13.5% | 19.3% | 43.8% | 26.5% | 39.5% |
| Minneapolis | 5.0% | 11.3% | 25.3% | 32.7% | 30.3% | 43.9% | ||
| Mid-Atlantic | 7.7% | 13.6% | 10.9% | 12.1% | 18.6% | 25.6% | 21.4% | 22.8% |
| So. California* | 9.4% | 22.4% | 6.8% | 16.2% | 16.2% | 38.6% | 30.9% | 36.9% |
| Hampton Roads | 30.7% | 34.2% | ||||||
| Memphis* | 22.1% | 29.0% | ||||||
| Springfield IL** | 17.9% | 26.4% | ||||||
| *share of existing home sales, based on property records **Single Family Only ***GAMLS | ||||||||
Retail Sales increased 0.3% in February
by Calculated Risk on 3/13/2014 08:55:00 AM
On a monthly basis, retail sales increased 0.3% from January to February (seasonally adjusted), and sales were up 1.5% from February 2013. Sales in December and January were revised down from a 0.4% decrease to a 0.6% decrease. From the Census Bureau report:
The U.S. Census Bureau announced today that advance estimates of U.S. retail and food services sales for February, adjusted for seasonal variation and holiday and trading-day differences, but not for price changes, were $427.2 billion, an increase of 0.3 percent from the previous month, and 1.5 percent above February 2013. ... The December 2013 to January 2014 percent change was revised from -0.4 percent to -0.6 percent.
 Click on graph for larger image.
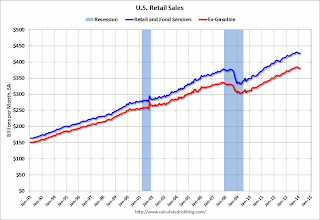
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows retail sales since 1992. This is monthly retail sales and food service, seasonally adjusted (total and ex-gasoline).
Retail sales ex-autos increased 0.3%.
The second graph shows the year-over-year change in retail sales and food service (ex-gasoline) since 1993.
 Retail sales ex-gasoline increased by 2.2% on a YoY basis (1.5% for all retail sales).
Retail sales ex-gasoline increased by 2.2% on a YoY basis (1.5% for all retail sales).The increase in February was above consensus expectations, but the downward revisions to December and January were negatives.
However, it appears much of the weakness in January and February was due to the weather.


