by Calculated Risk on 1/10/2013 05:00:00 PM
Thursday, January 10, 2013
The California Budget Surplus
Back in November I was interviewed by Joe Weisenthal at Business Insider. One of my comments during our discussion on state and local governments was:
I wouldn’t be surprised if we see all of a sudden a report come out, “Hey, we’ve got a balanced budget in California.”And today from Reuters: California Governor's budget has surprise: a surplus
The state expects $98.5 billion in revenues and transfers and plans spending $97.7 billion, according to the proposal published on the state Department of Finance website.This is a tentative surplus, and there is plenty of debt, but this is another small positive step. The plan in California is to increase spending slightly in the upcoming year after several years of budget cuts.
That leaves a surplus of $851 million for the year, in addition to a projected $785 million surplus for the current fiscal year, which ends in June, allowing the state to put $1 billion toward a rainy day fund.
Brown said he saw a balanced budget for the next four years.
Spending in the upcoming year is set to rise 5 percent, or $4.7 billion, from the current 2012-13 budget. Schools and universities will see a $4 billion boost, health care spending will rise $1.2 billion, while transfers to local government will drop $2.1 billion.
As I mentioned in the previous post, moving from state and local budget cuts to some small increases will be a plus for the economy.
Question #2 for 2013: Will the U.S. economy grow in 2013?
by Calculated Risk on 1/10/2013 01:30:00 PM
Note: Sometimes it is useful to jot down a few thoughts on how the economy is expected to perform. This isn't to test my forecasting skills; sometimes I learn more when I get something wrong!
Some years I make some big out-of-consensus calls, but my forecasts this year are mostly in line with the consensus.
Earlier I posted some questions for this year: Ten Economic Questions for 2013. I'll try to add some thoughts, and maybe some predictions for each question.
Note: Here is a review of my 2012 Forecasts
2) Economic growth: Heading into 2013 there are still significant downside risks from the European financial crisis and from U.S. fiscal policy. Will the U.S. economy grow in 2013? Or will there be another recession?
There are several positives for the economy at the beginning of 2013: residential investment is picking up (usually the best leading indicator for the economy), the state and local government layoffs and cutbacks appear to be ending, and a substantial amount of household deleveraging has already happened.
Here are a couple of graph on household debt (and debt service):

This graph from the the NY Fed shows aggregate consumer debt decreased in Q3. This was mostly due to a decline in mortgage debt.
Household debt peaked in Q2 2008 and has been declining for over four years. There is probably more deleveraging ahead (mostly from foreclosures and distressed sales), but this suggests some improvement in household balance sheets.
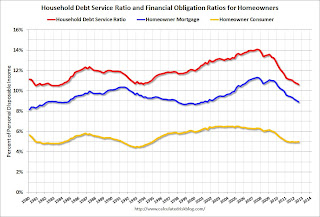 The second graph is from the Fed's Household Debt Service and Financial Obligations Ratios. These ratios show the percent of disposable personal income (DPI) dedicated to debt service (DSR) and financial obligations (FOR) for households.
The second graph is from the Fed's Household Debt Service and Financial Obligations Ratios. These ratios show the percent of disposable personal income (DPI) dedicated to debt service (DSR) and financial obligations (FOR) for households.
The graph shows the DSR for both renters and homeowners (red), and the homeowner financial obligations ratio for mortgages and consumer debt. The overall Debt Service Ratio has declined back to early 1980s levels, and is near the record low - thanks to very low interest rates. The homeowner's financial obligation ratio for consumer debt is at 1994 levels.
The blue line is the homeowner's financial obligation ratio for mortgages (blue). This ratio increased rapidly during the housing bubble, and continued to increase until 2008. Now, with falling interest rates, and less mortgage debt (mostly due to foreclosures), the ratio is back to 2001 levels. This will probably decline further, but for many homeowners, the obligation ratio is low.
There are always downside risks from Europe and China, but usually with these positive trends I'd expect a pickup in US growth in 2013. However, the recent austerity (aka "fiscal cliff") - especially the payroll tax increase compared to 2012 - will be a drag on economic growth this year.
 Here is a graph showing the rolling real GDP growth (over 4 quarters) since 2000 through Q3 2012. The rolling four quarter graph smooths out the quarterly up and downs, and show that the US economy has been growing at a little over 2% for the last few years.
Here is a graph showing the rolling real GDP growth (over 4 quarters) since 2000 through Q3 2012. The rolling four quarter graph smooths out the quarterly up and downs, and show that the US economy has been growing at a little over 2% for the last few years.
We still don't know the size of the "sequester", but right now it appears the drag from austerity will probably offset the pickup in the private sector - and we can expect another year of sluggish growth in 2013 probably in the 2% range again.
Here are the ten questions for 2013 and a few predictions:
• Question #1 for 2013: US Fiscal Policy
• Question #2 for 2013: Will the U.S. economy grow in 2013?
• Question #3 for 2013: How many payroll jobs will be added in 2013?
• Question #4 for 2013: What will the unemployment rate be in December 2013?
• Question #5 for 2013: Will the inflation rate rise or fall in 2013?
• Question #6 for 2013: What will happen with Monetary Policy and QE3?
• Question #7 for 2013: What will happen with house prices in 2013?
• Question #8 for 2013: Will Housing inventory bottom in 2013?
• Question #9 for 2013: How much will Residential Investment increase?
• Question #10 for 2013: Europe and the Euro
BLS: Job Openings "unchanged" in November
by Calculated Risk on 1/10/2013 10:15:00 AM
From the BLS: Job Openings and Labor Turnover Summary
The number of job openings in November was 3.7 million, unchanged from October.The following graph shows job openings (yellow line), hires (dark blue), Layoff, Discharges and other (red column), and Quits (light blue column) from the JOLTS.
...
The level of total nonfarm job openings was 2.4 million at the end of the recession in June 2009.
...
The number of quits (not seasonally adjusted) was little changed over the 12 months ending in November for total nonfarm and total private.
This series started in December 2000.
Note: The difference between JOLTS hires and separations is similar to the CES (payroll survey) net jobs headline numbers. This report is for November, the most recent employment report was for December.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.Notice that hires (dark blue) and total separations (red and light blue columns stacked) are pretty close each month. This is a measure of turnover. When the blue line is above the two stacked columns, the economy is adding net jobs - when it is below the columns, the economy is losing jobs.
Jobs openings increased slightly in November to 3.676 million, up from 3.665 million in October. The number of job openings (yellow) has generally been trending up, and openings are up about 12% year-over-year compared to November 2011.
Quits increased slightly in November, and quits are up 8% year-over-year. These are voluntary separations. (see light blue columns at bottom of graph for trend for "quits").
Not much changes month-to-month in this report, but the trend suggests a gradually improving labor market.
Weekly Initial Unemployment Claims at 371,000
by Calculated Risk on 1/10/2013 08:37:00 AM
The DOL reports:
In the week ending January 5, the advance figure for seasonally adjusted initial claims was 371,000, an increase of 4,000 from the previous week's revised figure of 367,000. The 4-week moving average was 365,750, an increase of 6,750 from the previous week's revised average of 359,000.
The previous week was revised down from 372,000.
The following graph shows the 4-week moving average of weekly claims since January 2000.

Click on graph for larger image.
The dashed line on the graph is the current 4-week average. The four-week average of weekly unemployment claims increased to 365,750.
Weekly claims are very volatile during and just after the holiday season, but even with the increase, the 4-week average is near the low for last year.
The recent spike was due to hurricane Sandy.
Weekly claims were above the 362,000 consensus forecast.

And here is a long term graph of weekly claims:
Note: There are large seasonal factors in December and January, and that can make for fairly large swings for weekly claims.
Wednesday, January 09, 2013
Thursday: Initial Unemployment Claims, Job Openings
by Calculated Risk on 1/09/2013 09:04:00 PM
A few articles on Jack Lew (Obama's pick for Treasury Secretary).
From the NY Times: Obama’s Pick for Treasury Is Said to Be His Chief of Staff
President Obama will announce on Thursday that he intends to elevate his chief of staff and former budget director, Jacob J. Lew, to be his next secretary of Treasury ...From the WSJ: Obama Aide Is Treasury Pick
While Mr. Lew has much less experience than Mr. Geithner in international economics and financial markets, he would come to the job with far more expertise in fiscal policy and in dealing with Congress than Mr. Geithner did when he became secretary at the start of Mr. Obama’s term. That shift in skills reflects the changed demands of the times, as emphasis has shifted from the global recession and financial crisis of the president’s first years to the continuing budget fights with Republicans in Congress ...
President Barack Obama plans to nominate Jacob Lew to be the 76th U.S. Treasury secretary, putting the White House's chief budget expert in a top economic post as it enters a grueling year of fiscal battles with Congress.From the WSJ: Jacob Lew, in His Own Words
...
Mr. Lew, 57 years old, is a veteran of numerous Washington budget battles, stretching back to his work as a senior congressional aide in the 1980s. He would likely draw on that experience during the looming fights over the debt ceiling, government spending levels and a possible overhaul of the tax code.
2010 – confirmation hearing before Senate Budget CommitteeThursday economic releases:
“Throughout my career, I have tried to work collaboratively across partisan and ideological divides to cut through gridlock and to help solve what seem like intractable problems. If confirmed as OMB Director, I will work in that bipartisan fashion again–with the members of this Committee, the leadership of both chambers, and with all those committed to taking constructive steps to rejuvenating our Nation’s economy and its fiscal standing.”
• At 8:30 AM ET, the initial weekly unemployment claims report will be released. The consensus is for claims to decrease to 362 thousand from 372 thousand last week.
• At 10:00 AM, the Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey for November will be released by the BLS. In general jobs openings have been trending up. Openings were up about 8% year-over-year in October.
• Also at 10:00 AM, the Monthly Wholesale Trade: Sales and Inventories report for November. The consensus is for a 0.3% increase in inventories.
Question #3 for 2013: How many payroll jobs will be added in 2013?
by Calculated Risk on 1/09/2013 05:49:00 PM
Note: Near the beginning of the year, I find it useful to jot down a few thoughts on how I expect the economy to perform. This isn't to test my forecasting skills - some times I learn more when I miss a forecast (As an example, I've spent a significant amount of time looking at the participation rate and demographics since I've been overly pessimistic on the unemployment rate the last couple of years).
Some years I make some big calls. Not this year. Although I think parts of the economy are poised for more growth, I think austerity at the Federal level means another year of sluggish growth. So my forecasts this year are mostly in line with the consensus (It is more fun being a contrarian - oh well).
Earlier I posted some questions for this year: Ten Economic Questions for 2013. I'll try to add some thoughts, and maybe some predictions for each question.
Note: Here is a review of my 2012 Forecasts
3) Employment: How many payroll jobs will be added in 2013? Will we finally see some pickup over the approximately 2 million private sector job creation rate of 2011 and 2012?
I've been hammering on two key positive themes: 1) the pickup in residential investment (RI), and 2) the end of state and local government layoffs. Both of these will be positive for employment next year (there seems to be a lag between increases in RI and employment).
The following table shows the annual change in State and Local government since 2008. The four years of declining employment appears to be ending. Note: This doesn't include the benchmark revision to be released in February. The preliminary revision showed even more government job losses.
| State and Local Government, Annual Change in Payroll (000s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | State Government | Local Government | Total |
| 2008 | 50 | 108 | 158 |
| 2009 | -41 | -88 | -129 |
| 2010 | -20 | -242 | -262 |
| 2011 | -80 | -150 | -230 |
| 2012 | 24 | -50 | -26 |
The second table shows the change in construction payrolls starting in 2006.
| Construction Jobs (000s) | |
|---|---|
| 2006 | 152 |
| 2007 | -195 |
| 2008 | -785 |
| 2009 | -1,051 |
| 2010 | -177 |
| 2011 | 69 |
| 2012 | 18 |
For construction jobs, the preliminary benchmark revision showed an increase in jobs - so 2011 and 2012 will both probably be revised upwards. It is also important to note that construction includes residential, commercial and public. Although residential is picking up (usually the largest category), public construction spending is still declining, and commercial is mostly moving sideways (energy construction is up).
Both state and local government and construction hiring should improve in 2013. Unfortunately there are other employment categories that will be hit by the austerity (especially the increase in payroll taxes). I expect that will offset any gain from construction and local governments. So my forecast is close to the previous two years, a gain of about 150,000 to 200,000 payroll jobs per month in 2013.
Here are the ten questions for 2013 and a few predictions:
• Question #1 for 2013: US Fiscal Policy
• Question #2 for 2013: Will the U.S. economy grow in 2013?
• Question #3 for 2013: How many payroll jobs will be added in 2013?
• Question #4 for 2013: What will the unemployment rate be in December 2013?
• Question #5 for 2013: Will the inflation rate rise or fall in 2013?
• Question #6 for 2013: What will happen with Monetary Policy and QE3?
• Question #7 for 2013: What will happen with house prices in 2013?
• Question #8 for 2013: Will Housing inventory bottom in 2013?
• Question #9 for 2013: How much will Residential Investment increase?
• Question #10 for 2013: Europe and the Euro
Question #4 for 2013: What will the unemployment rate be in December 2013?
by Calculated Risk on 1/09/2013 03:13:00 PM
Earlier I posted some questions for this year: Ten Economic Questions for 2013. I'll try to add some thoughts, and maybe some predictions for each question.
Note: Here is a review of my 2012 Forecasts
4) Unemployment Rate: The unemployment rate is still elevated at 7.7% in November [7.8% in the December report]. For the last two years I've been too pessimistic on the unemployment rate because I was expecting some minor bounce back in the participation rate. Instead the participation rate continued to decline.
Maybe 2013 will be the year the participation rate increases a little, or at least stabilizes. Economists at the SF Fed wrote about this last [month]: Will the Jobless Rate Drop Take a Break?
The recent recession was unusual in its depth and its duration. Labor market conditions have remained difficult for a long time. As a result, large numbers of discouraged workers have stopped looking for jobs. A big unknown is whether these workers will stay out of the labor force permanently or enter as the economy recovers. If these workers join the labor force, increasing participation could have a major impact on the unemployment rate in the coming years.What will the unemployment rate be in December 2013?
Forecasting the unemployment rate includes forecasts for economic and payroll growth, and also for changes in the participation rate. Note: The participation rate is the percent of the working age population (16 and over) that is in the labor force.
We can be pretty certain that the participation rate will decline over the next couple of decades based on demographic trends, but it is unclear what will happen in 2013. The participation rate could bounce back (increase), as the Fed paper excerpted above suggests. Or the participation rate could decline further as has happened over the last few years
Here is a table showing the participation and unemployment rates for December since 2008.
| Unemployment and Participation Rate for December each Year | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| December of | Participation Rate | Unemployment Rate | Using December 2010 participation rate1 |
| 2008 | 65.8% | 7.3% | |
| 2009 | 64.6% | 9.9% | |
| 2010 | 64.3% | 9.3% | |
| 2011 | 64.0% | 8.5% | 8.9% |
| 2012 | 63.6% | 7.8% | 8.8% |
| 1This is the estimated unemployment rate assuming the participation rate had stayed at the December 2010 level of 64.3%, and all of the additional participants were unemployed (same employment growth). | |||
The last column shows what would have happened to the unemployment rate if the participation rate had held steady for the last two years. Clearly the declining participation rate played a key role in the decline in the unemployment rate.
I could make an argument for some bounce back in the participation rate (see Fed paper above), and then, with sluggish growth, we'd probably see an increase in the unemployment rate in 2013 to over 8%. However - as we've seen over the last couple of years - sluggish growth probably isn't sufficient to draw many people back into the labor force, and I could make an argument for another decrease in the participation rate.
My guess is the participation rate will remain around 63.6% in 2013, and with sluggish employment growth, the unemployment rate will be in the mid-to-high 7% range in December 2013 (little changed from the current rate).
Here are the ten questions for 2013 and a few predictions:
• Question #1 for 2013: US Fiscal Policy
• Question #2 for 2013: Will the U.S. economy grow in 2013?
• Question #3 for 2013: How many payroll jobs will be added in 2013?
• Question #4 for 2013: What will the unemployment rate be in December 2013?
• Question #5 for 2013: Will the inflation rate rise or fall in 2013?
• Question #6 for 2013: What will happen with Monetary Policy and QE3?
• Question #7 for 2013: What will happen with house prices in 2013?
• Question #8 for 2013: Will Housing inventory bottom in 2013?
• Question #9 for 2013: How much will Residential Investment increase?
• Question #10 for 2013: Europe and the Euro
Question #5 for 2013: Will the inflation rate rise or fall in 2013?
by Calculated Risk on 1/09/2013 12:42:00 PM
Earlier I posted some questions for this year: Ten Economic Questions for 2013. I'll try to add some thoughts, and maybe some predictions for each question.
Note: Here is a review of my 2012 Forecasts
5) Inflation: The Fed has made it clear they will tolerate a little more inflation, but currently the inflation rate is running below the Fed's 2% target. Will the inflation rate rise or fall in 2013?
Here is a look at four key measures of inflation: core CPI (consumer price index), core PCE prices (Personal Consumption Expenditures), median CPI and the trimmed-mean CPI through November 2012.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.
On a year-over-year basis, the median CPI rose 2.2%, the trimmed-mean CPI rose 1.9%, the CPI rose 1.8%, and the CPI less food and energy rose 1.9%. Core PCE is for October and increased 1.7% year-over-year. These measures suggest inflation is mostly below the Fed's target of 2% on a year-over-year basis.
Here is what I wrote last year on inflation:
There are some people who have been predicting an imminent rapid increase in inflation for almost 3 years - in their view, a sharp increase in inflation is always just around the corner. That view has consistently been wrong, although some people also claim the government measures are not correct and that inflation is much higher than reported.I could just repeat that post with a few of minor changes. The first change is QE3 has already been announced. A second change is that now some people who have been predicting an imminent rapid increase in inflation for almost 4 years! Always wrong, but never in doubt.
However private measures show similar results as BEA and BLS measures (see The Billion Prices Project). ...
The bottom line is the inflation rate will probably stay low in 2012 with high unemployment and low resource utilization. I expect QE3 to be announced before mid-year, and that will probably keep the inflation rate near the Fed's target (as opposed to falling further). But I don't see inflation as a significant threat in 2012.
A third possible change is related to the recent FOMC statement that indicated the Fed will tolerate an inflation outlook "between one and two years ahead" of 2 1/2 percent. Given the Fed's tolerance for a little more inflation, we might see a little more inflation in 2013 than in 2012 - but I still expect inflation to be near the Fed's target. With high unemployment and low resource utilization, I don't see inflation as a threat in 2013.
Here are the ten questions for 2013 and a few predictions:
• Question #1 for 2013: US Fiscal Policy
• Question #2 for 2013: Will the U.S. economy grow in 2013?
• Question #3 for 2013: How many payroll jobs will be added in 2013?
• Question #4 for 2013: What will the unemployment rate be in December 2013?
• Question #5 for 2013: Will the inflation rate rise or fall in 2013?
• Question #6 for 2013: What will happen with Monetary Policy and QE3?
• Question #7 for 2013: What will happen with house prices in 2013?
• Question #8 for 2013: Will Housing inventory bottom in 2013?
• Question #9 for 2013: How much will Residential Investment increase?
• Question #10 for 2013: Europe and the Euro
Reis: Mall Vacancy Rate declines in Q4
by Calculated Risk on 1/09/2013 09:19:00 AM
Reis reported that the vacancy rate for regional malls declined to 8.6% in Q4 from 8.7% in Q3. This is down from a cycle peak of 9.4% in Q3 2011.
For Neighborhood and Community malls (strip malls), the vacancy rate declined to 10.7% in Q4, down from 10.8% in Q3. For strip malls, the vacancy rate peaked at 11.1% in Q3 2011.
Comments from Reis Senior Economist Ryan Severino:
[Strip mall] Vacancy declined by only 10 bps during the fourth quarter. This was an improvement versus the third quarter when the vacancy rate was unchanged. On a year‐over‐year basis, the vacancy rate declined by only 30 bps. During the quarter absorption exceeded construction by a sufficient enough margin to lower the vacancy rate, but only marginally. With only 915,000 square feet delivered, more robust demand would cause vacancy to compress expeditiously. But even with so few completions occurring, the economy is not generating enough demand for space.
...
Asking and effective rents grew by 0.2% and 0.1%, respectively, during the quarter. This was only a negligible increase versus the third quarter when both metrics increased by just 0.1%. It was the fifth consecutive quarter that asking and effective rents have increased.
...
[New construction] With tepid retail sales and scant demand for space, new construction remained near record‐low levels during the quarter. 915,000 square feet were delivered during the fourth quarter, versus 723,000 square feet during the third quarter. However, this is a slowdown compared to the 2.951 million square feet of retail space that were delivered during the fourth quarter of 2011. In fact, 915,000 square feet is the fifth‐lowest figure on record since Reis began tracking quarterly data in 1999.
...
[Regional] Malls continue to outperform their neighborhood and community shopping center comrades. The vacancy rate declined by another 10 basis points during the quarter. This is the fifth consecutive quarter with a vacancy decline. Asking rent growth declined slightly versus last quarter, growing by another 0.2%. This was the seventh consecutive quarter of asking rent increases. The improvement in mall subsector remains consistent if not exhilarating.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows the strip mall vacancy rate starting in 1980 (prior to 2000 the data is annual). The regional mall data starts in 2000. Back in the '80s, there was overbuilding in the mall sector even as the vacancy rate was rising. This was due to the very loose commercial lending that led to the S&L crisis.
In the mid-'00s, mall investment picked up as mall builders followed the "roof tops" of the residential boom (more loose lending). This led to the vacancy rate moving higher even before the recession started. Then there was a sharp increase in the vacancy rate during the recession and financial crisis.
The yellow line shows mall investment as a percent of GDP through Q3. This has increased from the bottom because this includes renovations and improvements. New mall investment has essentially stopped.
The good news is, as Severino noted, new square footage is near a record low, and with very little new supply, the vacancy rate will probably continue to decline slowly.
Mall vacancy data courtesy of Reis.
Tuesday, January 08, 2013
Wednesday: Mall Vacancy Rate
by Calculated Risk on 1/08/2013 09:10:00 PM
Over there ... from the NY Times: Unemployment Rises to New High in Euro Zone
The euro zone jobless rate rose to 11.8 percent in November from 11.7 percent in October, according to Eurostat, the statistical agency of the European Union. Eurostat estimated that 18.8 million people in the euro zone were unemployed in November, two million more than a year earlier.Austerity at work. The beatings will continue until morale improves.
... on Tuesday, the Federal Statistics Office in Berlin said that German exports declined 3.4 percent while imports slid 3.7 percent in November from a month earlier. The weakness narrowed Germany’s trade surplus to €14.6 billion ...
Wednesday economic releases:
• Early: Reis Q4 2012 Mall survey of rents and vacancy rates. In Q3 Reis reported the regional mall vacancy rate declined to 8.7%, from 8.9% in Q2. The vacancy rate peaked at 9.4% in Q3 2011. For Neighborhood and Community malls (strip malls), the vacancy rate was unchanged at 10.8% in Q3. For strip malls, the vacancy rate peaked at 11.0% in Q2 2011.
• At 7:00 AM ET, the Mortgage Bankers Association (MBA) will release the results for the mortgage purchase applications index.


