by Calculated Risk on 8/12/2011 04:30:00 PM
Friday, August 12, 2011
Misc: Market and Italy
Below is a stock market graph from Doug Short, but first ...
From the BBC: New Italian debt plan announced
The Italian government, led by Prime Minister Silvio Berlusconi, has announced a fresh round of austerity measures.
The 45bn euro ($64bn, £40bn) plan aims to balance the budget by 2013, a year earlier than planned. ... The cabinet agreed to 20bn euros of cuts in 2012 and 25bn in 2013.
The measures still need to be approved by the Italian parliament.
The measures include a new "solidarity tax" on high earners ...
Click on graph for larger image.
The Dow was up 125 points and the S&P 500 was up 0.5% - a mild day compared to the previous four days. The Dow was off about 175 points for the week.
Appeals Court Rules failure to properly disclose teaser rate for Option ARM might constitute Fraud
by Calculated Risk on 8/12/2011 01:05:00 PM
This is an interesting California Appeal Court ruling in the case BOSCHMA et al., Plaintiffs and Appellants, v. HOME LOAN CENTER, INC.
The plaintiffs are arguing that defendant failed to disclose prior to plaintiffs entering into their Option ARMs: (1) the loans were designed to cause negative amortization to occur; (2) the monthly payment amounts listed in the loan documents for the first two to five years of the loans were based entirely upon a low teaser‘ interest rate (though not disclosed as such by Defendants) which existed for only a single month and which was substantially lower than the actual interest rate that would be charged, such that these payment amounts would never be sufficient to pay the interest due each month; and (3) when [plaintiffs] followed the contractual payment schedule in the loan documents, negative amortization was certain to occur, resulting in a significant loss of equity in borrowers‘ homes, and making it much more difficult for borrowers to refinance the loans [because of the prepayment penalty included in the loan for paying off the loan within the first three years of the loan]; thus, as each month passed, the homeowners would actually owe more money than they did at the outset of the loan, with less time to repay it.
The court ruled that even though someone with industry knowledge could figure out the details, the teaser rate wasn't properly disclosed: The root of the alleged deficiencies in defendant‘s disclosures is defendant‘s use of a significantly discounted teaser rate rather than an initial rate set near the rate that would result from the application of the variable rate formula in the Note (an index plus 3.5/3.25 percent). The teaser rate creates an artificially low (compared to the actual cost of credit) initial payment schedule and guarantees that the actual applicable interest rate (after the first month of the loan) will exceed the interest rate used to calculate the payment schedule for the initial years of the loan. If the initial interest rate were set using the Note‘s variable rate formula, it would actually be possible that interest rates would adjust downward (or stay the same) after the first payment and no negative amortization would occur. In other words, the disclosures‘ conditional language is accurate absent a significantly discounted rate. An Option ARM loan without a teaser rate would result in a higher initial interest rate, higher initial minimum payments pursuant to the payment schedule, and a much narrower gap (even if interest rates increased) between the borrower‘s payment ―options. Of course, without a teaser rate, the surface attractiveness of Option ARMs would have been greatly diminished precisely because the stated (initial) interest rate and (initial) payment would be higher. (emphasis added).
The court wasn't sure about damages though: Did plaintiffs suffer damages as a result of defendant‘s fraud? Plaintiffs‘ theory of damages (lost home equity) is problematic. Every month in which plaintiffs suffered negative amortization was a month in which they enjoyed payments lower than the amount needed to amortize the loan (or even to pay off the accruing interest). In exchange for gradually declining equity, plaintiffs retained liquid cash that they otherwise would have paid to defendant (or another lender). Viewed in this manner, plaintiffs‘ only ―injury is the psychological revelation (whenever it occurred) that they were not receiving a free lunch from defendant: plaintiffs could have low payments or pay off their loan, but not both at the same time. But plaintiffs‘ allegation of lost equity in their homes is sufficient at this stage of the proceedings to overrule defendant‘s demurrer. We construe plaintiffs‘ allegations (including the allegation that the prepayment penalty precluded refinancing into a better loan) broadly to encompass an assertion that they were misled into agreeing to Option ARMs, which led to lost equity in their homes because the terms of the Option ARMs put them in a worse economic position than they would have been had they utilized a different credit product.
Although it is clear one plaintiff used the Option ARM to refinance (so the damages are "problematic"), it is unclear if the other plaintiff used the Option ARM to refinance or to purchase a home. I think the damages would be more clear for a home purchased in 2005 than for a refinance. At that time these products were being used inappropriately as affordability products, and if the teaser rate had been properly disclosed, the plaintiff might not have bought the home and wouldn't have suffered significant losses.
As a reminder, back in 2005 it was common to qualify borrowers not using a fully amortizing rate. Options ARMs were frequently used as an affordability product; they were the only way to buy a home for many borrowers. (I was actively contacting regulators in 2005 to try to get that changed). The rule wasn't changed until the Non-Traditional Mortgage Guidance was released in Sept 2006 (a little too late).
Consumer Sentiment declines sharply in August
by Calculated Risk on 8/12/2011 09:55:00 AM
The preliminary August Reuters / University of Michigan consumer sentiment index declined sharply to 54.9 from 63.7 in July.

Click on graph for larger image in graphic gallery.
In general consumer sentiment is a coincident indicator and is usually impacted by employment (and the unemployment rate) and gasoline prices. However I think this month was different. I think consumer sentiment declined sharply because of the heavy coverage of the debt ceiling debate (update: this was polled before the S&P downgrade).
This was well below the consensus forecast of 63.0.
Retail Sales increased 0.5% in July
by Calculated Risk on 8/12/2011 08:30:00 AM
On a monthly basis, retail sales increased 0.5% from June to July (seasonally adjusted, after revisions), and sales were up 8.5% from July 2010. From the Census Bureau report:
The U.S. Census Bureau announced today that advance estimates of U.S. retail and food services sales for July, adjusted for seasonal variation and holiday and trading-day differences, but not for price changes, were $390.4 billion, an increase of 0.5 percent from the previous month, and 8.5 percent above July 2010. ... The May to June 2011 percent change was revised from +0.1 percent to +0.3 percent.Retail sales excluding auto also increased 0.5% in July.
 Click on graph for larger image in graph gallery.
Click on graph for larger image in graph gallery.This graph shows retail sales since 1992. This is monthly retail sales and food service, seasonally adjusted (total and ex-gasoline).
Retail sales seemed to stall in March, but are now moving higher again.
Retail sales are up 17.4% from the bottom, and now 3.2% above the pre-recession peak.
The second graph shows the year-over-year change in retail sales and food service (ex-gasoline) since 1993.
 Retail sales ex-gasoline increased by 6.9% on a YoY basis (8.5% for all retail sales).
Retail sales ex-gasoline increased by 6.9% on a YoY basis (8.5% for all retail sales). The consensus was for retail sales to increase 0.6% in July, and for a 0.3% increase ex-auto.
The reported increase was slightly below expectations for total retail sales, however including the upward revision for June, this was a solid report.
Thursday, August 11, 2011
Gasoline Prices expected to decline sharply
by Calculated Risk on 8/11/2011 10:52:00 PM
Since I haven't posted on gasoline prices in some time ... from Ronald White at the LA Times: Gas prices expected to fall
"If oil remains low, the national average for gasoline will fall to $3.25 to $3.40 in the next two to three weeks as retailers slowly lower their prices to reflect their drop in cost," said Patrick DeHaan, senior energy analyst for GasBuddy.com, a website that lists retail gasoline prices.Another price decline would be good news, but it just takes us back close to the late February and early March levels - and March is when Personal Consumption Expenditure (PCE) growth slowed, and consumer sentiment fell sharply.
| Orange County Historical Gas Price Charts Provided by GasBuddy.com |
Distressed House Sales using Sacramento data
by Calculated Risk on 8/11/2011 06:51:00 PM
I've been following the Sacramento market to see the change in mix over time (conventional, REOs, and short sales) in a distressed area. The Sacramento Association of REALTORS® started breaking out REOs in May 2008, and short sales in June 2009.
I'm not exactly sure what I'm looking for, but hopefully I'll know it when I see it! As some point, the number (and percent) of distressed sales will start to decline without foreclosure moratoria, homebuyer tax credits or other distortions.
The percent of distressed sales in Sacramento declined in July compared to June. Some of this decline could be seasonal, and some could be due to further foreclosure delays. In July 2011, 61.3% of all resales (single family homes and condos) were distressed sales. This is down from 65.2% in June, and down from 63.0% in July 2010.
Here are the statistics.
 Click on graph for larger image in graph gallery.
Click on graph for larger image in graph gallery.
This graph shows the percent of REO, short sales and conventional sales. There is a seasonal pattern for conventional sales (strong in the spring and summer), and distressed sales happen all year - so the percentage of distressed sales decreases every summer.
Note: Prior to June 2009, it is unclear if short sales were included as REO or as "conventional" - or some of both. The tax credits might have also boosted conventional sales in 2009 and early 2010.
Total sales were up 15.1% over July 2010 (sales fell last July after the tax credit expired, so a year-over-year increase was expected). Sales are down 13% compared to July 2009 and 19% compared to July 2008 - mostly due to fewer distressed sales.
Active Listing Inventory is down 21.1% from last July - we are seeing a decline in inventory in most areas. Once the foreclosure delays end, this data might be helpful in determining when the market is improving.
Misc: Dow up 400+, S&P 500 up 4.6%
by Calculated Risk on 8/11/2011 04:26:00 PM
Below is a stock market graph from Doug Short, but first a few stories ...
UPDATE: Regulators Bans some short selling in Belgium, France, Italy and Spain. From European Securities and Markets Authority: ESMA promotes harmonised regulatory action on short-selling in the EU
• From the NY Times: Europe Considers Ban on Short-Selling
The European Securities and Markets Authority, a body that coordinates the European Union’s market policies, has been requesting information from member states about ... short-sales ... “We are discussing with national authorities and together we will decide whether we need coordinated action,” Victoria Powell, a spokeswoman for the authority, said Thursday.Banning short sales always looks like desperation.
• From MarketWatch: Second-quarter GDP view cut after trade data. With the higher than expected trade deficit in June it looks like Q2 real GDP growth might have been below 1% for the 2nd straight quarter. The 2nd estimate of Q2 GDP will be released on August 26th.
• From MasterCard: Total U.S. Retail Sales for July Up 8.7% Year-over-Year
Excluding auto sales retail sales grew by 8.7% year-over-year. Retail sales are on par with the average growth of the previous 3 months, and have held onto their momentum despite concerns from other areas of the economy.Retail sales for July will be released tomorrow.
Michael McNamara, VP of Research and Analysis for MasterCard Advisors SpendingPulse, noted: “Since March, non seasonally-adjusted retail sales have topped 8% year-over-year. However, much of the 8.7 percent growth is from commodity based inflation in areas such as gasoline, food and cotton prices. While the headline year-over-year increase resembles periods of strong economic growth, when you take a closer look at the comp environment and the year-over-year inflation, it tempers the enthusiasm that would normally accompany this level of year-over-year increase.”
Click on graph for larger image.
A crazy week with four straight days of 400+ point swings for the Dow.
U.S. Births Decline in 2010
by Calculated Risk on 8/11/2011 03:07:00 PM
This provisional data for 2010 was released in June and shows a possible impact of the serious recession ...
From the National Center for Health Statistics: Recent Trends in Births and Fertility Rates Through 2010. The NCHS reports (provisional):
The provisional count of births in the United States for 2010 (12-month period ending December 2010) was 4,007,000. This count was 3 percent less than the number of births in 2009 (4,131,019) and 7 percent less than the all-time high of 4,316,233 births in 2007.Here is a long term graph of annual U.S. births through 2010 ...
The provisional fertility rate for 2010 was 64.7 births per 1,000 women aged 15–44. This was 3 percent less than the 2009 preliminary rate of 66.7 and 7 percent less than the 17-year high of 69.5 in 2007.
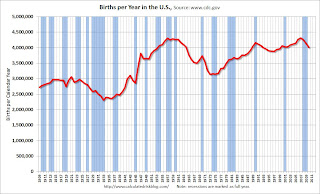 Click on graph for larger image in new window.
Click on graph for larger image in new window.Births have declined for three consecutive years, and are now 7% below the peak in 2007. I suspect certain segments of the population were under stress before the recession started - like construction workers - and even more families were in distress in 2008 through 2011. Of course it takes 9 months to have a baby, so families in distress in 2010 probably put off having babies in 2011 too.
Notice that the number of births started declining a number of years before the Great Depression started. Many families in the 1920s were under severe stress long before the economy collapsed. By 1933 births were down by almost 23% from the early '20s levels.
Of course economic distress isn't the only reason births decline - look at the huge decline following the baby boom that was driven by demographics. But it is not surprising that the number of births slow or decline during tough economic times - and that appears to be happening now.
I don't think the percentage decline in births will be anything like what happened during the Depression, but a 7% decline is pretty significant.
Hotels: Occupancy Rate increased 1.4 Percent compared to same week in 2010
by Calculated Risk on 8/11/2011 12:08:00 PM
Note: This is one of the industry specific measures that I follow. I only post this once a month or so. Looking back at this data during the recession, hotel occupancy first declined in Dec 2007, and then declined sharply in the fall of 2008. Right now I don't see any special weakness in the occupancy rate that would suggest another recession.
From HotelNewsNow.com: STR: Midscale lags in weekly hotel results
Overall, the U.S. hotel industry’s occupancy rose 1.4% to 71.2%, ADR increased 3.3% to US$102.52, and RevPAR finished the week up 4.8% to US$72.99.Note: ADR: Average Daily Rate, RevPAR: Revenue per Available Room.
The following graph shows the seasonal pattern for the hotel occupancy rate using a four week average for the occupancy rate.
 Click on graph for larger image in graph gallery.
Click on graph for larger image in graph gallery.The summer leisure travel season has peaked, and the 4-week average of the occupancy rate will now start to decrease. Right now the occupancy rate is tracking just above 2008 - and well above 2009 - but still below the "normal" level.
Data Source: Smith Travel Research, Courtesy of HotelNewsNow.com
Trade Deficit increased in June
by Calculated Risk on 8/11/2011 09:15:00 AM
The Department of Commerce reports:
[T]otal June exports of $170.9 billion and imports of $223.9 billion resulted in a goods and services deficit of $53.1 billion, up from $50.8 billion in May, revised. June exports were $4.1 billion less than May exports of $175.0 billion. June imports were $1.9 billion less than May imports of $225.8 billion.The trade deficit was well above the consensus forecast of $48 billion.
The first graph shows the monthly U.S. exports and imports in dollars through June 2011.
 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.Both exports and imports decreased in June (seasonally adjusted). Exports are well above the pre-recession peak and up 13% compared to June 2010; imports are almost back to the pre-recession peak, and up about 13% compared to June 2010.
The second graph shows the U.S. trade deficit, with and without petroleum, through June.
 The blue line is the total deficit, and the black line is the petroleum deficit, and the red line is the trade deficit ex-petroleum products.
The blue line is the total deficit, and the black line is the petroleum deficit, and the red line is the trade deficit ex-petroleum products.Oil averaged $106.00 per barrel in June, down from $108.70 per barrel in May. There is a bit of a lag with prices, and import prices will fall further in July.
The trade deficit with China increased to $26.7 billion; trade with China remains a significant issue.


