by Calculated Risk on 7/16/2006 08:31:00 PM
Sunday, July 16, 2006
Energy Consumption as Percent of GDP
From this Christian Science Monitor article: Oil spike: a surmountable challenge?
... back in 1981, energy was a much larger part of the US economy, representing 14 percent of the gross domestic product, Wyss says. Because energy was so crucial back then, the Federal Reserve pushed interest rates sharply higher to curtail inflation.I've heard this statement before on CNBC several times. Is energy consumption really only 7% of GDP?
Today, energy represents 7 percent of GDP. "The Fed will not have to jerk interest rates up," says Wyss. "We are in better shape."
First, I checked with the EIA: Table 1.5 Energy Consumption, Expenditures. Sure enough, for the last 2 years reported, energy consumption was 7% and 6.8% of GDP. Of course those were for the years 2000 and 2001, respectively.
Energy prices have increased significantly faster than GDP over the last 5 years. Sure enough, it appears Mr. Wyss is using old numbers.
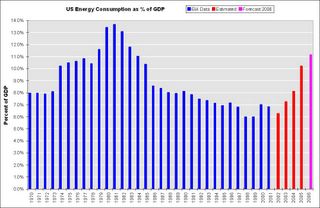
Click on graph for larger image.
Using a combination of EIA numbers for energy sources, and BLS numbers for price changes, and holding consumption steady (very conservative), this graph shows that US Energy Consumption is around 11.2% of GDP right now. (UPDATE NOTE: I'll try to do a more comprehensive calculation later this week - with links and my calculations. this was a rough estimate)
As an aside, ignore Mr. Wyss' comments on the FED. The FED looks primarily at core inflation rates (like Core CPI and PCE). Alhtough the FED is concerned about higher energy prices feeding through to core inflation rates, they aren't really focused directly on energy prices.
On energy issues, see Dr. Hamilton's: Can the economy shrug off $80 oil?
Saturday, July 15, 2006
Retail Employment
by Calculated Risk on 7/15/2006 07:00:00 PM
Danielle DiMartino writes: Retailers' actions point to recession
... we already know, from last week's labor report, that retailers were compelled to cut payrolls for a third consecutive month in June.Is this decline in retail employment 'unprecedented outside of recessions'?
"More strikingly," Goldman Sachs chief economist Jan Hatzius wrote, "the year-on-year growth rate has plummeted from 1.3 percent in 2005 to -0.2 percent as of June 2006. Year-on-year declines in retail employment are unprecedented outside of recessions."

Click on graph for larger image.
Shaded areas are recessions according to NBER.
It appears that Hatzius is correct. But is it different this time? Maybe, with the rapid expansion of internet shopping, the model of retail has changed.
Or, as DiMartino apparently believes, the retailers are the first to detect the coming recession. She relates the decrease in retail employment to the slowdown in the housing market:
During the housing boom, home-equity withdrawals were a big contributor to consumers' ability to spend.
But in the first half of 2006, nearly 90 percent of refinancings were cash-outs, up from 20 percent in 2003.
In other words, it used to be that people refinanced their homes to lower their payments. Today almost all go through the exercise just to unlock cash.
...
It stands to reason that retailers would be the first to detect the diminution of this source of disposable income, which is at least partially to blame for the 86,000 jobs the sector has shed in the last three months.
"Retailers may have decided that the recent weakness in personal consumption will persist," Mr. Hatzius added.
Of course, the spin doctors are sure to dismiss the negative growth in retail employment. Sure, every time it's happened since 1945 it's presaged a recession. But it's bound to be different this time. Of course.
Friday, July 14, 2006
Volcker: Bernanke Faces Tougher Task Than Volcker
by Calculated Risk on 7/14/2006 03:07:00 PM
From Bloomberg:
Paul Volcker, who took over the Federal Reserve a generation ago at a time of soaring prices and stagnant growth, said the current central bank chief, Ben S. Bernanke, faces an even tougher challenge.Clearly the economy is better today than in 1979. However the imbalances are much worse, and fiscal / public policy has been a disaster. I agree that Bernanke has the more difficult task.
``It was easier for me,'' Volcker, 78, said in an interview to be broadcast this weekend on ``Political Capital With Al Hunt,'' a Bloomberg television program. ``While the economic situation was much worse, it was easier to act because it was clear what the enemy was.''
Volcker, appointed by President Jimmy Carter in 1979, is credited with defeating inflation, which was 13 percent when he took the Fed's helm. Volcker raised the benchmark interest rate to a record, helping send the economy into recession.
While he said the global economy is doing well, Volcker voiced concern that the good times can't last.
``We are skating along quite nicely,'' said Volcker, though ``the ice is not as thick as I would like it to be.''
The U.S. current-account deficit exceeded $208 billion in the first quarter. The figure, which includes trade as well as transfer payments and investment income, declined from $223 billion the previous quarter. It was still the second-largest on record and requires the U.S. to attract $2.3 billion in foreign capital each day fund the gap.
``We are consuming too much and investing too little,'' said Volcker, who also indicated that higher taxes may be needed to narrow the budget deficit.
...
``Revenues have gotten too low'' relative to what the government wants to spend, Volcker said.
Because of U.S. dependence on foreign capital to fund trade and budget gaps, ``it is critical that we maintain confidence in our currency,'' said Volcker.
U.S. retail sales fall 0.l% in June
by Calculated Risk on 7/14/2006 08:46:00 AM
From Rex Nutting at MarketWatch: U.S. retail sales fall 0.l% in June
U.S. consumers cut back in June, sending retail sales down 0.1% for the month, the Commerce Department reported Friday. It was the second straight month of tepid retail sales. Sales rose 0.1% in May.Here is the report.
Percent Change in Retail and Food Services Sales

Click on graph for larger image.
The other shoe? Housing and equity extraction slowdown. Then retail sales slows?
Thursday, July 13, 2006
Budget Improvement?
by Calculated Risk on 7/13/2006 03:01:00 PM
The Treasury Department released the Monthly Treasury Statement for June today. See Table 2: On Budget Surplus / Deficit
For fiscal year-to-date, the budget deficit is $374.3 Billion compared to $410.1 Billion for fiscal 2005. That is the "extraordinary" improvement announced by the White House.
Meanwhile the YTD annual increase in the National Debt is larger in fiscal 2006 than 2005 - so even the small improvement in the budget deficit is possibly an accounting illusion.
Bottom line: There has been little or no improvement in the budget deficit.
UPDATE: pgl reminds me: Repatriation Relief and that “Surge” in Tax Revenues
So as the Bush Administration crows about the “surge” in taxes, let’s just remember that this is yet another example of Enron accounting where in reality the government gave away $50 billion on net.I suspect even the minor improvment will be transitory. Not only is the repatriation give away over, but "not withheld" taxes will be negatively impacted next year by the housing and stock market performance in 2006.
Wednesday, July 12, 2006
Two Posts on Economy
by Calculated Risk on 7/12/2006 11:54:00 PM
Dr. Thoma has two excellent posts on the economy.
The first is the Dallas Fed's Economic Outlook.
The second is Selling the Economy.
The economy is clearly slowing, especially housing and consumer spending. I'd argue cause and effect: the slowing housing market is leading to less borrowing, and less consumer spending. I'm less confident in the Dallas Fed's views on inflation.
On consumer spending, ac provided a link to this BusinessWeek story in the comments: The Real Problem with Job Growth, U.S. retailers are no longer the job-creation engine they were, suggesting that consumers may finally be crying "uncle"
"We have to work hard to keep our labor and hiring in check given our outlook in same store sales," says Mike Marchetti, Finish Line's executive vice-president of store operations.
Around the country, retailers are echoing similar sentiments, and many are holding off on their hiring plans.
...
It's unusual that retailers are trimming their workforces when the rest of the economy is growing. For years, retailers have been the source of significant job creation in the U.S. During the 1990s, department stores, groceries, and other retailers added 2.3 million jobs, or an average of almost 20,000 a month, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Now, the concern is that retailers, who are positioned to detect the pulse of consumers more quickly than many other types of companies, are sensing trouble ahead. "Something is screamingly wrong with consumers, and retailers are reacting," says Richard Hastings, economic advisor to the Federation of Credit and Financial Professionals and a senior retail analyst at Bernard Sands, a retail credit rating firm.
The outlook for the U.S. economy, in its fifth year of expansion, is already weakening.

Click on graph for larger image.
From the Cleveland Fed: Fed Funds Rate Predictions
Even though the economy is clearly slowing, expectations are for another 25 bp rate hike in August.
San Diego: YoY Home Prices Decline
by Calculated Risk on 7/12/2006 04:58:00 PM
UPDATE: Also see VoiceofSanDiego: First Yearly Home Price Drop in a Decade. Excerpts:
Chris Thornberg a senior economist at the University of California, Los Angeles Anderson Forecast, said dropping home prices can have a powerful psychological effect on homeowners.The San Diego Union-Tribune reports: County housing market continues to soften
"When your house keeps appreciating by 10 or 20 percent a year, easier to buy that nicer bottle of wine, perhaps go out to that slightly fancier restaurant -- what the hell, right?" Thornberg said. "But when that goes flat, suddenly, oh geez, the house isn't going to be this big boom of new wealth. Boy, I'm going to have to be a bit more careful with my dollar."
San Diego County's housing market continued to lose steam in June, with median home prices posting their first year-over-year decline in a decade and sales dropping for the 24th straight month.There it is: a year-over-year price decline in San Diego. Also sales are down and inventory up.
...
Last month's median home price dropped to $488,000, a 1 percent decline from a year earlier and a 6 percent decrease from last November's peak of $518,000.
... sales increased slightly from May but were down 24 percent from June of 2005.They didn't mention how many homes were on the market in June 2005. The article has many positive comments, "a good time for the buyer to jump into the market" and "this is just part of a plateauing of prices", but I think the numbers tell the real story.
Yet another indicator of the county's flattening market is the growing supply of homes for sale. As of Wednesday, there are 22,460 homes on the market, according to Sandicor, the multiple listing service subscribed to by area real estate offices.
Science of Climate Change
by Calculated Risk on 7/12/2006 04:19:00 PM
I'd like to discuss policy proposals to address Global Warming on this blog, not the science of global warming. I am interested in the science, but I think too many posts on that subject will detract from economic issues.
I understand many readers are very interested in the science of climate change. That is wonderful. I recommend asking questions at RealClimate.org; "Climate science from climate scientists".
For my occasional off-topic posts, I'll stick to hiking / mountain climbing and, of course ...
Enjoy.
May Trade Deficit: $63.8 Billion
by Calculated Risk on 7/12/2006 11:08:00 AM
The Census Bureau reports:
The U.S. Census Bureau and the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, through the Department of Commerce, announced today that total May exports of $118.7 billion and imports of $182.5 billion resulted in a goods and services deficit of $63.8 billion, $0.5 billion more than the $63.3 billion in April, revised. May exports were $2.7 billion more than April exports of $115.9 billion. May imports were $3.2 billion more than April imports of $179.3 billion.For an excellent analysis See Dr. Setser's: How long can non-oil imports remain flat if the US economy continues to grow?
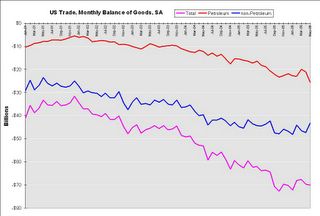
Click on graph for larger image.
The non-Petroleum goods balance has stabilized since the end of last year. This might suggest that US economic growth is slowing. From a post in March:
"Interestingly, the change in U.S. home mortgage debt over the past half-century correlates significantly with our current account deficit. To be sure, correlation is not causation, and there have been many influences on both mortgage debt and the current account."
Alan Greenspan, Current account, Feb 4, 2005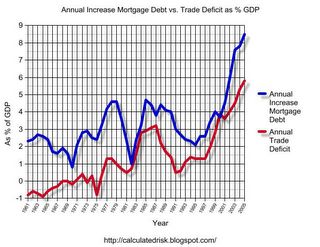
I expect the annual increase in mortgage debt to decline in 2006. This is because I expect new and existing home purchases to decline, and homeowners to extract less equity from their homes in 2006.
The drop in mortgage activity is is one of the reasons I expect the trade deficit to stabilize in 2006.
MBA: Mortgage Application Volume Steady
by Calculated Risk on 7/12/2006 10:21:00 AM
The Mortgage Bankers Association (MBA) reports: Mortgage Application Volume Steady
Click on graph for larger image.
The Market Composite Index, a measure of mortgage loan application volume, was 566.8, an increase of 1.0 percent on a seasonally adjusted basis from 561.0 one week earlier. On an unadjusted basis, the Index decreased 29.1 percent compared with the previous week and was down 36.3 percent compared with the same week one year earlier.Mortgage rates increased slightly:
The seasonally-adjusted Purchase Index increased by 2.6 percent to 425.0 from 414.2 the previous week and the Refinance Index decreased by 1.6 percent to 1400.5 from 1423.9 one week earlier.
The average contract interest rate for 30-year fixed-rate mortgages increased to 6.81 percent from 6.80 percent ...Change in mortgage applications from one year ago (from Dow Jones):
The average contract interest rate for one-year ARMs increased to 6.41 percent from 6.39 percent ...
| Total | -36.3% |
| Purchase | -23.4% |
| Refi | -52.0% |
| Fixed-Rate | -37.0% |
| ARM | -34.5% |
Purchase activity is off 23.4% compared to the same week last year. The MBA Purchase Index is indicating that the housing market is continuing to slow compared to 2005.


